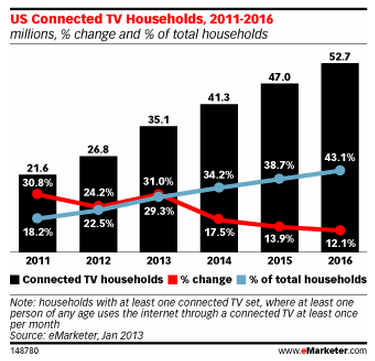
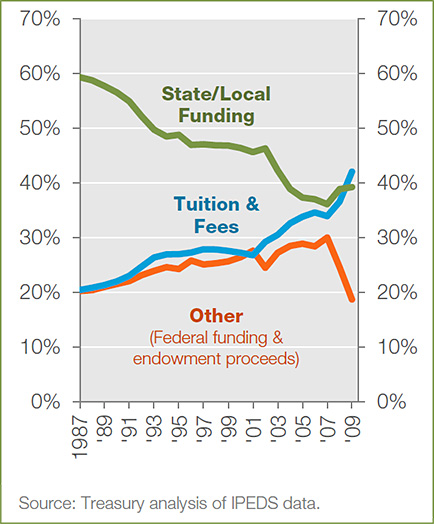
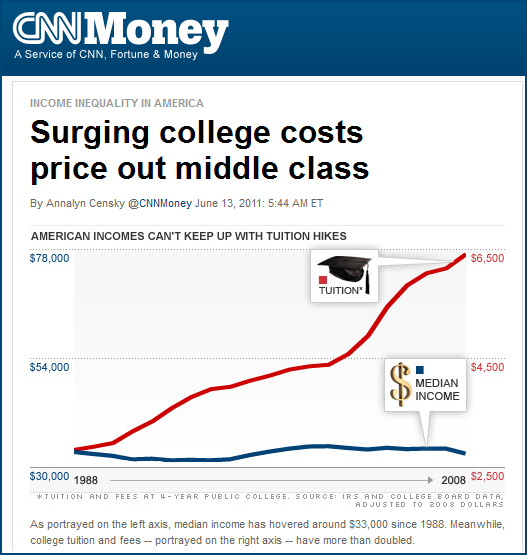
Also see:
- Sebastian Thrun: Udacity announces for-credit course pilot with San Jose State University — from Udacity’s blog; with thanks to Mr. Peter Snyder, Assistant Professor of Business at Calvin College for the resource
Excerpt:
Today Udacity is thrilled to announce a partnership with San Jose State University to pilot three courses — Entry-Level Mathematics, College Algebra, and Elementary Statistics — available online at an affordable tuition rate and for college credit. To my knowledge, this is the first time a MOOC has been offered for credit and purely online. Much credit for this partnership goes to Mo Qayoumi and Ellen Junn, president and provost of SJSU, and to the five fearless SJSU professors who have chosen to work with us at Udacity to explore this new medium. The offices of Governor Brown and CSU Chancellor White have also been critically important to this partnership for their leadership and expediency. Last but not least, I want to personally thank our great Udacians who, like everyone on this list, have worked endless hours to drive innovation.
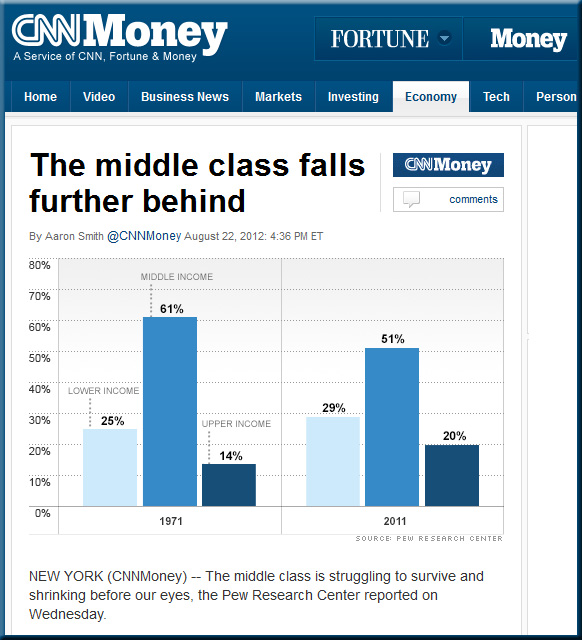
Over the past year, MOOCs have received a lot of attention in the media and education circles mostly because so many students are taking advantage of the course for free. Predictions that MOOCs would fundamentally change higher education often revolved around the fact that the courses have unprecedented reach and affordability.
