Some excerpts of this infographic:
From DSC:
For example, fast forward a few years from the technologies found in “The Video Call Center” and one could imagine some powerful means of collaborating from one’s living room:
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)
Also see:
Micro-credentials offer universities an opportunity to bridge skill gaps — from centerdigitaled.com by Tanya Roscorla
By working with employers, universities can help students of all ages learn skills that industry leaders need.
Excerpt:
Higher education leaders are pondering how to make bite-sized, low-cost learning opportunities available to students in different ways.
Working adults who change jobs and careers frequently often don’t need to go through an entire degree program to learn different skills. However, they do need a flexible way to earn credentials that are recognized by employers and that demonstrate their ability to apply the skills they learn, said David Schejbal, dean of continuing education, outreach and e-learning at University of Wisconsin-Extension. University micro-credentials can help fill that role.
Six universities have been working with employers to find out what skills they need their employees to have, including the Georgia Institute of Technology, University of California Davis Extension, University of California Irvine Extension, University of Wisconsin-Extension, University of Washington and University of California, Los Angeles.
As a result of collaborating with industry, these universities created short courses and certification programs for the University Learning Store that launched last week. These courses fall into three categories: power skills, technical skills and career advancement skills. Power skills used to be called “soft skills” and include communication, collaboration and critical thinking.
Here’s how Maine students will have access to courses at 500 colleges — from bangordailynews.com by Christopher Cousins
Excerpt:
AUGUSTA, Maine — Maine college students will soon have seamless access to hundreds of higher education courses in 35 states thanks to a new program to which the state has just been accepted.
The New England Board of Higher Education announced Monday that Maine has been accepted to the New England State Authorization Reciprocity Agreement (N-SARA). Here are the details:
What is SARA?
SARA is a 36-state coalition through which colleges and universities, as well as individual students, can access courses at institutions in other participating states. Reciprocally, Maine institutions also will be allowed to share their online offerings in other states in the coalition. Maine passed a law earlier this year to allow the state’s application to the coalition.
There are about 500 higher education institutions participating in the program nationally.
Also see:
General Information
Higher Education needs a new way for states to oversee the delivery of postsecondary distance education.
The current process is too varied among the states to assure consistent consumer protection, too cumbersome and expensive for institutions that seek to provide education across state borders, and too fragmented to support our country’s architecture for quality assurance in higher education — the quality assurance “triad” of accrediting agencies, the federal government, and the states.
A new, voluntary process of state oversight of distance education has been created to redress these problems. The State Authorization Reciprocity Agreement is a voluntary agreement among its member states and U.S. territories that establishes comparable national standards for interstate offering of postsecondary distance-education courses and programs. It is intended to make it easier for students to take online courses offered by postsecondary institutions based in another state.
…
The State Authorization Reciprocity Agreement (SARA) establishes a state-level reciprocity process that will support the nation in its efforts to increase the educational attainment of its people by making state authorization:
Florida Universities take system approach in addressing growth of online — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
Excerpt:
The Board of Governors for the State University System of Florida is putting final touches on a strategic plan for online education. The idea is to create a framework around which all 10 institutions in the system with online programs can pool their “collective talents and resources toward a common purpose” — helping Florida citizens earn credentials that will “improve their lives, lead to new discoveries and advanced Florida’s economy.” The plan was first begun a year ago when the board created a task force to examine how the state could better meet workforce needs through online education and increase effectiveness while reducing costs.
The goal of the “2025 Strategic Plan for Online Education” is intended to guide development and implementation of system policies and legislative budget requests related to online education with a focus on three primary elements: quality, access and affordability.
Also see:
Embracing failure to spur success: A new collaborative innovation model — from educause.com by Kim Wilcox and Edward Ray
Excerpt:
The implied message is clear: We’d prefer not to talk about what isn’t working at the postsecondary level.
We’re in a competitive sector, and there is misplaced pressure on all higher education institutions to achieve top placement in U.S. News & World Report and other annual rankings, regardless of whether or not those rankings make any sense. We all feel significant pressure to make sure that our constituents—from board members to faculty to parents to legislators—are happy with the direction of the institution. And we also know that those constituents can be impatient in waiting for substantive change to produce positive results. Honest discourse on new initiatives that seem unproductive or in need of modification is likely to lead to unpleasant conversations that few of us would relish.
This is not the way to foster innovation and improvement in higher education. The best innovators in the world typically follow the mantra that failure is acceptable, helpful, and sometimes even necessary to ultimately achieving an objective. Many of the products we rely on today, from Post-it Notes to pacemakers, resulted from mistakes or failures in the search for other innovations. And just about any founder of a successful Silicon Valley start-up has a track record of ventures that failed.
Successful innovation requires experimentation and learning from failure.
…
At the University of California, Riverside, and Oregon State University, we are engaged in one effort to achieve these goals: the University Innovation Alliance. The UIA is a consortium of eleven major public research universities that are working together to identify new solutions to challenges found throughout the higher education community, and then to share information about failures and successful solutions among institutions.
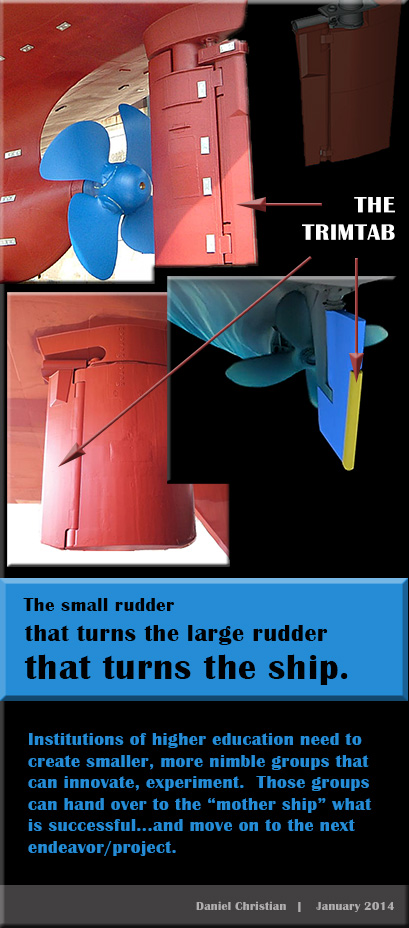
From DSC:
Some images that are along these lines:

Cross-college collaboration — from insidehighered.com by Megan Rogers
Excerpt:
Faced with increasingly tight budgets, liberal arts colleges are looking to share resources to reduce costs and expand programs. But when the end goal is collaboration and not a merger, how should administrators decide which services are appropriate to share?
St. Olaf and Carleton Colleges, both liberal arts colleges in Northfield, Minn., have received a $1.4 million grant from the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation to increase collaboration over the next four years, but are drawing the line at sharing career services departments. And it’s hard to imagine the colleges collaborating in areas where they are competitors, such as fund-raising or admissions, St. Olaf President David Anderson said.
From DSC:
In order to survive within higher ed — and if things migrate to more of a team-based approach to content creation and delivery — I’ve often wondered if the following will occur:
Microsoft joins Degreed’s crusade to ‘jailbreak the degree’ – from gigaom.com by Ki Mae Heussner
Excerpt:
Degreed, a San Francisco startup taking on traditional degrees and diplomas with a digital credential that reflects lifelong learning, has recruited its first corporate partner to its corner.
This week the startup said it will launch a partnership with Microsoft Virtual Academy, the tech giant’s online IT training site, which will give students who complete the program’s classes a way to display their achievements on Degreed.
From DSC:
AT&T and Georgia Tech.
Google and edX.
Microsoft and Degreed.
IBM sending Watson to school and partnering with 1000+ universities (see here and here).
JP Morgan and University of Delaware (see this addendum from 10/7/13)
Is there a new trend forming here?
MOOC-Skeptical Provosts — from insidehighered.com by Ry Rivard
Excerpt:
The provosts of Big 10 universities and the University of Chicago are in high-level talks to create an online education network across their campuses, which collectively enroll more than 500,000 students a year.
And these provosts from some of America’s top research universities have concluded that they – not corporate entrepreneurs and investors — must drive online education efforts.
…
But the provosts are now questioning universities’ need to partner with external providers in the first place.
…
“The main thing for us is… how can the CIC schools be proactive in terms of innovation and learning?” he said. “How can we be of more benefit to students jointly?”
…
Right now, the high-level talks among administrators has yet to trickle down to faculty. Provost Adesida said the Illinois faculty will play a big role in deciding whatever comes next. “We don’t move without consulting with faculty,” Adesida said.
.
From DSC:
Don’t get me wrong, I don’t think MOOCs are done baking yet…but…
I wonder how much more innovation we might actually see from insider higher education if a big player does purchase Coursera…?
Addendums: