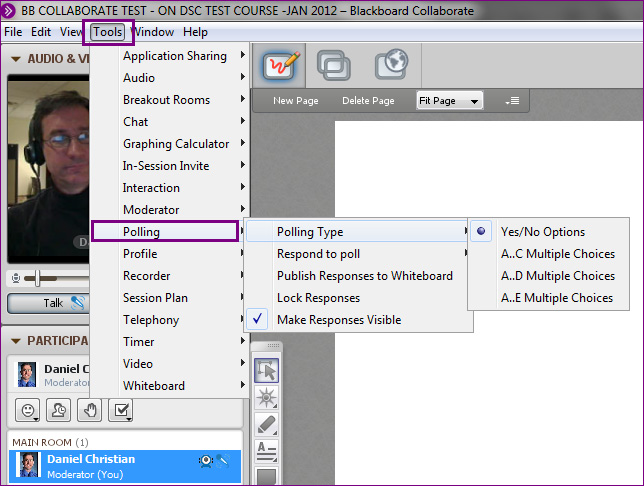
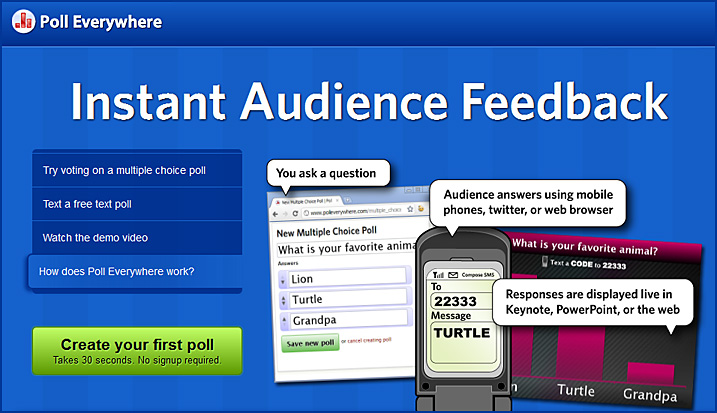
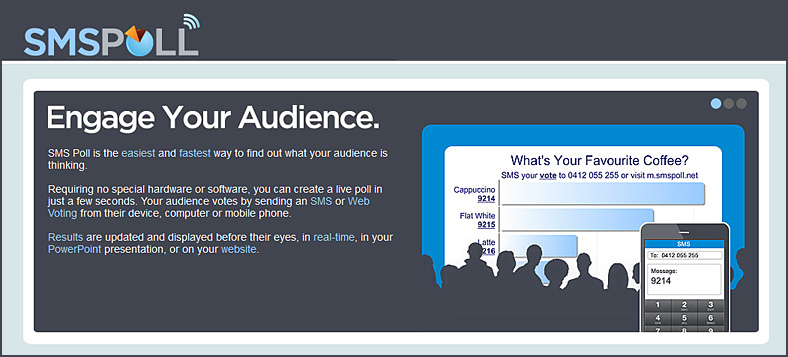
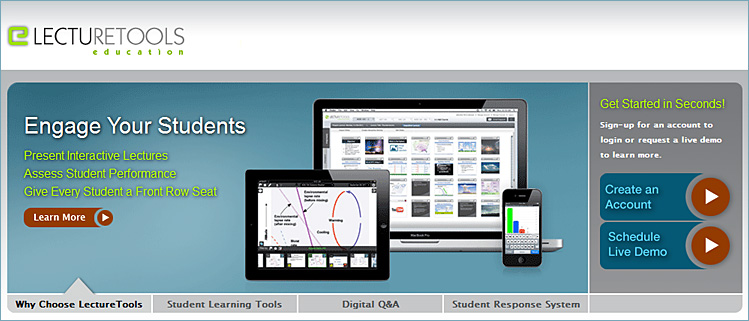
.
From DSC:
If you doubt that…read on…
The New Normal: Universities Sponsoring Online High Schools — from EdReformer.com
K12 announced today that they are partnering with George Washington University to launch The George Washington University Online High School. This private high school will serve students from the US and countries around the world January 2011.
Students are constantly trying to find options that will set them apart from others and participating in this rigorous college preparatory program could be the key. In addition to the curriculum, students who attend an online high school connected to a University such as GWUOHS will have college counseling, personalized learning tools, test preparation, even guidance through the scholarship process.
GWU is not the only university sponsoring online high schools. Stanford has the EPGY Online High School. University of Missouri High School and The University of Oklahoma offer year-round and dual enrollment courses. Whether public or private schools, the possibilities are endless for students. Training for sports, starting a business, volunteering, working in the arts, all can become easier by signing in to your online courses from the nearest computer.
Through major universities in partnership with online providers, students are reaping the benefits of university resources online high schools. It is interesting that we do not see this type of partnership more often.
MIT tries new approach for some OpenCourseWare (OCW) — from The Chronicle by Jeff Young
New MIT OpenCourseWare Initiative Aims to Improve Independent Online Learning — from the NYT by Aurey Watters of ReadWriteWeb
MIT OpenCourseWare is launching five new courses today that mark a new model for one of the world’s premier open educational resources. These OCW Scholar courses are designed for use by independent learners, and like the other material made available through MIT OCW, are freely available for anyone to pursue. These aren’t distance learning classes – there is no instructor, no contact with MIT, no credit. But the courses are meant to be stand-alone offerings, not requiring any additional materials for learning.
