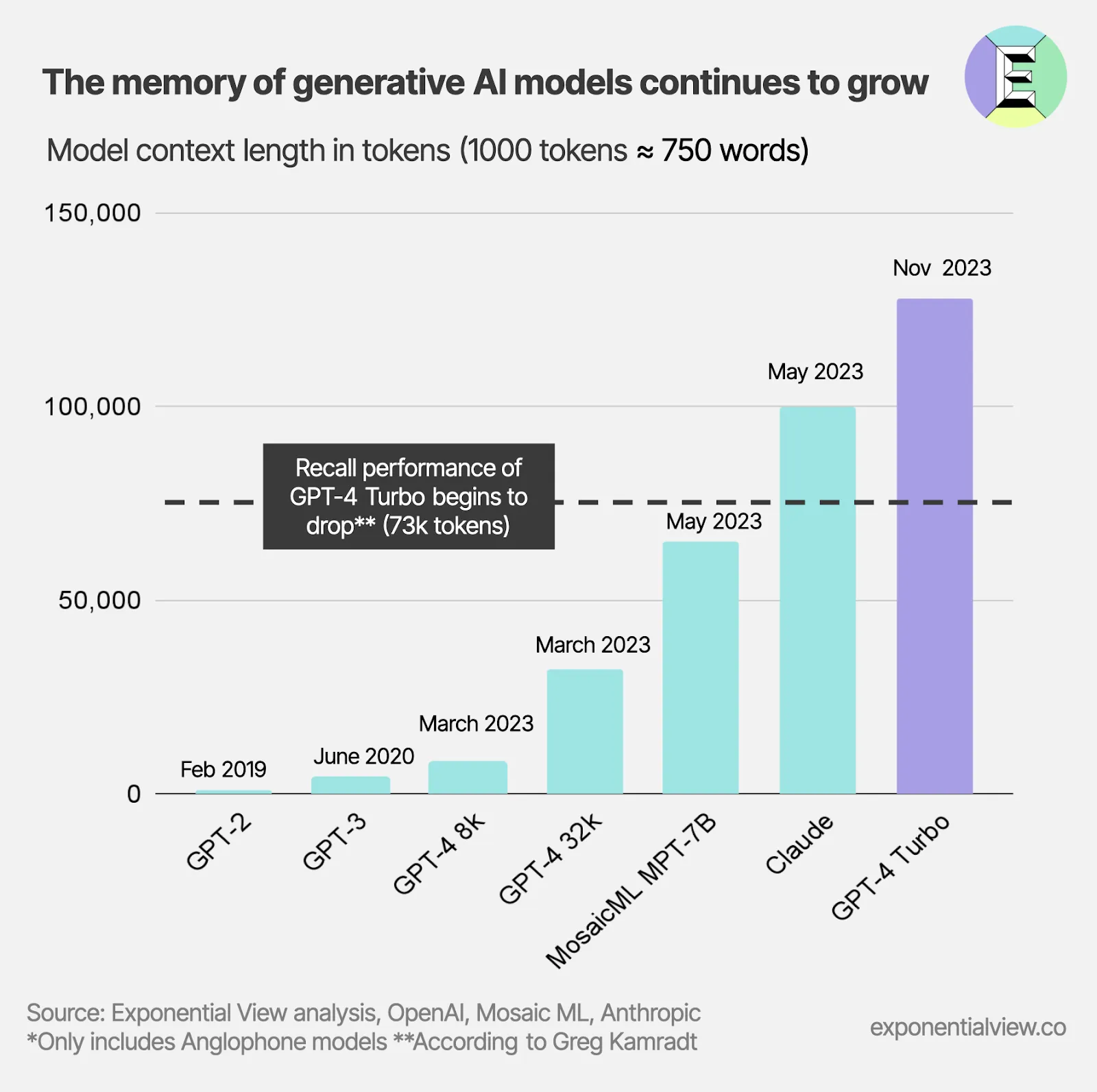
How Early Adopters of Gen AI Are Gaining Efficiencies — from knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu by Prasanna (Sonny) Tambe and Scott A. Snyder; via Ray Schroeder on LinkedIn
Enterprises are seeing gains from generative AI in productivity and strategic planning, according to speakers at a recent Wharton conference.
