If not now, when? –– from Educause ReviewMagazine by Adrian Sannier
Adrian Sannier is Digital Strategist and Senior Vice President of Product at Pearson eCollege and is Professor of Computing Studies at Arizona State University, where he was also the University Technology Officer prior to joining Pearson eCollege.
Excerpt:
Strong signs are indicating that higher education is finally on the verge of a long-awaited digital shift. Given that experts have been prophesying such a shift for more than forty years, with little if any real change, it’s reasonable to approach such a statement with healthy skepticism. Various factors—some cultural, some technological—have indeed retarded progress along this path to the future. Nevertheless, the unprecedented challenges facing the educational system, combined with higher education’s cultural success at solving daunting challenges through the widespread application of information technology, have created the conditions for rapid change. In the coming months, we will see major shifts in the role that technology plays in the creation, distribution, consumption, and improvement of learning experiences. And education will never be the same.
…
Beyond Textbooks, Beyond Bookstores, Beyond Learning Management Systems, Beyond School—the changes introduced by technology have already begun. The digital shift is upon us. If other industries and other fields are any guide, once the dominos begin to fall, progress will be swift and irreversible.
I, for one, can’t wait to be a part of it. If not now, when?
From DSC:
Readers of this blog will not be surprised at what I’m about to say…
Higher ed, if we are wise, will quickly wake up and heed the disruptive changes that have already occurred within other industries (i.e. those caused by a variety of technologies). The following quote is especially relevant for those of us in higher education, because the conversation is no longer being controlled by those within the world of higher education.
“For the first time, the tools to drive change and improve learning lie beyond the scope and the control of the academy, in the community which surrounds it. So, for the first time in our history, colleges and universities do not control either the conversation or the drive to innovate. As a consequence, also for the first time, if they stand still, they will be left behind, bobbing in the wake of rapid change.” — HEMG
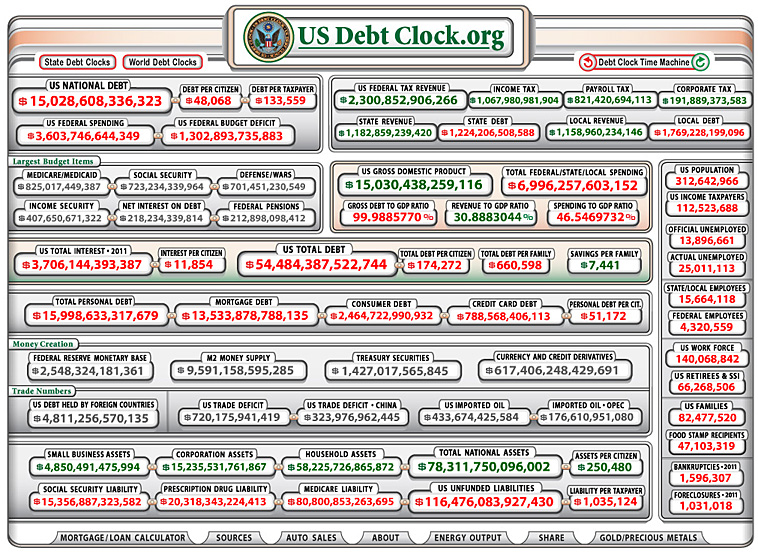
The writing on the wall is coming into a bolder/stronger/clearer view: Higher ed needs to respond to society’s needs and to its own customers…otherwise, it will become irrelevant. Much of this is due to what things often come down to — money.
The cost of education is one of the most potent forces acting as a catalyst to these changes — and the tidal waves of technological change will finish the job.

…and more forcefully illustrated: