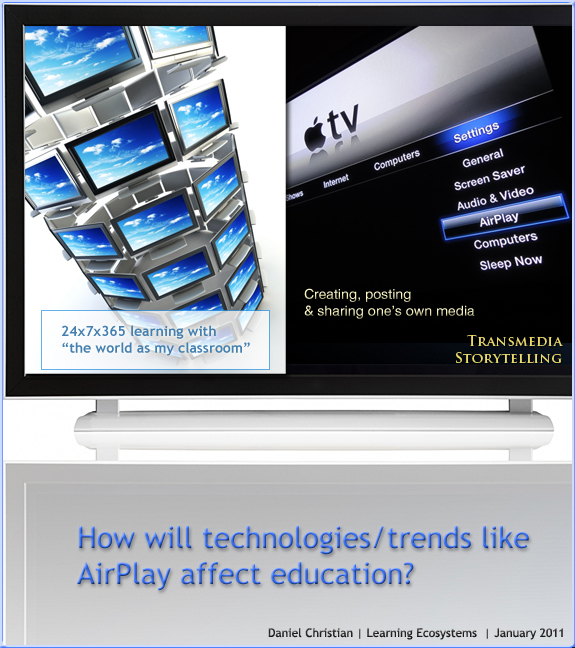
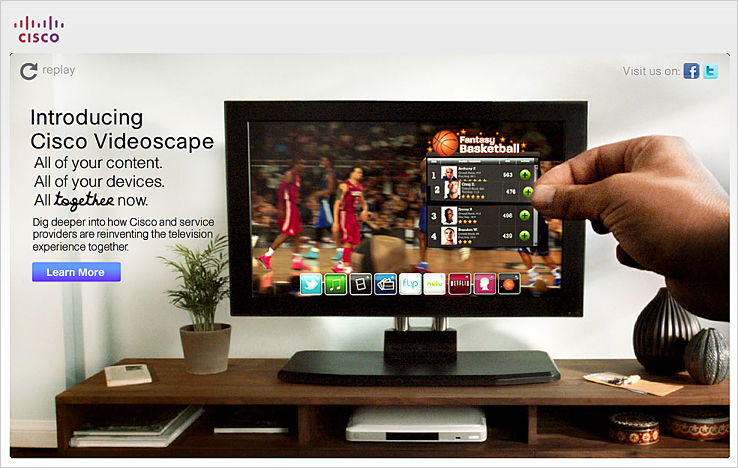
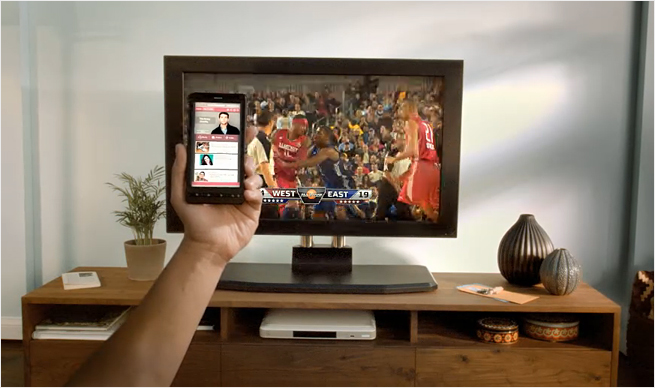
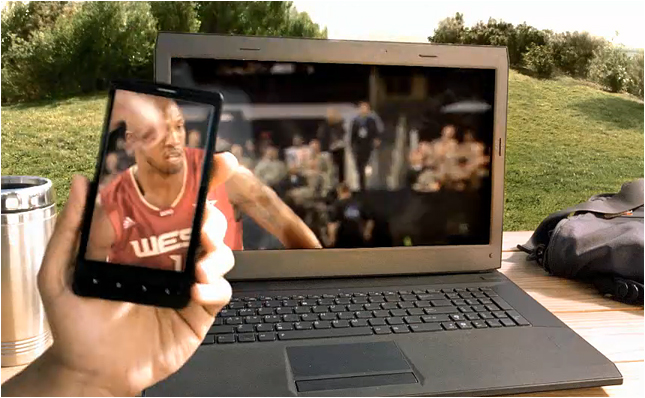
E-Learning Trends 2011 — ASTD
Excerpt:
Learning Circuits recently polled readers on how they’re using e-learning in their organizations. Here’s what they had to say.
How does your company use e-learning? (check all that apply)
| Customer service training | 34.2% |
| Enterprise transformations | 12.7% |
| External customers/clients | 20.3% |
| General business skills (leadership, sexual harassment, etc.) | 30.4% |
| IT (end user/desktop applications) | 39.2% |
| IT (network.infrastructure) | 12.7% |
| IT (programming languages) | 6.3% |
| Keeping staff up-to-date on acquisitions | 6.3% |
| Military | 2.5% |
| Product updates and rollouts | 20.3% |
| Regulatory/compliance issues | 35.4% |
| Salesforce training | 20.3% |
| Supply chain or channel partner training | 5.1% |
| Task-specific skills | 35.4% |
| Technical/manufacturing issues | 15.2% |
| We are in initial stages of implementing e-learning | 15.2% |
| Other (please specify) | 13.9% |