From DSC:
As Brian Crosby points out in the title of his blog — “Learning is Messy.”
There is no silver bullet in the world of education that can be used to effectively teach everyone. In fact, if you were to get 100 instructional designers/teachers/professors/instructors/trainers in the same room, you will not be able to find anything close to a strong agreement on what constitutes the best and most effective learning theory as well as the practical implementations of applying that learning theory (even if we were to be talking about the same age range of students). In my Master’s work, I was looking for that silver bullet…but I never found one.
It is very difficult for a professor or a teacher to deliver truly personalized/customized learning to each student in their classroom:
- How can a teacher consistently know and remember what motivates each particular student?
- Because so much of learning depends upon prior learning, what “hooks” exist — per student — that he/she can use to hang new information on?
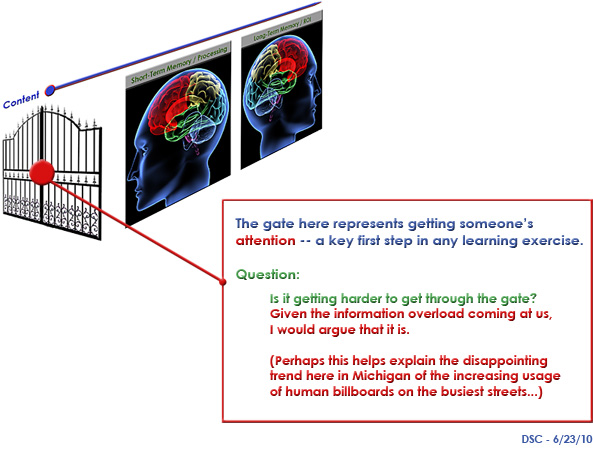
- Then, what’s the most effective method of delivering the content for each particular student that might shift the content from their working memories to their long-term memories? (And in the process, do so in a way that develops a love for learning that will serve the student well over his lifetime)
- What’s the best way to assess the learning for each student?
- Which students cognitive loads are being eaten up due to the nervousness around being assessed?
- What are the best methods of passing along those learnings onto the students’ future teachers’ for the students’ benefit?
In my estimation, the way we have things setup throughout most K-16 education, this is an impossible task. When there’s typically only 1-2 teachers trying to teach to 20-30 students at a time, how can this type of personalized instruction occur?
However, I believe digital learning and its surrounding tools/ecosystems hold enormous promise for delivering truly customized/personalized learning opportunities. Such technologies will be able to learn where a student is at, how to motivate them, how fast to push them, and how they best progress through a type of content. Such tools will provide real-time, learning-related, diagnostic dashboards for professors or teachers to leverage in order to guide and optimize a student’s education.
.

.
So I believe that the promise is there for delivering truly customized/personalized learning opportunities available 24x7x365 — even though we aren’t completely there yet. But think of the power a teacher would have if he or she had IBM’s Watson AI-based analysis on each student at their disposal! A “guide on the side” using such diagnostic tools could be a ***potent*** ally for a student.*
As such, I see innovative approaches continuing to come to fruition that will harness the power of serious games, analytics, web-based learner profiles, and multimedia-based/interactive learning content. Eventually, a piece of this type of personalized education will enter in via the Smart/Connected TVs of our living rooms…but that’s a post I’m building out for another day in the near future.
.
*Another hope I have here is that such technologies will
enable students to identify and pursue their passions.
Some items that reinforced this notion for me include:
The key link from Bloom (1913-1999) one e-learning paper you must read plus his taxonomy of learning — an excellent item from Donald Clark Plan B (also see Donald’s archives for postings re: 50 top learning theorists)
The 2 Sigma Problem: The Search for Methods of Group Instruction as Effective as One-to-One Tutoring
Benjamin Bloom
University of Chicago | Northwestern University
Excerpt:
Most striking were the differences in final achievement measures under the three conditions. Using the standard deviation (sigma) or the control (conventional) class, it was typically found that the average student under tutoring was about two standard deviations above the average of the control class (the average tutored student was above 98% of the students in the control class). The average student under mastery learning was about one standard deviation above the average of the control class(the average mastery learning student was above 84% of the students in the control class).
Two key items from EdNet Insight’s Anne Wujcik:
Mapping a Personalized Learning Journey – K-12 Students and Parents Connect the Dots with Digital Learning — from Project Tomorrow
Personalizing Learning in 2012 — The Student & Parent Point of View [infographic] — from Project Tomorrow
Excerpt from Anne’s posting:
This first report focuses on how today’s students are personalizing their own learning, and how their parents are supporting this effort. That personalization centers around three student desires: including how students seek out resources that are digitally-rich, untethered and socially-based. The report share the unfiltered views of K-12 students and parents on these key trends and documents their aspirations for fully leveraging the technologies supporting these trends to transform their learning lives.