College crackup and the online future — from bloomberg.com by Mark C. Taylor
.

Illustration by Keith Shore
Excerpt:
In the coming decade, emerging technologies will thoroughly transform higher education. Although distance learning and computer-assisted education have been around since the 1960s, financial pressures are forcing institutions to develop aggressive online programs.
…
These practical considerations shouldn’t overshadow one of the most promising innovations that online education will bring: The very structure of knowledge will change.
…
As students mix and match courses online, pressure will increase for professors to develop classes that integrate different approaches and disciplines.
.
.
Also see:
- Business model innovation: A blueprint for higher education — from businessinnovationfactory.com by Christine Flanagan, BIF’s Student Experience Lab Director. This article is featured in the December 2012 issue of the EDUCAUSE Review.
- Designing colleges for more than just connectivity — from fastcoexist.com by Maddy Burke-Vigeland
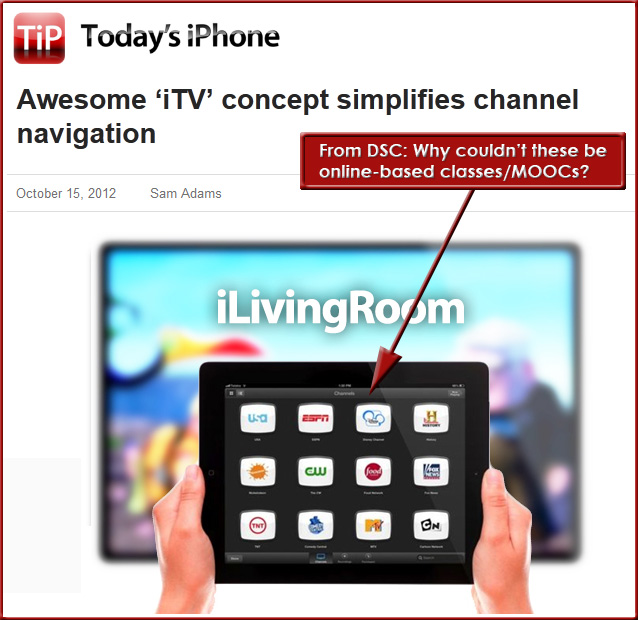
From DSC:
Creating “Innovation Labs” within each institution of higher education sounds like a good idea to me…we can experiment with things at smaller scales and see what works and what doesn’t.
Also see:
Take a lesson from Apple: A strategy to keep customers in your ecosystem — from forbes.com by Alonzo Canada
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
1. Set focused, strategic targets.
2. Create a portfolio of experiments. Like Apple or Mercedes Benz, once you have focused, strategic targets set, create a series of experiments. A general rule of thumb is the 7-2-1 rule: one experiment should be big and relatively safe. Two experiments should be slightly more risky and moderately sized. Then seven experiments should be highly risky and low cost. These experiments can be scaled accordingly across teams, business units, and the entire company. 3M is one of the first companies to mandate that its employees spend 20% of their time thinking up blue sky ideas beyond its current lines of business and this is how Post-It Notes were born. Art Fry, an engineer at 3M wanted to find a better way to manage notes in his hymnal on Sundays at church.
3. Leverage learnings to inform new experiments.















![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)