From DSC:
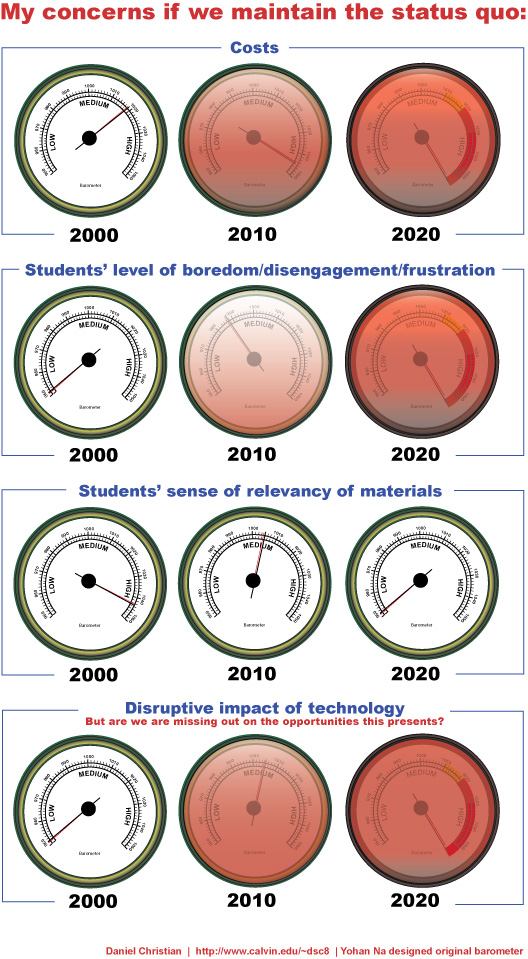
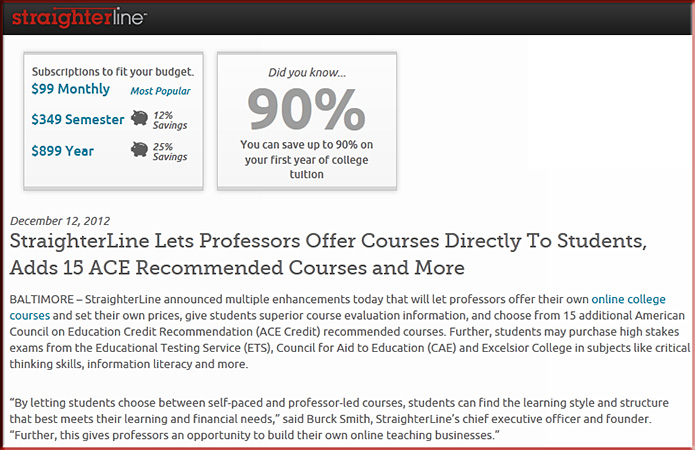
Given that such “Walmarts of Education” (i.e. solid learning at a greatly reduced prices) continue to develop, what’s our/your plans for responding to this trend? How are we/you going to compete? What’s our/your vision and strategy? By the way, you can look all you want to for data — but at the end of the day, it’s likely with this sort of thing that you won’t find all of the data that you require to make a decision. Examples:
- When I began working for Kraft Foods in 1990 (brought in to roll out email to 66 plants at the time), I believed in the power of email when few others did. Email was viewed as “fluff” and it would never be used for solid business practices; management put the project on hold. But I kept working with email at Kraft — trying to get others to use it. If you looked for data back then, you wouldn’t find it. But by the time I left Kraft in 1997, thousands of people could communicate with thousands of other people throughout the world — within minutes.
. - When Alexander Graham Bell introduced the telephone, what data would support the success of his invention? I suppose you could have pulled some data on the usage of the telegraph, but even then, vision would have had to trump the data (the ancestor of Western Union rejected his invention, as they questioned why anyone would need/use a telephone when there was already the telegraph in usage).
. - Such technological developments often are not so easy to back up with data; they require some vision, experimentation, and risk taking.















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)