How to use Perplexity in your daily workflow — from ai-supremacy.com by Michael Spencer and Alex McFarland
“I barely use Google anymore (for anything)” says today’s guest author.
- Morning briefings: Start your day by asking Perplexity for the latest news in your field. (I personally like to use Perplexity to curate the top AI news of the day to consider writing about for Unite AI and Techopedia.)
- Fact-checking: Use it to quickly verify information before including it in your work.
- Brainstorming: Generate ideas for projects or content by asking open-ended questions.
- Learning new concepts: When you encounter an unfamiliar term or idea, turn to Perplexity for a quick, comprehensive explanation.
- Writing assistance: Use it to find relevant statistics, examples, or counterarguments for your content.
From DSC:
So I used it to ask “What is Elon Musk’s Memphis Supercluster?” (which went online yesterday I believe) — which resulted in this reply:
Elon Musk’s Memphis Supercluster is a newly activated AI training cluster that is claimed to be the most powerful in the world. Here are the key details about this supercomputer:
1. Location: The supercluster is located in Memphis, Tennessee[1][2].
2. Hardware: It consists of 100,000 liquid-cooled Nvidia H100 GPUs connected through a single RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) fabric[1][3].
3. Purpose: The supercluster is designed for training large language models (LLMs) and other advanced AI technologies for Musk’s xAI company[1][2].
4. Activation: The Memphis Supercluster began training at approximately 4:20 AM local time on July 22, 2024[1][3].
5. Collaboration: The project is a result of collaboration between xAI, X (formerly Twitter), Nvidia, and other supporting companies[1][2].
6. Investment: With each H100 GPU estimated to cost between $30,000 to $40,000, the total investment in GPUs alone is estimated to be between $3 billion to $4 billion[5].
7. Goals: Musk claims that this supercluster will be used to develop “the world’s most powerful AI by every measure” by December 2024[1].
8. Comparison: The Memphis Supercluster’s 100,000 H100 GPUs significantly outclass other supercomputers in terms of GPU horsepower, such as Frontier (37,888 AMD GPUs) and Microsoft Eagle (14,400 Nvidia H100 GPUs)[3].
9. Infrastructure: The project required significant infrastructure development, including fiber optic networking[5].
While Musk’s claims about the supercluster’s capabilities are ambitious, it remains to be seen how it will perform in practice and whether it will meet the stated goals within the given timeframe[1].
Citations:
[1] https://venturebeat.com/ai/elon-musk-announces-most-powerful-ai-training-cluster-in-the-world/
[2] https://www.tuaw.com/2024/07/22/elon-musks-xai-unveils-worlds-most-powerful-ai-training-cluster/
[3] https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/gpus/elon-musk-fires-up-the-most-powerful-ai-training-cluster-in-the-world-uses-100000-nvidia-h100-gpus-on-a-single-fabric
[4] https://www.thestack.technology/xai-elon-musk-ai-supercomputer/
[5] https://www.benzinga.com/news/24/07/39881748/elon-musks-xai-flips-the-switch-on-100k-nvidia-h100-gpus-worth-up-to-4b-in-memphis-supercluster-most
[6] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JhtJa05C2Y
—–
Elon’s AI empire expands — from theneurondaily.com by Grant Harvey
Elon Musk’s team at xAI just powered on the “World’s Most Powerful AI Training Cluster.”
If you don’t know what a supercluster is, it’s basically a massive network of Nvidia GPUs (computer chips) working together as a single unit to solve “super” complex calculations at unprecedented speeds.
And this Memphis Supercluster is the most “super” supercluster we’ve ever seen. The new facility, dubbed the “Gigafactory of Compute”, is a beast:
- 100,000 liquid-cooled Nvidia H100 GPUs on a single RDMA fabric (for context, Google snagged only 50,000 H100 GPUs last year).
- Up to 150 megawatts of electricity usage per hour—enough for 100K homes.
- At least one million gallons of water per day to keep cool!
