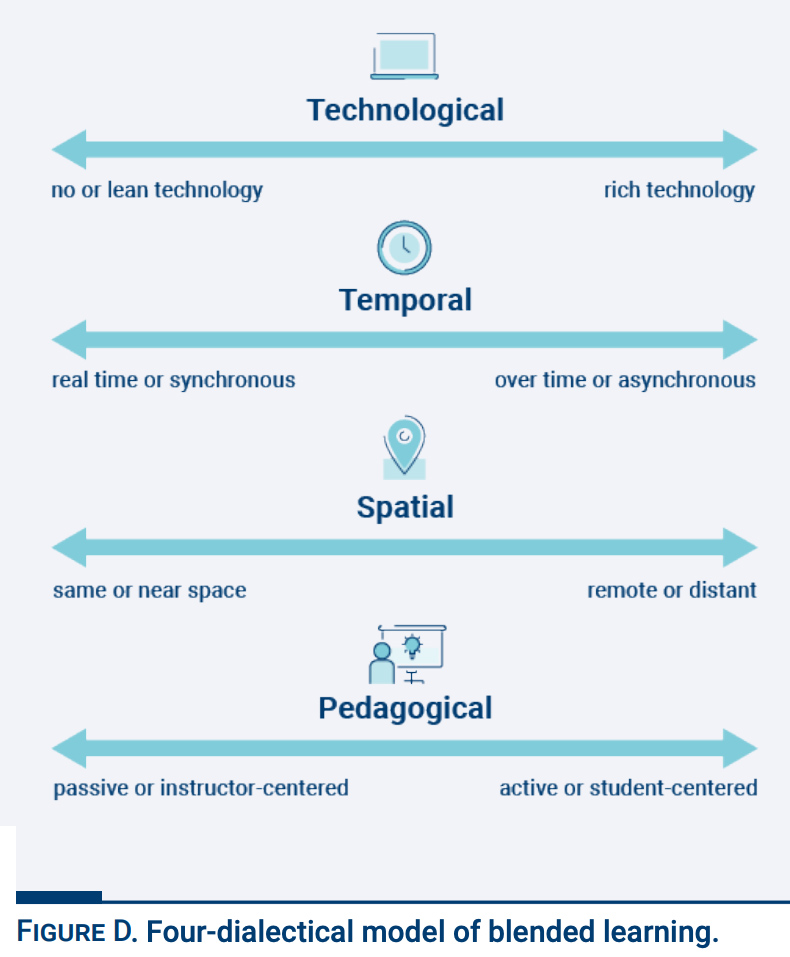
Teaching: What’s the right measure of good teaching? — from chronicle.com by Beth McMurtrie
There are several elements to this challenge. The first is that many campuses depend largely, if not exclusively, on student course evaluations when it comes to measuring instructional quality. And often those evaluations are not particularly well designed or substantive.
…
But even when course evaluations are better designed, I’m not sure any teaching experts would argue that they should be the exclusive measure of whether a faculty member is an effective teacher. That brings us to the second element of the challenge: What else can a college do?
Several readers offered suggestions, such as to include classroom observations, peer evaluation, and teaching portfolios — in which, say, an instructor describes their teaching philosophy and classroom practices, along with evidence that they are working to strengthen their teaching.
Why Labor Shortages on Campus-Building Staffs Are Reaching ‘Crisis Situations’ — from an email newsletter from The Chronicle of Higher Education which eventually links to this article
Who will keep the buildings open?
It’s no secret colleges have struggled to fill staff positions like administrative assistants, information-technology specialists, and admissions officers in today’s tight labor market. But many institutions are grasping for ways to fill key facilities positions that literally keep the doors open, such as custodians, electricians, carpenters, and maintenance workers, our Scott Carlson writes.
Staffing shortages strain the employees and contractors already on the payroll. Facilities-staff members are aging and often juggling project backlogs.
Remember: Building services were the third-most-difficult area to hire in, according to a Chronicle survey conducted earlier this year, behind information technology and dining services. Six in 10 respondents said hiring building-services staff was a serious or moderate problem.
Higher ed may be a victim of its own success. The country has emphasized college after high school over the last four decades, while trades have struggled to attract workers.
An eye-opening stat: Even with a recently renewed emphasis on the trades, the U.S. has only about 600,000 people in apprenticeships, far below the 17 million students enrolled in college.
Which Colleges Pay Off for Low-Income Students? — from edsurge.com by Nadia Tamez-Robledo
Colleges and universities that specialize in health and technology proved to serve low-income students who end up with the highest starting salaries six years after they enrolled. For this earnings data, College Scorecard does not take into account whether students graduated or not.
Hover your cursor over each bar to read details about each institution.
Brave New Classrooms — from Dr. Philippa Hardman
Why 2023-2024 will be remembered as the academic year that education embraced AI
After a rocky start, more and more evidence suggests that the academic year 2023-2024 will likely prove to be a defining year for higher education: the year higher education embraced AI.
Over the course of the next academic year, we will likely see three main changes in the world of education:
- More education institutions will embrace AI & develop policies & guidance on its appropriate use at the institution, department & classroom level.
- We will see a wave of assessment reform, with a new focus on the assessment of learners’ process and skills, including the effective use of AI.
- To enable this chance, we will see a rapid increase in the provision of AI training for leaders, educators and administrators.
While risks and barriers to entry remain real, supported by well-rounded strategic frameworks, the education system has the potential to leverage AI reinvent itself and improve its ability to deliver on the promise to deliver real-world-relevant education.
Two-thirds of colleges are adding online programs, survey finds — from highereddive.com by Natalie Schwartz
The annual CHLOE report tracks changing student demand for virtual education and how institutions are adapting their offerings in response.