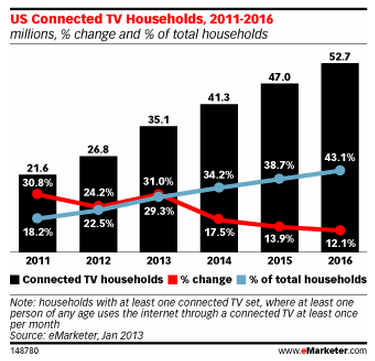
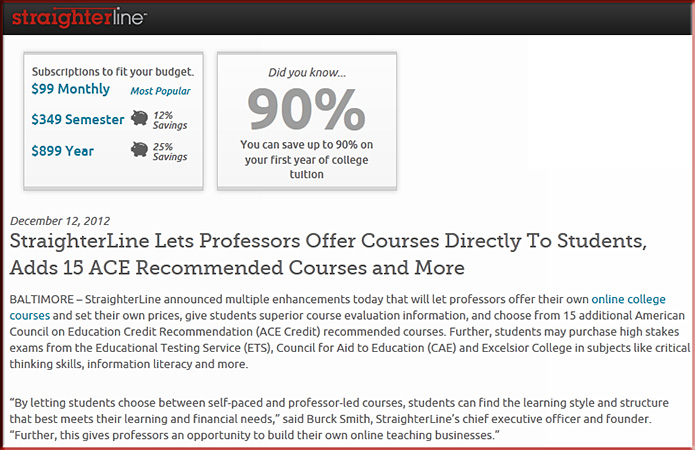
Curbing the cost of college: Coursera wins approval to offer online courses for credit for under $200 — from techcrunch.com by Rip Empson
Excerpt:
Up until now, the startup has not offered degrees or credits for its online classes, which has meant that Coursera classes have existed mostly as a way to pursue supplementary or continuing education — not as part of degree programs. But that changed today, as Coursera announced [last Thursday morning] that five of its courses have been approved for “credit equivalency” by the American Council on Education (ACE). This means that students who complete these five courses can receive college transfer credit at institutions that accept ACE recommendations.
So, importantly, Coursera’s new credit equivalency doesn’t automatically mean that every university it has partnered with automatically guarantees credit for the approved courses; instead, institutions have the option to accept or decline credit. In other words, it’s up to them.
Also see:
Creative learning on mass, or the MIT MOOC –– from daveswhiteboard.com by Dave Ferguson
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Just this morning, I came across MIT Media Lab’s announcement for its Learning Creative Learning online course. You can read about it or skim the outline to make your own judgment; I’m enjoying the laid-back description, which tracks with my previous massive open online course experience:
- “This is a big experiment. Things will break. We don’t have all the answer.”
- “We hope that participants will jump in as collaborators rather than passive recipients.”
- “Check out our shiny new platform. Actually, don’t, because we didn’t build a shiny new platform.”












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)