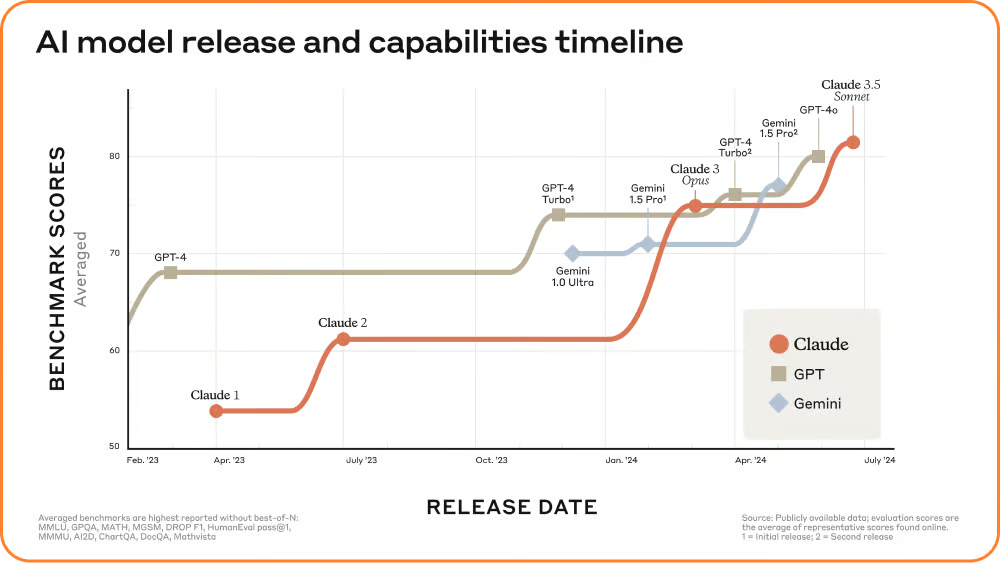
What to expect: Better models, more frequently. That’s been the trend, at least—look at how the last few model releases have become more squished together.
OpenAI to make GPT-4o Advanced Voice available by the end of the month to select group of users — from tomsguide.com by Ryan Morrison
GPT-4o Advanced Voice is an entirely new type of voice assistant, similar to but larger than the recently unveiled French model Moshi, which argued with me over a story.
In demos of the model, we’ve seen GPT-4o Advanced Voice create custom character voices, generate sound effects while telling a story and even act as a live translator.
This native speech ability is a significant step in creating more natural AI assistants. In the future, it will also come with live vision abilities, allowing the AI to see what you see.
Could AGI break the world? — from theneurondaily.com by Noah Edelman
“Biggest IT outage in history” proves we’re not ready for AGI.
…
Here’s the TL;DR—a faulty software update from cybersecurity firm Crowdstrike made this happen:
- Grounded 5,000+ flights around the world.
- Slowed healthcare across the UK.
- Forced retailers to revert to cash-only transactions in Australia (what is this, the stone ages?!).
…
Here’s where AI comes in: Imagine today’s AI as a new operating system. In 5-10 years, it’ll likely be as integrated into our economy as Microsoft’s cloud servers are now. This isn’t that far-fetched—Microsoft is already planning to embed AI into all its programs.
So what if a Crowdstrike-like incident happens with a more powerful AI system? Some experts predict an AI-powered IT outage could be 10x worse than Friday’s fiasco.
The Crowdstrike outage and global software’s single-point failure problem — from cnbc.com by Kaya Ginsky
KEY POINTS
- The CrowdStrike software bug that took down global IT infrastructure exposed a single-point-of-failure risk unrelated to malicious cyberattack.
- National and cybersecurity experts say the risk of this kind of technical outage is increasing alongside the risk of hacks, and the market will need to adopt better competitive practices.
- Government is also likely to look at new regulations related to software updates and patches.
The “largest IT outage in history,” briefly explained — from vox.com by Li Zhou
Airlines, banks, and hospitals saw computer systems go down because of a CrowdStrike software glitch.