Its unique strengths in translation, summation, and content generation are especially useful in processing unstructured data. Some 80% of all new data in enterprises is unstructured, he noted, citing research firm Gartner. Very little of that unstructured data that resides in places like emails “is used effectively at the point of decision making,” he noted. “[With gen AI], we have a real opportunity” to garner new insights from all the information that resides in emails, team communication platforms like Slack, and agile project management tools like Jira, he said.
6 YouTube Channels to Stay Up to Date with AI — from heaigirl.substack.com by Diana Dovgopol
Here are some cool AI YouTube channels.
Here are 6 YouTube channels I watch to stay up to date with AI. This list will be useful whether you’re a casual AI enthusiast or an experienced programmer.
1. Matt Wolfe: AI for non-coders
This is a fast-growing YouTube channel focused on artificial intelligence for non-coders. On this channel, you’ll find videos about ChatGPT, Midjourney, and any AI tool that it’s gaining popularity.
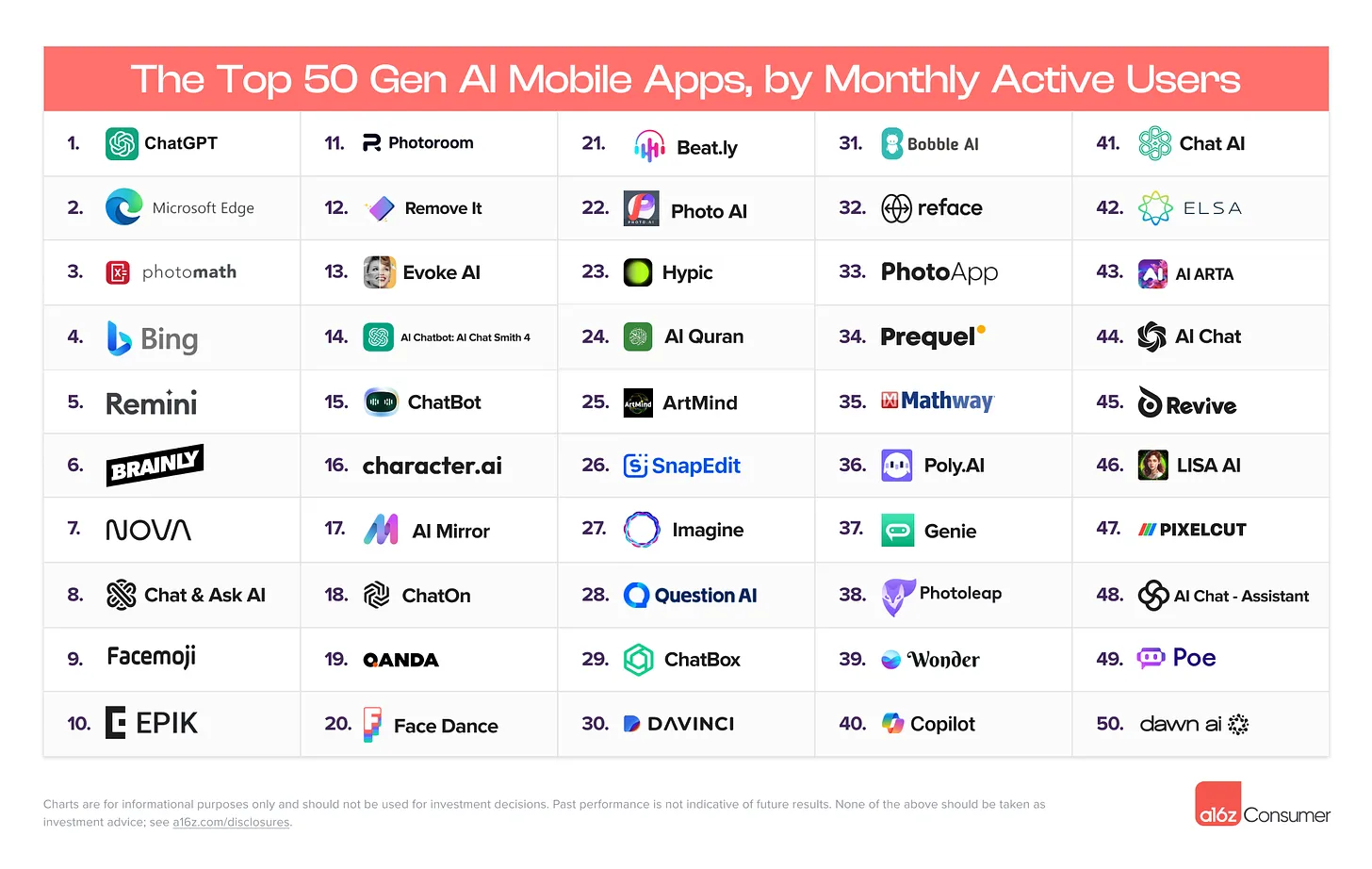
Top AI mobile apps, Stable Video 3D, & my AI film workflow — from by Heather Cooper
Plus 1-Click 3D animation and other cool AI tools
#3 Photomath
Photomath is a comprehensive math help app that provides step-by-step explanations for a wide range of math problems, from elementary to college level. Photomath is only available as a mobile app. (link)
Features:
- Get step-by-step solutions with multiple methods to choose from
- Scan any math problem, including word problems, using the app’s camera
- Access custom visual aids and extra “how” and “why” tips for deeper understanding
Google researchers unveil ‘VLOGGER’, an AI that can bring still photos to life — from venturebeat.com by Michael Nuñez
Google researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence system that can generate lifelike videos of people speaking, gesturing and moving — from just a single still photo. The technology, called VLOGGER, relies on advanced machine learning models to synthesize startlingly realistic footage, opening up a range of potential applications while also raising concerns around deepfakes and misinformation.
