From DSC: First, some articles that caused these reflections
Discounting heads — from insidehighered.com by Kevin Kiley
Excerpt:
Despite spending nearly 43 percent of their gross tuition revenue from first-time, full-time freshmen on institutional aid for those students, many private colleges and universities had a harder time enrolling students last year, with almost half seeing no growth or a decline in enrollment for 2011, according to survey results released today by the National Association of College and University Business Officers.
From DSC:
It seems to me that it’s highly-possible that the higher ed bubble has started to pop — at least at private colleges and universities. So why doesn’t change occur? See the next article for several reasons.
Failure to change — from insidehighered.com by Robert J. Sternberg
Excerpts:
Universities teach about the importance of societal and organizational change, but often have trouble changing themselves in any but the most superficial ways. As a psychology professor interested in both individual and organizational modifiability, I have studied organizations, including universities, and why it is so difficult for them to change. Meaningful organizational change requires five elements, and unless all five of them are present, the organization — whether a department, school, college, or university — remains static.
…
Change is not always for the better, of course. But a college or university that is static will inevitably fall behind more dynamic, positively changing institutions. And like any institution that fails to compete, it is on the path to stagnation or death. A dynamic institution will change and, if the change proves to be in the wrong direction, will redirect itself until it finds a sustainable path.
From DSC:
As a relevant aside, it’s not just the “younger folk” who are struggling with student loans either:
Student loans saddle both kinds of seniors: graduates and grandparents — from the Washington Post by Michelle Singletary
Excerpt:
Using data from Equifax credit reports, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York found that people 50 and older are carrying nearly $135 billion in student-loan debt. Those 60 or older have student-loan balances of more than $36 billion.
It’s these types of dynamics and trends that are catalysts for what I call:
“Learning from the Living Room”
Though 2-5 years away, signs point to it coming to fruition (my prediction is that this movement will really gain traction when Apple’s Connected/Smart TV hits the market and as more people get fed up with the current, unresponsive accredidation monopolies within higher ed). Some example/recent articles:
- The Evolution of the Digital Living Room — from digitalvideospace.blogspot.com by Chuck Parker
Excerpt:
Apple with its iPad, Apple TV and iCloud for movies and TV shows has delivered a seamless ecosystem to the consumer’s digital living room for owning and watching content from multiple devices in the home. The rest of the industry (SmartTVs, connected devices, Android tablets) struggles to create a similar experience when they are a single-brand ecosystem and fail miserably when there are devices from multiple manufacturers in the household.
.
- Google and Microsoft’s new battleground: Your living room — from ComputerWorld by Preston Gralla
The upshot will have surprising implications for IT
.
- Why the future of Shazam is TV, not music — from readwriteweb.com by Richard MacManus
Excerpt:
Shazam is in the midst of a major pivot. Currently it earns most of its revenue off advertising from the music app. But within two years, the company told ReadWriteWeb, TV will provide the majority of Shazam’s revenue. Just how big an opportunity is TV for Shazam? According to statistics from the company, it is already outpacing both Facebook and Twitter in second screen user engagement.
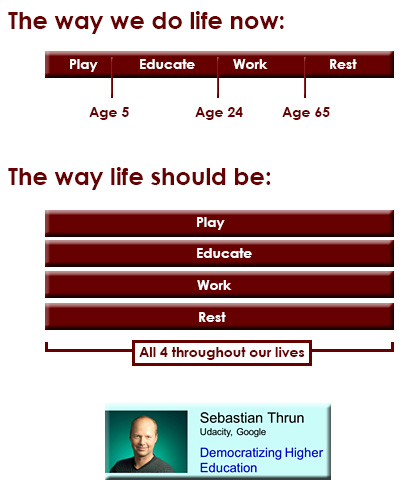
“The Forthcoming Walmart of Education” …which is already happening, but far more significant changes will come in the next 1-5 years as people look for more affordable alternatives. A graphic I created back in 2008 states what I see developing and will be a piece of the higher ed landscape in the future:
.

.
Besides the items mentioned above (i.e. changes in price and delivery mechanisms),
what might some of these innovations look like? Here are some ideas/articles/examples:
- Be more responsive to real-world/market needs
Example:
12 college majors we hope to see soon — from bestcollegesonline.com
While some college majors have been around for decades or even centuries, others are relatively new and some are still waiting on the horizon to be added to college programs around the world as new technologies and demands shape the needs of modern students. While a host of degree programs have been added over the past 10 or 20 years, many related to computers and other forms of technology, many more will be needed in the future to keep up with a world that is rapidly changing.
.
- Introduce more innovations and be willing to experiment with different models
Examples besides MITx, Udemy, U of People, iTunes U, YouTube Edu, etc.:
ANGELS, a new European research project, a gateway to the future.
ANGELS project (Augmented Reality Network Generating Learning on Safety), is the training system that will revolutionize education and learning on safety and health at work, particularly in the hospital facilities. This tool aims at innovating in terms of training on health and safety at work with the use of augmented reality (computer system that can superimpose 3D image on a real image to combine real and virtual). ANGELS introduces 4 key innovations: A practice adapted to an innovative new technology, a realistic assessment in tune with the XXIst century in the area of education and training, a large field of application in the health care facilities and the creation of a starter kit for public and private organizations, training centers and academic centers.
.
- …and bring the prices WAAAY down!!!