Daniel Christian:
A Vision of Our Future Learning Ecosystems
In the near future, as the computer, the television, the telephone (and more) continues to converge, we will most likely enjoy even more powerful capabilities to conveniently create and share our content as well as participate in a global learning ecosystem — whether that be from within our homes and/or from within our schools, colleges, universities and businesses throughout the world.
We will be teachers and students at the same time — even within the same hour — with online-based learning exchanges taking place all over the virtual and physical world. Subject Matter Experts (SME’s) — in the form of online-based tutors, instructors, teachers, and professors — will be available on demand. Even more powerful/accurate/helpful learning engines will be involved behind the scenes in delivering up personalized, customized learning — available 24x7x365. Cloud-based learner profiles may enter the equation as well.
The chances for creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship that are coming will be mind-blowing! What employers will be looking for — and where they can look for it — may change as well.
What we know today as the “television” will most likely play a significant role in this learning ecosystem of the future. But it won’t be like the TV we’ve come to know. It will be much more interactive and will be aware of who is using it — and what that person is interested in learning about. Technologies/applications like Apple’s AirPlay will become more standard, allowing a person to move from device to device without missing a beat. Transmedia storytellers will thrive in this environment!
Much of the professionally done content will be created by teams of specialists, including the publishers of educational content, and the in-house teams of specialists within colleges, universities, and corporations around the globe. Perhaps consortiums of colleges/universities will each contribute some of the content — more readily accepting previous coursework that was delivered via their consortium’s membership.
An additional thought regarding higher education and K-12 and their Smart Classrooms/Spaces:
For input devices…
The “chalkboards” of the future may be transparent, or they may be on top of a drawing board-sized table or they may be tablet-based. But whatever form they take and whatever is displayed upon them, the ability to annotate will be there; with the resulting graphics saved and instantly distributed. (Eventually, we may get to voice-controlled Smart Classrooms, but we have a ways to go in that area…)
Below are some of the graphics that capture a bit of what I’m seeing in my mind…and in our futures.
Alternatively available as a PowerPoint Presentation (audio forthcoming in a future version)

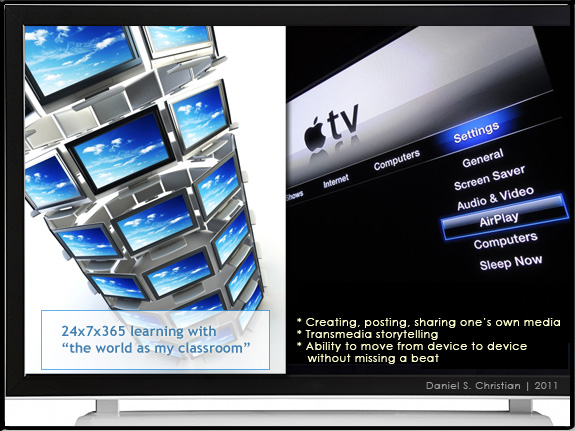
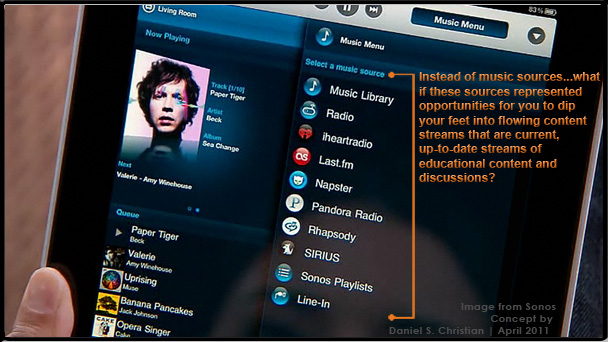
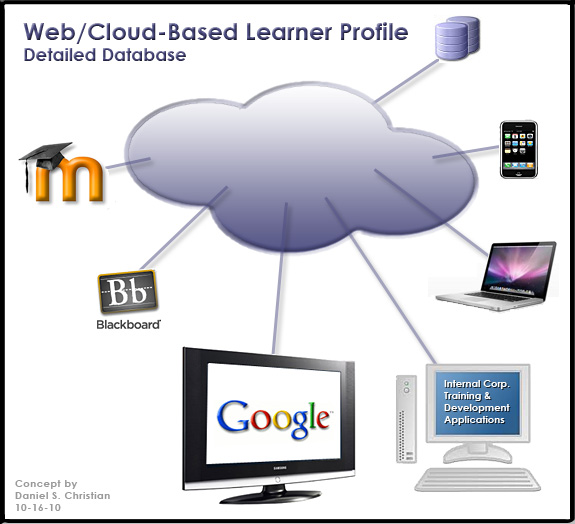




— from Daniel S. Christian | April 2011
See also:
- Hunch brings predictions to Internet TV — from ReadWriteWeb.com by Mike Melanson
- Group video calling comes to iPhone & Android in Fring beta test – from Mashable.com by Jennifer Van Grove
- State of the Art Tutoring is Going Online — from chatam.patch.com by K.F. Rogers (originally saw at Ray Schroeder’s blog)
- Storytelling: Video games’ next killer app — from CNN.com by Scott Steinberg
- YouTube finally launches live streaming portal to select partners — from ReadWriteWeb.com by Marshall Kirkpatrick
- The art of immersion, digital storytelling and transmedia — from Six Pixels of Separation
- Reversing course, U. of California to borrow millions for online classes — from The Chronicle by Josh Keller
- Non-stop Learning Futures conference spans three time zones to mirror demands of 24/7 global society — from 24dash.com
- Call for presentations: Online learning, teaching, and research in the new media ecology — from Ray Schroeder and the Sloan Consortium
…It is clear that we are in the midst of rapid and ongoing changes in the way that we communicate and represent ideas and these changes have profound consequence for how we know, learn, think, and teach in higher education and beyond. The dizzying pace of change is highlighted by the fact that even the relatively new conventions of online education associated with asynchronous learning networks are being challenged by emerging means of access, such as mobile and cloud computing, new forms of communication, such as video streaming and instant messaging, as well as the innovative modes of participation represented in social media.
Addendum on 4-14-11: