Excerpt from introduction (emphasis DSC):
Three factors are driving this new interest and enthusiasm for digital learning by educators. First, teachers and administrators are increasingly become technology-enabled themselves, using emerging technologies such as mobile devices, online classes and digital content to improve their own productivity. This development of a personal value proposition with the technology is propelling educators to think creatively about how to leverage these same tools in the classroom. Second, students and increasingly parents are demanding a different kind of learning experience and that is forcing even the most reluctant teachers and administrators to re-evaluate their perspectives about the value of technology within learning. As noted in prior Speak Up national reports, students have a very clear vision for 21st century learning. Their preference is for learning environments that are socially-based, un-tethered and digitally rich. Parents are also supportive of this new learning paradigm and as we noted in our first Speak Up 2010 report (released in April 2011) the emergence of a new trend of parental digital choice is an indication of this unprecedented support level. And schools and districts are waking up to this new trend. Concerns about parents’ capability to, for example, enroll their children in non-district provided online classes are compelling many districts to start virtual schools themselves. The third factor, the economy, and its resulting financial pressures on school and district budgets, has created a sense of urgency to more fully investigate how technologies can help educators meet their instructional goals with less expense.
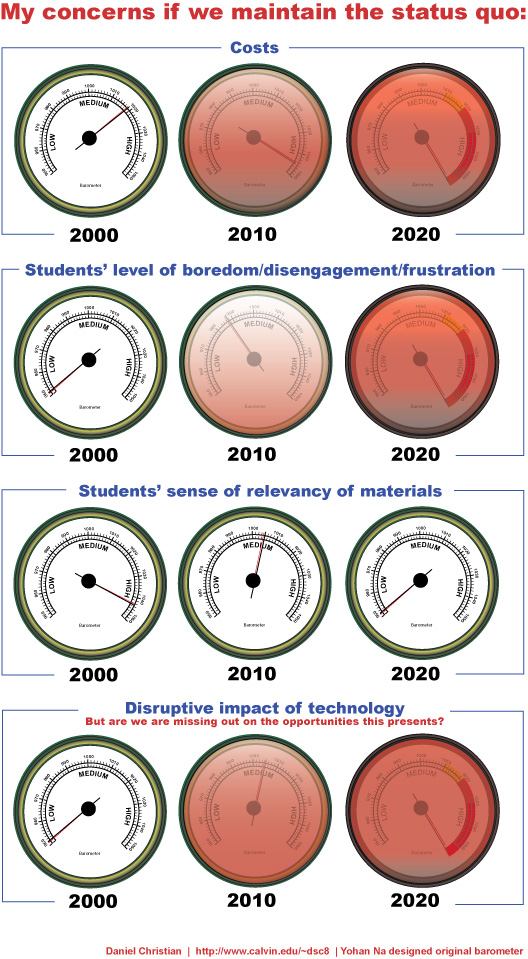
All three factors converging at the same time has opened up a new window of possibilities for achieving the promise of technology to transform education. Evidence of this shift in perspective and vision by educators is noted in some comparative Speak Up findings over the past few years.
…
This report is the second in a two-part series to document the key national findings from Speak Up 2010.
…
In this companion report, “The New 3E’s of Education: Enabled, Engaged, Empowered – How Today’s Educators are Advancing a New Vision for Teaching and Learning,” we explore how teachers, principals, district administrators, librarians and technology coordinators are addressing the student vision for learning around three key trends. These trends have generated significant interest in the past year at conferences, in policy discussions and within our schools and districts: mobile learning, online and blended learning and digital content.
While each of these trends includes the essential components of the student vision of socially-based, un-tethered and digitally-rich learning, they also provide a unique backdrop for investigating the role of educators to engage, enable and empower students through the use of these emerging technologies.
• Role of Librarians and Technology Coordinators: To enable student use of the emerging technologies through their planning, support and recommendation responsibilities.
• Role of Classroom Teachers: To engage students in rich, compelling learning experiences through the effective use of these technologies in the classroom.
• Role of School and District Administrators: To empower both teachers and students to creatively envision the future of digital learning, and to provide opportunities for exploring the elements of a new shared vision for learning.