From DSC:
Great…we have another tool called Canvas. Or did you say Canva?
Introducing canvas — from OpenAI
A new way of working with ChatGPT to write and code
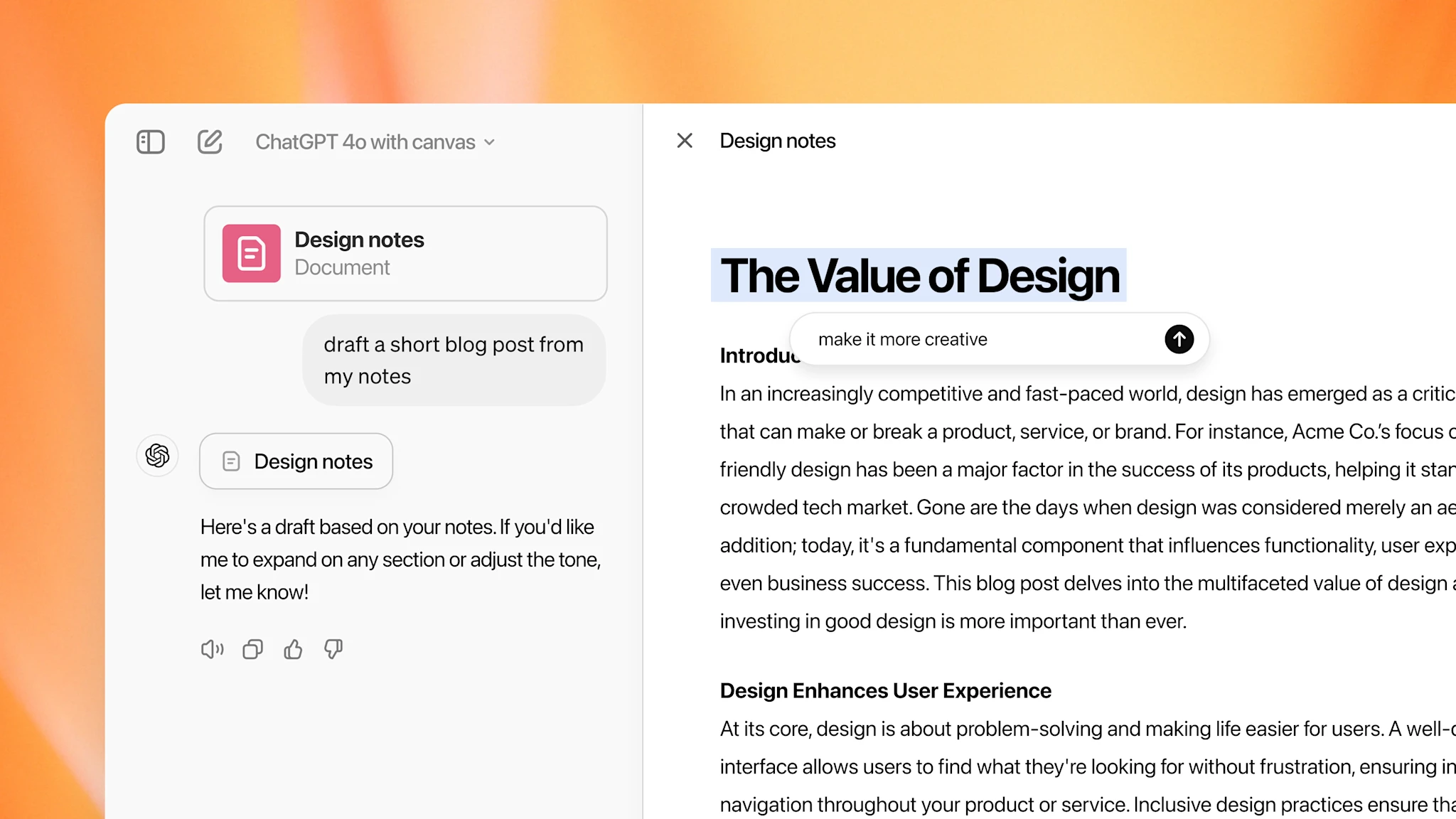
We’re introducing canvas, a new interface for working with ChatGPT on writing and coding projects that go beyond simple chat. Canvas opens in a separate window, allowing you and ChatGPT to collaborate on a project. This early beta introduces a new way of working together—not just through conversation, but by creating and refining ideas side by side.
