First day of school: Anastasis Academy #standagain — from iLearnTechnology.com
Today was one for the books. We did it! We opened a school with a radical new vision for what a school should look like in light of learning. It was a truly great day!
Mission:
[Anastasis Academy’s mission] is to apprentice children in the art of learning through inquiry, creativity, critical thinking, discernment and wisdom. We strive to provide an educational model that honors and supports children as the unique and creative individuals that God created them to be. We work to shape the development of the whole-child by engaging the mind, body and spirit while inspiring each to personal excellence.
Also see:
Look where you want to go and steer in that direction: How a blog started a school — from Dreams of Education (6/24/11)
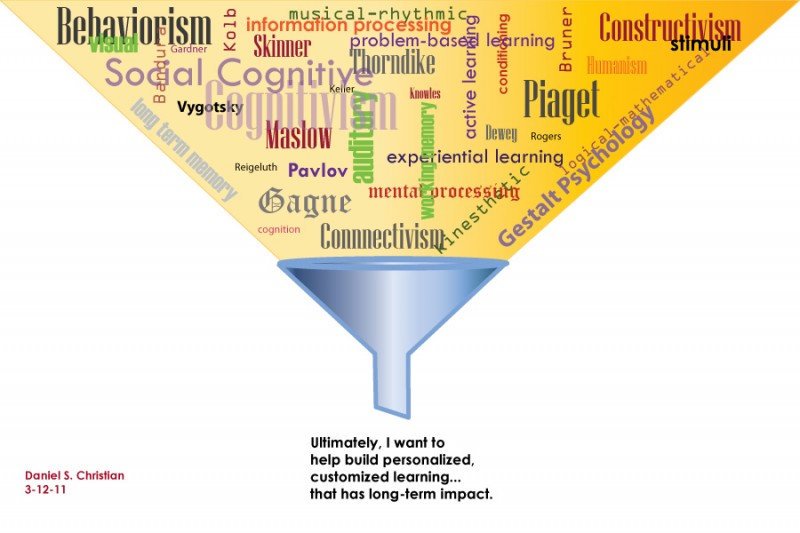
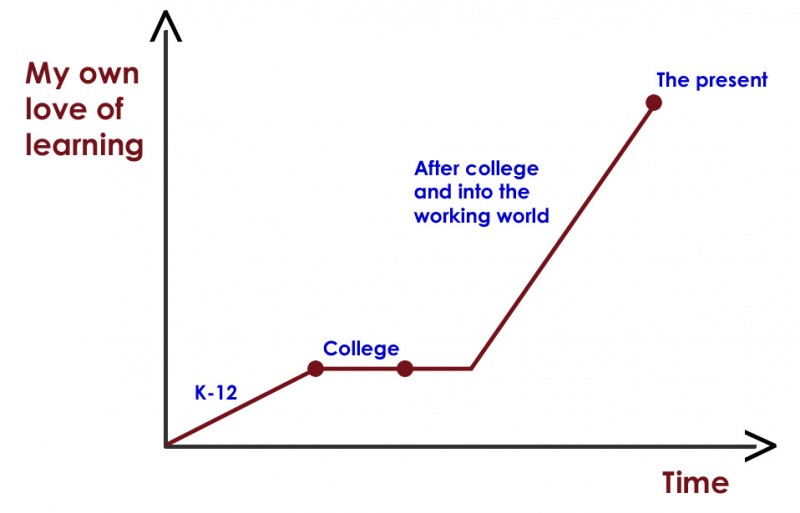
From DSC:
24 “The LORD bless you and keep you; 25 the LORD make his face shine on you and be gracious to you; 26 the LORD turn his face toward you and give you peace.” (Numbers 6:24-26) May He bless your efforts as you seek to not only impact the minds of — but also the hearts of — your students.
We really need to impact both in order for our future students to make significant, positive impacts around the globe. Way to go Kelly!