Technology Empowering Online Learning at Post-Secondary Level — from TMCNet by Beecher Tuttle
Times have changed, however. With lower budgets, limited physical space and new insight into the effectiveness of online learning, a myriad of highly regarded public and private colleges and universities have begun transitioning their curriculum to a digital world. In fact, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, one of the most well thought-of state institutions on the East Coast, recently announced its plans to offer its prestigious MBA program completely online. The business school’s dean told Mashable that the university made the move because it did not see online learning as a lesser form of education, if delivered properly.
Quick aside from DSC:
Re: that last sentence…please…let’s stop asking the question if online learning is as good as face-to-face learning. That question has been answered time and again.
The question now is, how will face-to-face learning begin to keep up and measure up to online learning as online learning begins to hit its real stride? We haven’t seen anything yet; and at this point, innovation is happening at much faster speeds in the online world. Those professors, teachers, and trainers used to working solely in the face-to-face teaching and learning environments better really start asking themselves how they will innovate, and how they will respond to the K-12 students (and employees) that are changing right in front of our eyes!
New Web Venture Offers ‘Syndicated Courses’ — from The Chronicle by Tusher Rae
Omnicademy, a for-profit institution conceived at Louisiana State University, hopes to allow professors to syndicate their courses this fall.
The company’s system will let professors upload material from courses they’re already teaching and offer the courses to students at other colleges through the Omnicademy site, said the company’s founder, Stacey Simmons, associate director for economic development at Louisiana’s Center for Computation and Technology.
Universities can review the courses and decide which ones they want to adopt and offer credit for. When students log into Omnicademy—using a .edu e-mail address—they will only be allowed to select from courses that have been approved by their institution.
If a student wishes to take a course offered through Omnicademy that is not on the list approved by his or her university, Omnicademy will negotiate on behalf of that student with the university, Ms. Simmons added.
2020 Vision — from neXtedu
The MEGATRENDS I see changing the Education Industry are:
1) The Knowledge Economy:
Prediction: By 2020, Assessment becomes the currency for the Knowledge Economy, not where you went to school. In other words, opportunity will truly be driven by what you know, not by where your degree is from.
2) Globalization:
Prediction: By 2020, there will be Global Schools like Avenues and Mosaica in the primary and secondary market and an acceleration of Global Universities will be driven by online offerings. Moreover, study abroad will become a standard part of a college education (up from 1% of the students currently) and will even be an important feature for top-tier private K-12 schools.
3) The Internet: …Web 2.0 is truly about “democratizing” education, not only increasing access and lowering cost but also improving quality.
Prediction: By 2020, all college students will have a “blended” or “hybrid” learning experience, as will nearly all high school students. Virtual School operators such as K12, Connections Academy and Florida Virtual have millions of students and Arizona State University Online becomes the largest University in the World. The information that is made readily available by new media education sites such as Center for Education Reform’s “Media Bullpen” and the Education Breakthrough Network create a “dismantling of the Berlin Wall” moment for school choice, with a flood of opportunities coming to parents and students throughout the United States.
4) Outsourcing:
Prediction: By 2020, students in Charter Schools will have more than tripled from 3% to 10% of America’s student body, and it will become standard to integrate specialists, from foreign languages to mathematics, into the “traditional” school. Teach for America becomes a “for profit” as does KIPP, eliminating the ongoing need to raise tens of millions of dollars every year and instead utilize investor capital to sustain and grow their businesses. I predict over 25% of Universities will have partnerships with outsourced providers to manage their online offering. Several states will decide to “privatize” their public university system.
5) Consolidation:
Prediction: By 2020, the trend of less power and money from local coupled with a rationalization of the market will see many districts consolidate under either regional or state governance. As many as 1/3 of the private colleges and universities will either “merge” with other universities or go away.
6) Demographics:
Prediction: By 2020, Education is the #1 national issue driven by minorities understanding that equal access to education is key to their future — and zip code shouldn’t determine a student’s earnings power. Early stage childcare becomes much more of a national priority with leaders such as Bright Horizons being the model for how corporations and parents work together to provide the early learning needed to be “school ready”. Gaming will be a standard component of core curriculum and supplementary learning with companies like Dreambox, Tabula Digita , Knewton and Grockit creating powerful adaptive platforms.
7) Network Effects:
Prediction: By 2020, large learning networks are created in K12, Higher Ed and the Corporate Marketplace driven by gigantic network effects. Platforms that support “apps” such as digital content, assessment, and social collaboration are supported by three or four large players.
8) Freemium:
Prediction: By 2020 some of the largest education companies will be “freemium” models with revenues driven by premium services, sponsorships and ads. In a world where “assessment is the currency” for opportunity, freemium models that deliver high value knowledge at no cost or a fraction of the cost (like Academic Earth) will be very disruptive to high cost providers.
9) Open:
Prediction: By 2020, most colleges and universities have abandoned their captive LMS and have adopted open solutions, and service providers such as RSmart and Moodle Rooms are thriving.
10) Brands:
Prediction: By 2020, institutions with substantial brand equity will have multiple partners to leverage into cash to supplement endowments and flattish tuitions. As with case studies from other sectors that have created network effects with freemium models, GLOBAL MEGABRANDS will be created with a number of education companies obtaining $10 billion plus market caps.
Arizona State University’s Education Innovation Network
The Education Innovation Network is an open innovation platform where entrepreneurs can find the resources to validate concepts, accelerate growth and reach transformative scale.
From DSC:
Again…do you hear the waves of change crashing on our shores? Do you sense the increased speeds of the “cars on the racetrack”?