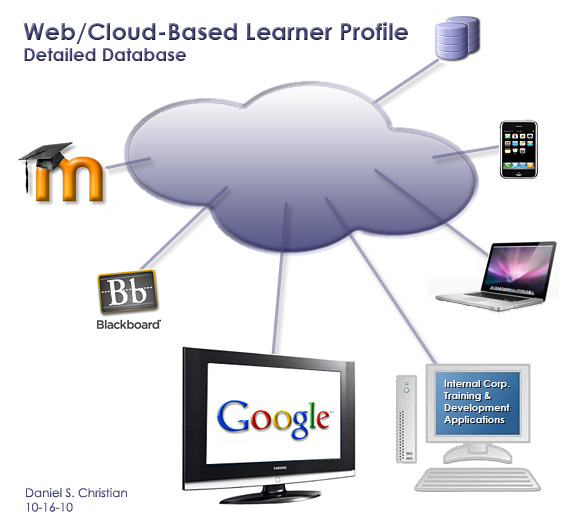
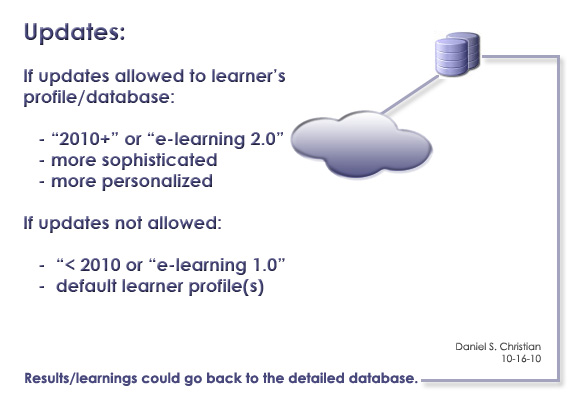
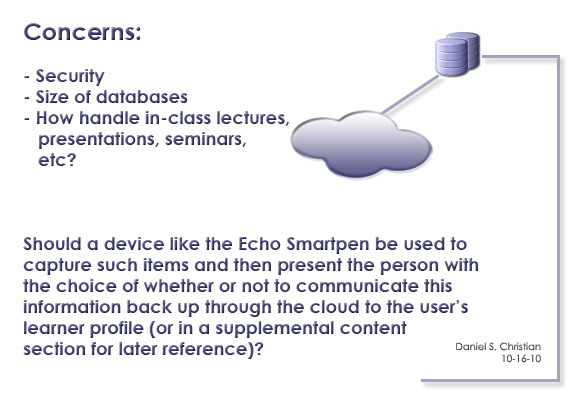
From DSC:
Though I can’t re-publish this article (it costs $19), I do hope it’s ok that I share the abstract and the references of the article (if not Birol or Mustafa, please advise). They are definitely onto something here, and we all need to continue to keep our eyes on such keywords as:
- learning agents
- multi agent systems
- 1:1
- personalized/customized learning
- artificial intelligence (AI)
- the semantic web
- …as these items represent where technology can be powerfully leveraged in the future.
Developing Adaptive and Personalized Distributed Learning Systems with Semantic Web Supported Multi Agent Technology
Birol Ciloglugil
Dept. of Comp. Engineering
Ege UniversityIzmir, Turkey
Mustafa Murat Inceoglu
Dept. of Comp. Education and Instructional Technology
Ege University
Izmir, Turkey
Abstract—The early e-learning systems were developed with the one-size-fits-all approach where the differences among the learners were disregarded and the same learning materials were supplied to each user. Nowadays, with the technological advances and the new trends in system design, the newly-developed systems take into consideration the needs, the preferences and the learning styles of the learners. As a result of this, more personalized e-learning systems have been developed. This thesis will investigate how possible technologies such as multi-agent systems and semantic web can be used to achieve more adaptive and more personalized distributed e-learning environments.
Keywords-adaptive systems; e-learning, multi agent systems; personalized e-learning systems; semantic web
REFERENCES
[1] H. Wang, P. Holt, “The design of an integrated course delivery system for Web-based distance education”, Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference on Computers and Advanced Technology in Education (CATE 2002), 2002, pp. 122-126.
[2] F. O. Lin, Designing Distributed Learning Environments with Intelligent Software Agents, Information Science Publishing, 2004.
[3] B. Ciloglugil, M. M. Inceoglu, “Exploring the state of the art in adaptive distributed learning environments”, LNCS, vol. 6017, 2010, pp. 556-569.
[4] I. S. B. Gago, V. M. B. Werneck, R. M. Costa, “Modeling an Educational Multi-Agent System in MaSE”, LNCS, vol. 5820, 2009, pp. 335-346.
[5] S. Garruzzo, D. Rosaci, G. M. L. Sarne, “ISABEL: A multi agent elearning system that supports multiple devices”, IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Intelligent Agent Technology, 2007, pp.85-88.
[6] T. Berners-Lee, J. Hendler, O. Lassila, The semantic web, Scientific American, 2001, pp. 34-43.
[7] A. Gladun, J. Rogushina, F. Garc?a-Sanchez, R. Martínez-Béjar, J. T. Fernández-Breis, “An application of intelligent techniques and semantic web technologies in e-learning environments”, Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 36, 2, 2009, pp. 1922-1931.
[8] M. Gaeta, F. Orciuoli, P. Ritrovato, “Advanced ontology management system for personalised e-learning”, Know.-Based Syst., vol. 22, 4, 2009, pp. 292-301.
[9] B. G. Aslan, M. M. Inceoglu, “Machine learning based learner modeling for adaptive Web-based learning”, LNCS, vol. 4705, 2007, pp. 1133-1145.
[10] W. S. Lo, I. C. Chung, H. J. Hsu, “Using ontological engineering for computer education on online e-Learning community system”, International Conference on Education Technology and Computer, Singapore, 2009, pp. 167-170.
[11] L. Romero, H. P. Leone, “An ontology on learning assessment domain”, New Perspectives on Systems and Information Technology, vol. 2, 2007, pp. 137-148.
[12] A. Canales-Cruz, V. G. Sanchez-Arias, F. Cervantes-Perez, R. Peredo-Valderrama, “Multi-agent system for the making of intelligence and interactive decisions within the learner’s learning process in a web-based education environment”, Journal of Applied Research and Technology, vol. 7, 3, 2009, pp. 310-322.