Living room wars — from tnl.net by Tristan Louis
Excerpt:
Control of the TV screen is seen as a major step in the next iteration of computing. The field can be divided between hardware manufacturers, content providers and end-to-end players who are looking to provide a complete solution. The net result is that while everyone is trying to get into every other player’s field, the emerging winners may not be the ones who grab most of the headlines.
Also see:
- The four screens — from tnl.net
Excerpt:
The battle for digital supremacy is increasingly being waged on 4 different screens, with much of the focus in the computing industry being focus on 2 of them. When one looks at the expanding field, however, the dynamics may be radically different than expected.
Addendums/see:
- Singapore moving toward future with artificial intelligence in schools — from education4site.org by Tryggvi Thayer
- Using technology to personalize learning and assess students in real-time — from brookings.edu
.

From DSC:
What might H2O-like functionality look like on a Smart TV?
.
.
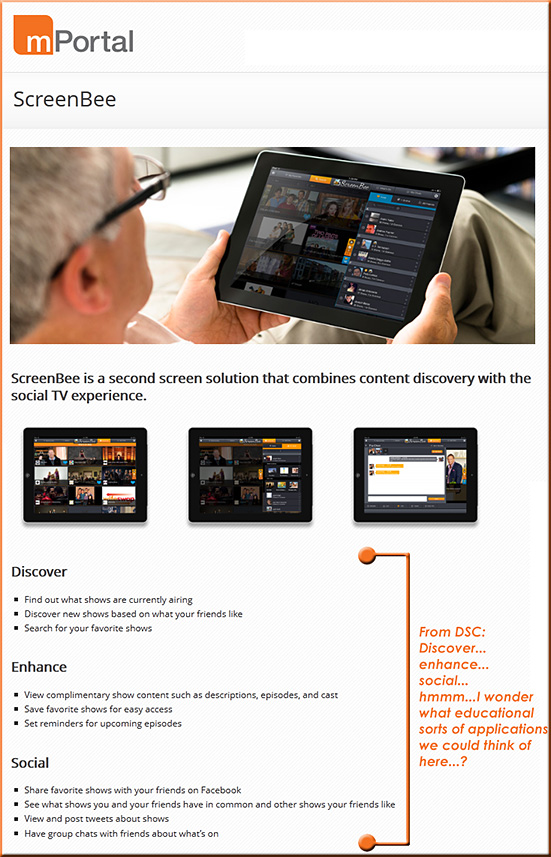
From DSC:
What educationally-related apps could something like ScreenBee address?
.