Canvas was built with GPT-4o and can be manually selected in the model picker while in beta. Starting today we’re rolling out canvas to ChatGPT Plus and Team users globally. Enterprise and Edu users will get access next week. We also plan to make canvas available to all ChatGPT Free users when it’s out of beta.
Using AI to buy your home? These companies think it’s time you should — from usatoday.com by Andrea Riquier
The way Americans buy homes is changing dramatically.
New industry rules about how home buyers’ real estate agents get paid are prompting a reckoning among housing experts and the tech sector. Many house hunters who are already stretched thin by record-high home prices and closing costs must now decide whether, and how much, to pay an agent.
A 2-3% commission on the median home price of $416,700 could be well over $10,000, and in a world where consumers are accustomed to using technology for everything from taxes to tickets, many entrepreneurs see an opportunity to automate away the middleman, even as some consumer advocates say not so fast.
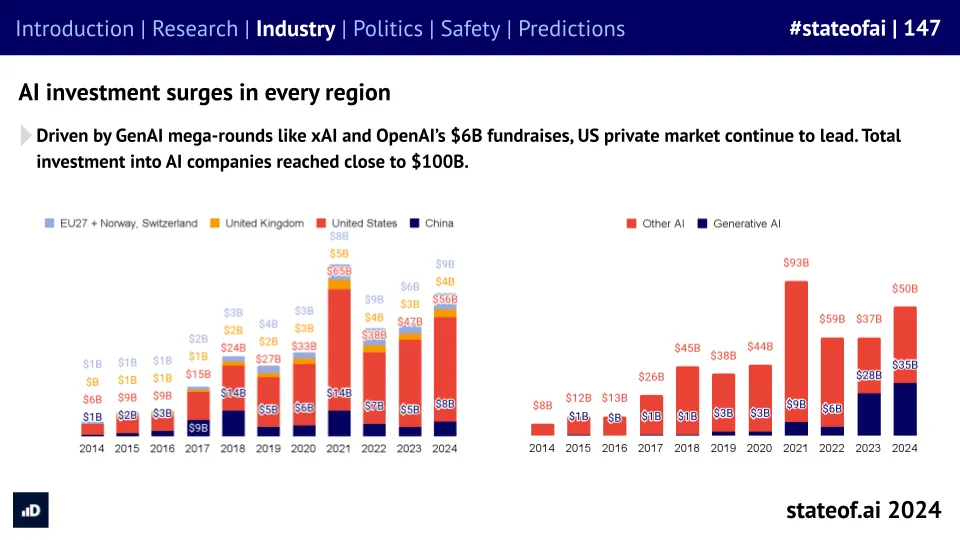
The State of AI Report 2024 — from nathanbenaich.substack.com by Nathan Benaich
The Great Mismatch — from the-job.beehiiv.com. by Paul Fain
Artificial intelligence could threaten millions of decent-paying jobs held by women without degrees.
Women in administrative and office roles may face the biggest AI automation risk, find Brookings researchers armed with data from OpenAI. Also, why Indiana could make the Swiss apprenticeship model work in this country, and how learners get disillusioned when a certificate doesn’t immediately lead to a good job.
…
A major new analysis from the Brookings Institution, using OpenAI data, found that the most vulnerable workers don’t look like the rail and dockworkers who have recaptured the national spotlight. Nor are they the creatives—like Hollywood’s writers and actors—that many wealthier knowledge workers identify with. Rather, they’re predominantly women in the 19M office support and administrative jobs that make up the first rung of the middle class.