What We Risk By Automating Tasks We Loathe — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
I’m fascinated by the potential of these tools to augment and enhance our work and creativity. There’s no denying the impressive capabilities we’re already seeing with text generation, image creation, coding assistance, and more. Used thoughtfully, AI can be a powerful productivity multiplier.
At the same time, I have significant concerns about the broader implications of this accelerating technology, especially for education and society at large. We’re traversing new ground at a breakneck pace, and it’s crucial that we don’t blindly embrace AI without considering the potential risks.
My worry is that by automating away too many tasks, even seemingly rote ones like creating slide decks, we risk losing something vital—humanity at the heart of knowledge work.
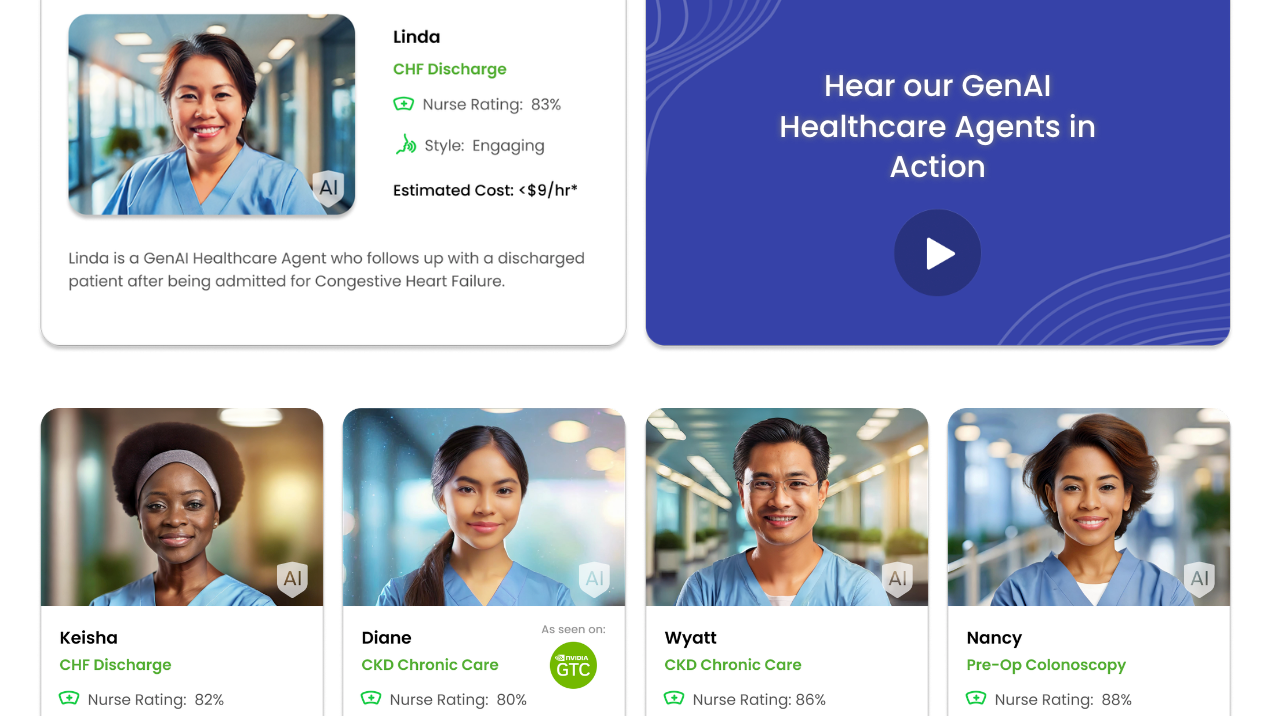
Nvidia Introduce AI Nurses — from wireprompt.substack.com | Weekkly AI Report from WirePrompt
Nvidia has announced a partnership with Hippocratic AI to introduce AI “agents” aimed at replacing nurses in hospitals. These AI “nurses” come at a significantly low cost compared to human nurses and are purportedly intended to address staffing issues by handling “low-risk,” patient-facing tasks via video calls. However, concerns are raised regarding the ethical implications and effectiveness of replacing human nurses with AI, particularly given the complex nature of medical care.
