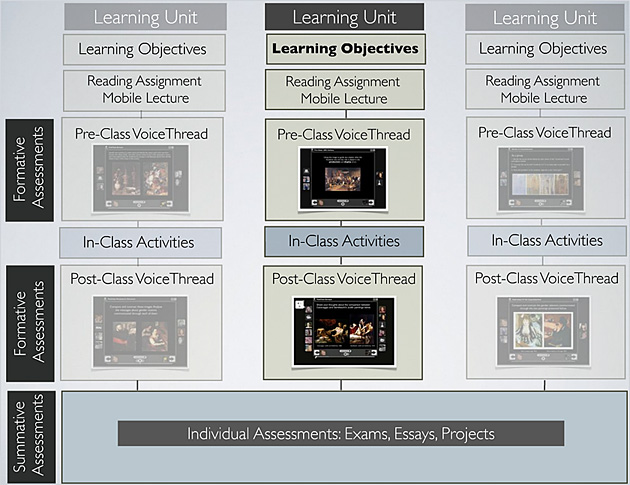
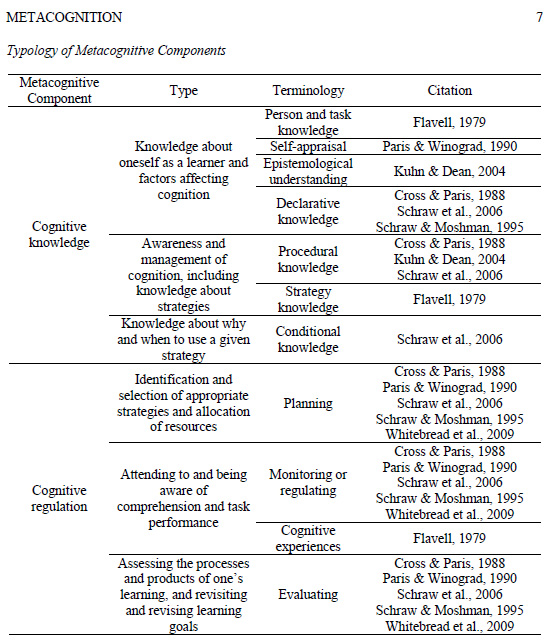
Passion-based learning in the 21st century: An interview with Sheryl Nussbaum-Beach — from plpnetworks.com by John Norton
Sheryl Nussbaum-Beach often speaks of the “moral imperative” for K12 educators to assure that all students gain the skills, knowledge and dispositions they need to be successful in a connected world “where the ability to think critically, collaborate effectively and master increasingly powerful digital technologies” will determine their success in school, college and careers.
Nussbaum-Beach has been an educator for 20 years, serving as a public school classroom teacher, technology coach, charter school principal, district administrator, university instructor, and digital learning consultant. She is a frequent international speaker and the chief executive officer of Powerful Learning Practice LLC, a company she founded with educator-author Will Richardson to provide “professional development for 21st century educators.” PLP’s client list includes public, parochial and independent schools in the United States, Canada, Australia and Norway.
Nussbaum-Beach is also president of the digital consulting firm 21st Century Collaborative, LLC and a doctoral candidate at The College of William and Mary. She serves on the advisory board for the 2011 Horizon Report on trends in K12 education. Her first book, The Connected Educator, will be published by Solution Tree later this year.
In this interview, Sheryl describes the “shift” she believes must take place in teaching and learning practices if elementary and secondary schools expect to remain relevant in an era when information and communication technologies will continue to expand exponentially.
Also see: