Harvard’s plan to dominate higher education — from jumpthecurve.net by Jack Uldrich
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Critics of online education and MOOCs may delude themselves by thinking an online course can never offer the same level of intimacy or interaction as a traditional college course but they are missing a key component of the MOOC movement: analytics.
What Harvard and other MOOC providers understand is that every time a student interacts with the material on an online course, she provides the institution feedback that allows it to learn a little more about how that student learns. Armed with this information they can then offer future courses designed not only to meet that individual’s specific educational needs but which are delivered in a manner personally tailored to his or her unique learning style.
…
Imagine Harvard charges a $100 accrediting fee to every student who takes one of its free courses. If one million students—students who formerly populated state universities and colleges—opt instead to take just one accredited course a year from Harvard that amounts to $100 million a year.
From DSC:
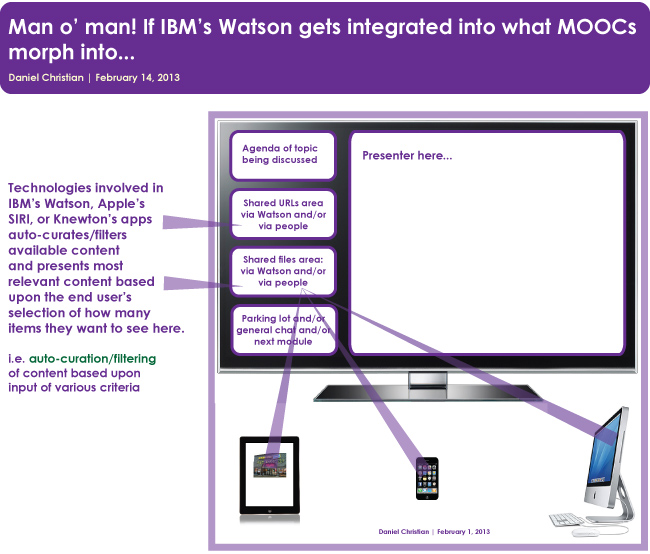
Readers of this blog will know that I think MOOCs are in an iterative process of morphing into something else, something new. MOOCs are half-baked at this point. I say that because it’s like drinking from a firehose (at least as of early March 2013). But what Jack Uldrich points out is what I was trying to get at in the graphic below. That is, if technologies that can capture, filter, curate, provide relevant information based upon analytics, one doesn’t have to drink from a fire hose anymore…the drinking fountain now becomes a better metaphor.
On a potentially related note — and a veeeerrrryyyy interesting question asked at this article out at Chief Learning Officer:
Either one of these forces could create what I’ve been calling “The Forthcoming Walmart of Education” (since 2008). As Smart/Connected TVs proliferate, Apple’s developing infrastructure and ecosystem could easily fill the bill.











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)