“Unfortunately the technology and automation risks facing women have been overlooked for a long time,” says Molly Kinder, a fellow at Brookings Metro and lead author of the new report. “Most of the popular and political attention to issues of automation and work centers on men in blue-collar roles. There is far less awareness about the (greater) risks to women in lower-middle-class roles.”
Is this how AI will transform the world over the next decade? — from futureofbeinghuman.com by Andrew Maynard
Anthropic’s CEO Dario Amodei has just published a radical vision of an AI-accelerated future. It’s audacious, compelling, and a must-read for anyone working at the intersection of AI and society.
But if Amodei’s essay is approached as a conversation starter rather than a manifesto — which I think it should be — it’s hard to see how it won’t lead to clearer thinking around how we successfully navigate the coming AI transition.
Given the scope of the paper, it’s hard to write a response to it that isn’t as long or longer as the original. Because of this, I’d strongly encourage anyone who’s looking at how AI might transform society to read the original — it’s well written, and easier to navigate than its length might suggest.
That said, I did want to pull out a few things that struck me as particularly relevant and important — especially within the context of navigating advanced technology transitions.
And speaking of that essay, here’s a summary from The Rundown AI:
Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei just published a lengthy essay outlining an optimistic vision for how AI could transform society within 5-10 years of achieving human-level capabilities, touching on longevity, politics, work, the economy, and more.
The details:
- Amodei believes that by 2026, ‘powerful AI’ smarter than a Nobel Prize winner across fields, with agentic and all multimodal capabilities, will be possible.
- He also predicted that AI could compress 100 years of scientific progress into 10 years, curing most diseases and doubling the human lifespan.
- The essay argued AI could strengthen democracy by countering misinformation and providing tools to undermine authoritarian regimes.
- The CEO acknowledged potential downsides, including job displacement — but believes new economic models will emerge to address this.
- He envisions AI driving unprecedented economic growth but emphasizes ensuring AI’s benefits are broadly distributed.
Why it matters:
- As the CEO of what is seen as the ‘safety-focused’ AI lab, Amodei paints a utopia-level optimistic view of where AI will head over the next decade. This thought-provoking essay serves as both a roadmap for AI’s potential and a call to action to ensure the responsible development of technology.
AI in the Workplace: Answering 3 Big Questions — from gallup.com by Kate Den Houter
However, most workers remain unaware of these efforts. Only a third (33%) of all U.S. employees say their organization has begun integrating AI into their business practices, with the highest percentage in white-collar industries (44%).
…
White-collar workers are more likely to be using AI. White-collar workers are, by far, the most frequent users of AI in their roles. While 81% of employees in production/frontline industries say they never use AI, only 54% of white-collar workers say they never do and 15% report using AI weekly.
…
Most employees using AI use it for idea generation and task automation. Among employees who say they use AI, the most common uses are to generate ideas (41%), to consolidate information or data (39%), and to automate basic tasks (39%).
Nvidia Blackwell GPUs sold out for the next 12 months as AI market boom continues — from techspot.com by Skye Jacobs
Analysts expect Team Green to increase its already formidable market share
Selling like hotcakes: The extraordinary demand for Blackwell GPUs illustrates the need for robust, energy-efficient processors as companies race to implement more sophisticated AI models and applications. The coming months will be critical to Nvidia as the company works to ramp up production and meet the overwhelming requests for its latest product.
Here’s my AI toolkit — from wondertools.substack.com by Jeremy Caplan and Nikita Roy
How and why I use the AI tools I do — an audio conversation
1. What are two useful new ways to use AI?
- AI-powered research: Type a detailed search query into Perplexity instead of Google to get a quick, actionable summary response with links to relevant information sources. Read more of my take on why Perplexity is so useful and how to use it.
- Notes organization and analysis: Tools like NotebookLM, Claude Projects, and Mem can help you make sense of huge repositories of notes and documents. Query or summarize your own notes and surface novel connections between your ideas.