The IT conversation we should be having — from HBR.org by Jim Stikeleather
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
It is a conversation about the increasing importance of information technology and the role it must assume in every enterprise, regardless of size, industry or geography.
…
Our observations:
- CEOs are demanding more visible value from their CIOs, in terms of generating revenue, gaining new customers, and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Increasingly, the CIO and IT must be seen less as developing and deploying technology, and more as a source of innovation and transformation that delivers business value, leveraging technology instead of directly delivering it.
- The CIO must be responsible and accountable if technology enables, facilitates or accelerates competition that the C-suite didn’t see coming, or allows the enterprise to miss opportunities because the C-suite did not understand the possibilities technology offered.
- CIOs today must adapt or risk being marginalized.
From DSC:
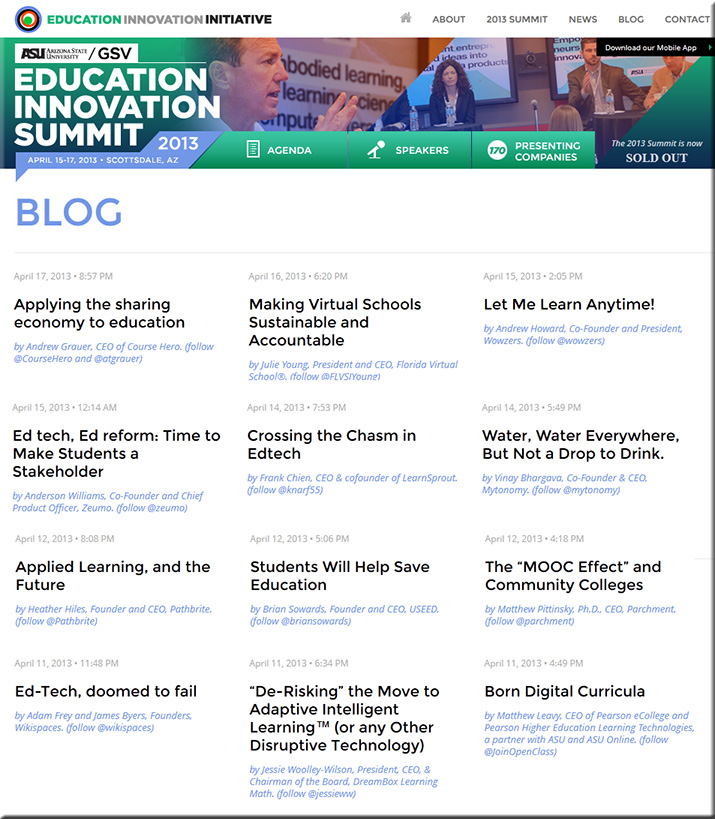
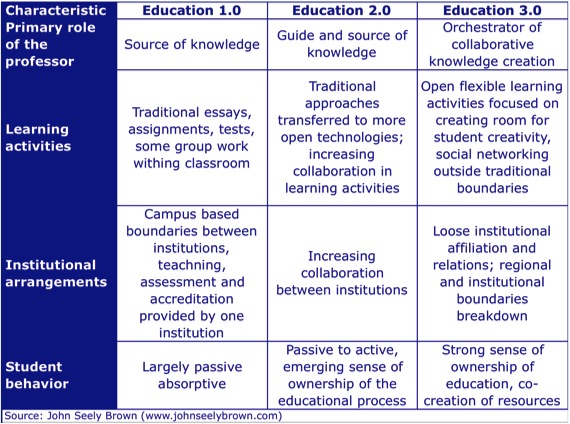
This is critical in the higher ed space as well!
The majority of the higher education industry still isn’t getting it — we are operating in a brand new ball game where technology must be used strategically. It’s not just about building and maintaining the infrastructure/plumbing anymore (though that is extremely important as well). It’s about the strategic, innovative use of IT that counts from here on out.