It’s a 401(k) world — from nytimes.com by Thomas Friedman
Excerpts:
Something really big happened in the world’s wiring in the last decade, but it was obscured by the financial crisis and post-9/11. We went from a connected world to a hyperconnected world.
…
…the combination of these tools of connectivity and creativity has created a global education, commercial, communication and innovation platform on which more people can start stuff, collaborate on stuff, learn stuff, make stuff (and destroy stuff) with more other people than ever before.
…
But this huge expansion in an individual’s ability to do all these things comes with one big difference: more now rests on you.
…
Government will do less for you. Companies will do less for you. Unions can do less for you. There will be fewer limits, but also fewer guarantees. Your specific contribution will define your specific benefits much more. Just showing up will not cut it.
From DSC:
Makes me reflect on if we’re preparing our youth for the world that they will encounter. Makes me wonder…how does all of this emphasis on standardized tests fit into this new/developing world? Does the Common Core address these developing needs/requirements for survival? Are we preparing students to be able to think on their feet? To “pivot?” To adapt/turn on a dime? Or does K-20 need to be rethought and reinvented?
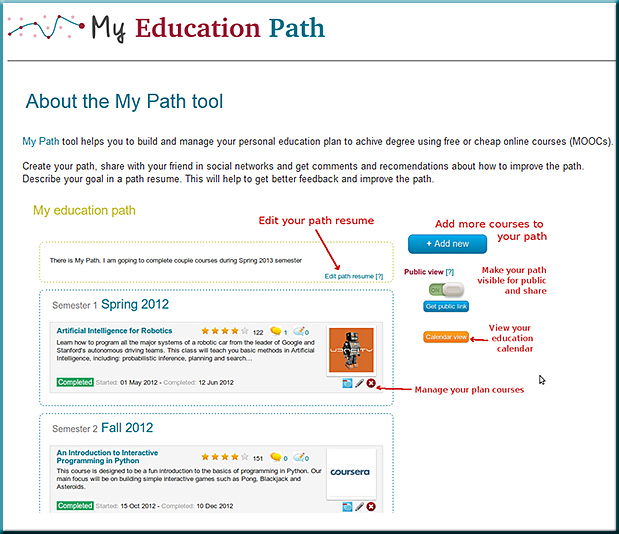
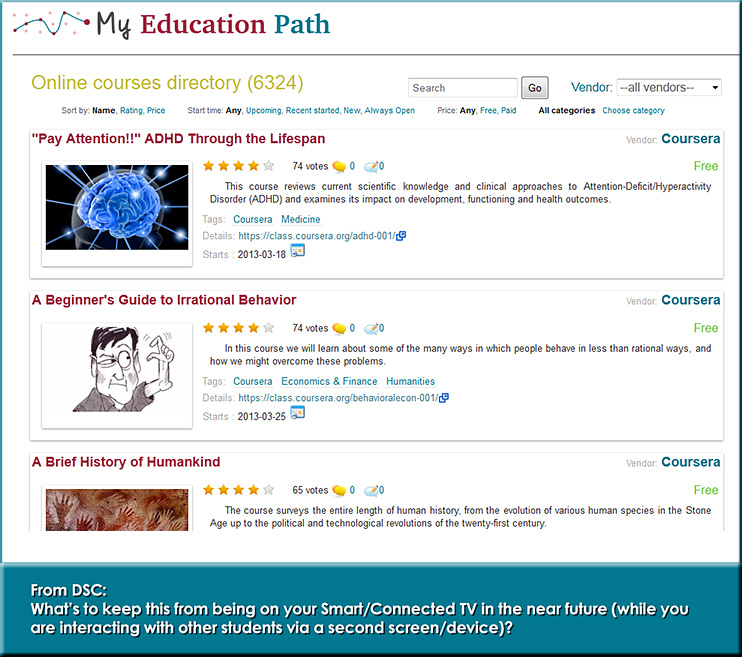
It seems that creativity, innovation, entrepreneurship, and lifelong learning are becoming more important all the time.
What say ye teachers and professors? If your students could have a super job tomorrow, would they come back to your class/school/program? If not, what would make them come back — and w/ eagerness in their step? That’s where we need to head towards — and I think part of the solution involves more choice, more control being given to the students.
The new term (at least to me) that is increasingly coming to my mind is:
Heutagogy — from Wikipedia (emphasis DSC)
In education, heutagogy, a term coined by Stewart Hase of Southern Cross University and Chris Kenyon in Australia, is the study of self-determined learning. The notion is an expansion and reinterpretation of andragogy, and it is possible to mistake it for the same. However, there are several differences between the two that mark one from the other.
Heutagogy places specific emphasis on learning how to learn, double loop learning, universal learning opportunities, a non-linear process, and true learner self-direction. So, for example, whereas andragogy focuses on the best ways for people to learn, heutagogy also requires that educational initiatives include the improvement of people’s actual learning skills themselves, learning how to learn as well as just learning a given subject itself. Similarly, whereas andragogy focuses on structured education, in heutagogy all learning contexts, both formal and informal, are considered.