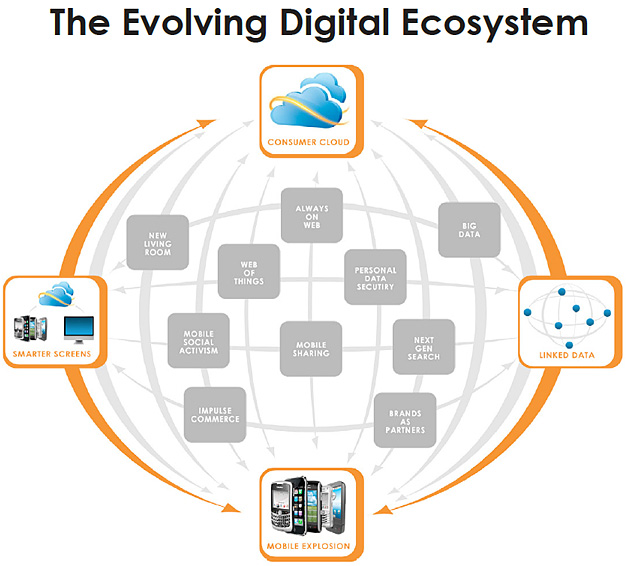
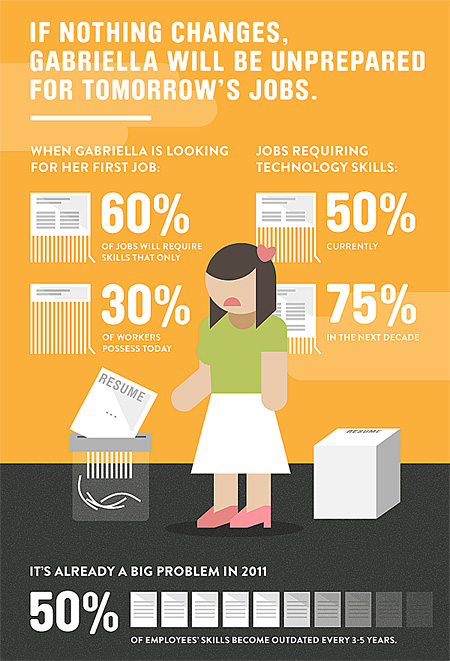
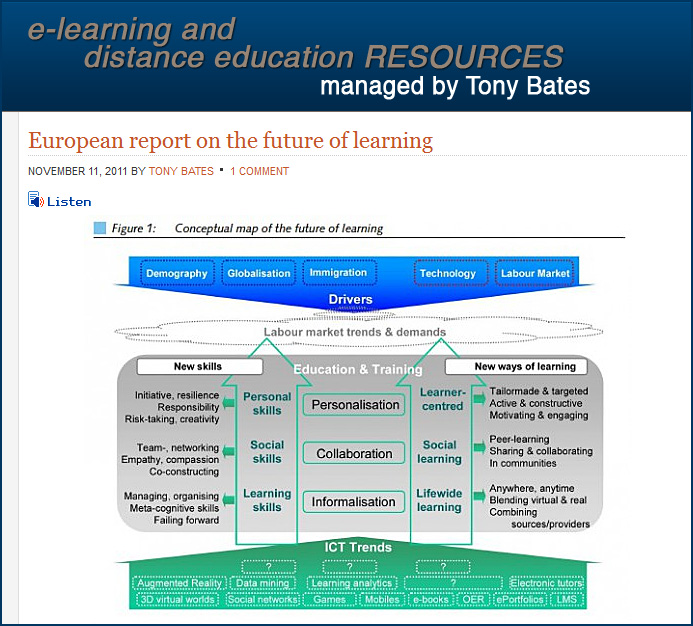
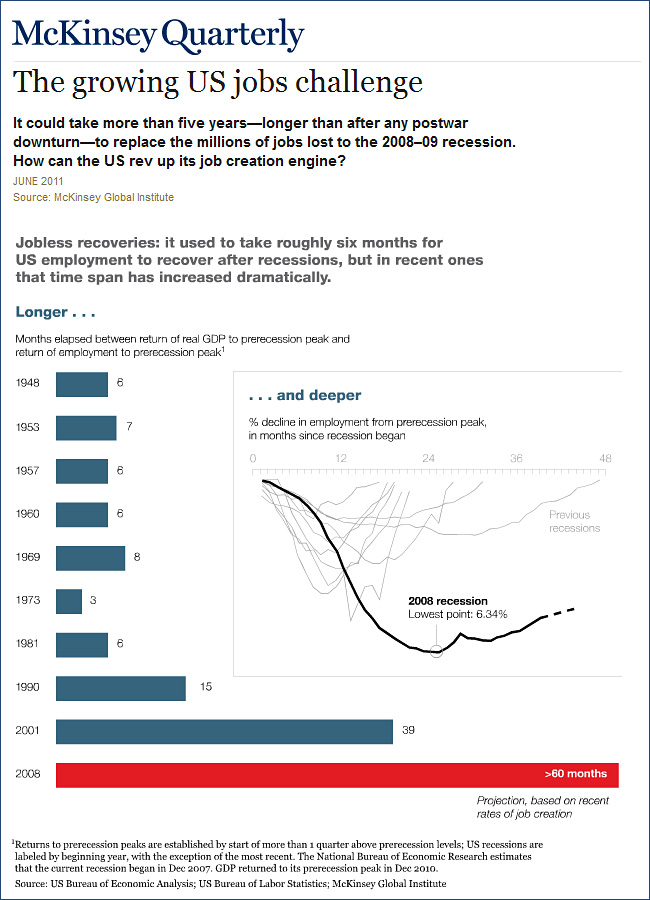
.