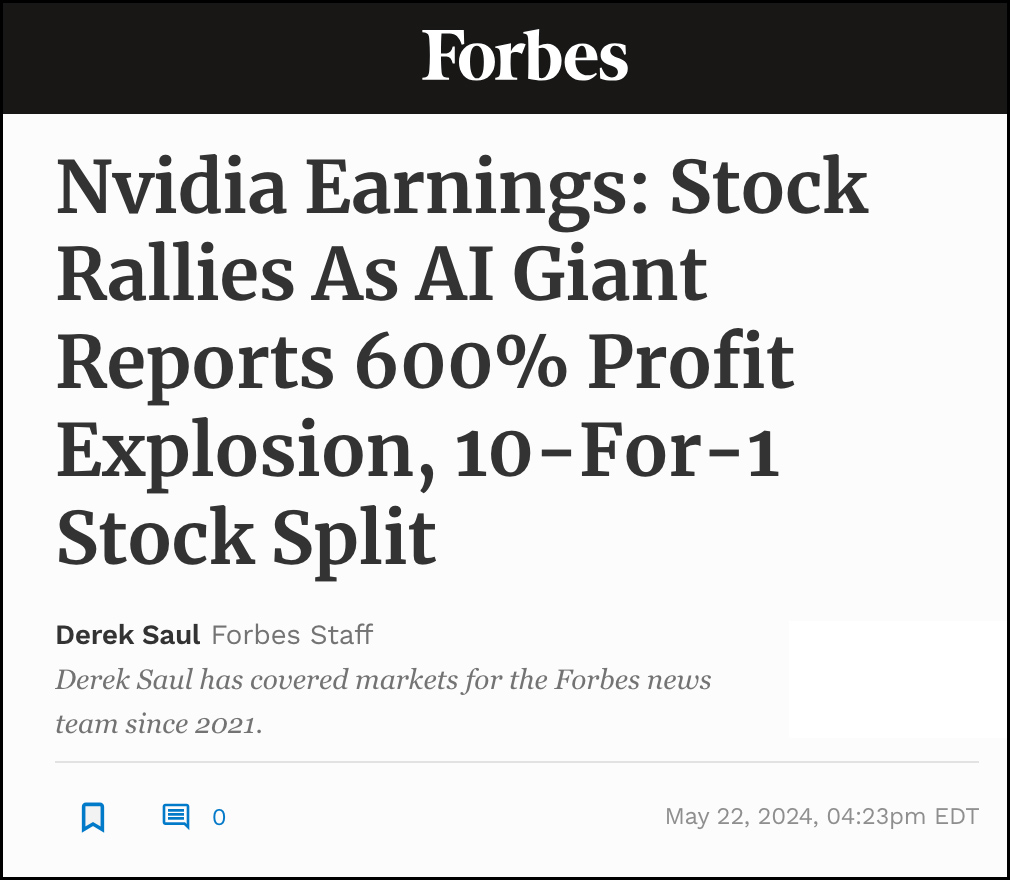
16 Changes to the Way Enterprises Are Building and Buying Generative AI — from a16z.com by Sarah Wang and Shangda Xu
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Resourcing: budgets are growing dramatically and here to stay
- Models: enterprises are trending toward a multi-model, open source world
- Use cases: more migrating to production
- Size of total opportunity: massive and growing quickly


















.webp)