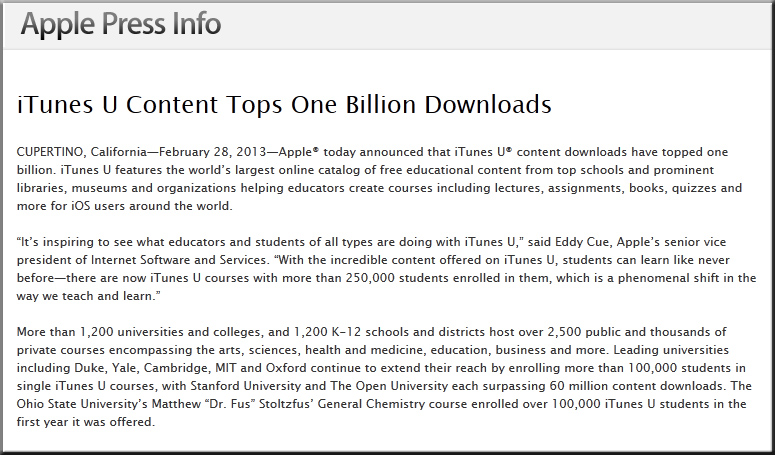
The coming automatic, freaky, contextual world and why we’re writing a book about it — from scobleizer.comby Robert Scoble
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
First, the short version of today’s news. Shel Israel and I are collaborating on a book, titled, The Age of Context: How it Will Change Your Life and Work.
The long version:
A new world is coming. It’s scary. Freaky. Over the freaky line, if you will. But it is coming. Investors like Ron Conway and Marc Andreessen are investing in it. Companies from Google to startups you’ve never heard of, like Wovyn or Highlight, are building it. With more than a couple of new ones already on the way that you’ll hear about over the next six months.
First, the trends. We’re seeing something new happen because of:
- Proliferation of always-connected sensors.
- New kinds of cloud-based databases.
- New kinds of contextual SDKs.
- A maturing in social data that nearly everyone is participating in.
- Wearable computers and sensors like the Nike FuelBand, FitBit, and soon the Google Glasses.
Also see:

Also see:
.

Book Description
Release date: January 18, 2013
The Information Age? Think again.
Change is everywhere: how we communicate, what we do for a living, the values we hold, the way we raise our children, even the way we access information. Thanks to a global economy, the force of the Internet, and the explosion of mobile technology, we have—almost imperceptibly—been ushered into a new era, the Shift Age, in which change happens so quickly that it’s become the norm.
Man-made developments—such as tools, machines, and technology—defined previous ages, but the Shift Age will be defined by our own power of choice. In Entering the Shift Age, leading futurist David Houle argues that we are going through a major collapse of legacy thinking, eroding many of the thought structures that have defined the last two hundred years of humanity. Houle identifies and explains the new forces that will shape our lives—including remote workplaces, the cloud, “24/7” culture, speed-of-light connectivity, creativity, and the influence of Millenials and Digital Natives—for the next twenty years.
In this eye-opening book, Houle navigates this pivotal point in human history with clarity and anticipation, focusing on the power of human consciousness and the direct influence we can impart on everything from healthcare to media to education. According to Houle, we are more independent than ever before. We are in control.
There’s no “going back” to the way things were. Reality is changing ever faster, and ENTERING THE SHIFT AGE is your guide to keeping up.
From DSC:
Though I haven’t read the book, I would probably take a different angle/perspective on some things here. Yet, this work seems important in that it addresses the constant change — and pace of change — that we find ourselves and our world in.