From DSC:
I originally saw this at Gerd Leonhard’s MediaFuturist.com where he entitles a blog posting:
- Thomas Friedman video on ‘That used to be us’: Must-watch for everyone in the U.S.!
(Thanks Gerd!!!)
Some of my notes on this video — Friedman’s main talk finishes around 35:45 w/ a Q&A beginning at 36:00
(From DSC: I’ve added my own thoughts in red)
- Non-routine work — is the kind of work that you want to be able to do (there’s also the non-routine, local work — butcher, grocier — but that wasn’t the focus here)
- Routine work — has been crushed via algorithms, outsourcing, (robotics), etc.
The bar has risen in non-routine work as we’ve moved from connected to hyper-connected world.
We are in the middle of an IT revolution/transformation — cloud, mobile, social, other — where Information Technology changes and globalization are creating global supply changes. Tom’s key point is that the United States needs to be involved in these changes or we’ll get left in the dust.
In their Help Wanted chapter, the following skills are wanted:
- Critical reasonsing
- Problem solving
- Non-routine work oriented
- But most of all, you must be able to invent and reinvent your job WHILE you are doing the job
- Creative
- Innovative
- (Pulse-checker and responder; which is why universities and colleges must begin offering classes on futurism/developing scenarios)
- Unique value creation
- Be able to bring your EXTRA
Average is over. Now that we are hyper-connected, “average” is over. If average is over — you must bring your “extra”.
From DSC:
If “average” is over, are we developing and raising up a generation of students who are learning how to bring their “extra”? Does standardized testing help us or hurt us in this regard?
3 key attitudes you need if you want to “lean into this world”:
- Think like a new immigrant
No legacy place waiting for me; I better figure out what world I’m living in, and then I better work hard to uncover and pursue the opportunities that current world presents; nothing is owed to me - Think like an artisan
Unique, hand-made; one-off’s, work in ways that you would be proud to carve your initials into your work - Think like the waitress at Perkins Pancake House in MN
Where she gave Thomas’ friend extra fruit and she mentioned that to them both; she brought her extra in areas where she had the control to do so
United States may be in relative decline — as we experience the “rise of the rest”; but what the US has to worry about it absolute decline
American exceptionalism — hogwash; no one owes us anything; have to earn our way; formula for success was a great private public partnership going back to Alexander Hamilton and built upon by Lincoln, Eisenhower, other (person asking question used the word ecosystem). 5 main pillars of this formulate for success/ecosystem:
- Education
- Infrastructure
- Open immigration policy
- Best rules for capital formation and risk taking
- Solid gov’t funded research
We’ve moved away from these 5 puillars of success and we’ve treated our nation like it’s a football that can be dropped w/ no resulting issues; the reality is we’re more like an egg; in another analogy, we can cut and hit arteries quickly…doing actual damage.
We misread environment — at end of cold war we put our feet up, thinking victory was won; the U.S. chased Al Queda instead of China, Brazil, other
Q&A
- Q: Influence — how changed and how stay the same
A: To have influence, must get substance right — content is key; diamond-hard realities are key; not the spins; still need to do grunt, basic work; can never be a Thor throwing down lightning bolts from on high - Q: Labor arbitrage
A: Rebalancing happening, but may take time; what was outsourced may not stay where originally went to - Q & A about Occupy Wall Street — was/is about injustice; taking $ and treating it like they were in a casino; people doing that got away with it; what will leadership look like in a hyperconnected world?
Final thoughts:
- Idea of OODA loop from the world of Air Force pilots — observe, ___ decide, act — speed of OODA loops are key; our political leaders are talking about A when X,Y, and Z are really happening (and the two circles rarely intersect)
- How long can we be a great country when our political systems cannot deliver optimal results?
- Our political system needs shock therapy — Friedman argues that we need a 3rd party — see AmericansElect.org
From DSC:
Each of us must be able to continually do pulse checks on a variety of forces that may be affecting our domains/places of work. We must be able to develop future scenarios and our responses to those scenarios. The ability to do that will become even more important as we move forward at ever-increasing speeds.
We can’t be looking 5-10 feet ahead when we’re driving at 180 miles per hour in this new, hyper-connected world!