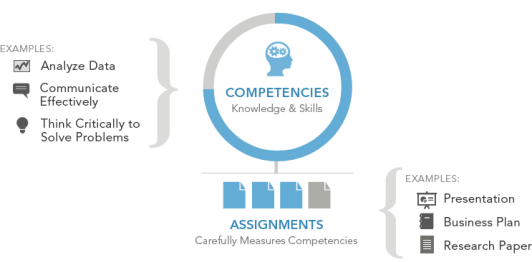
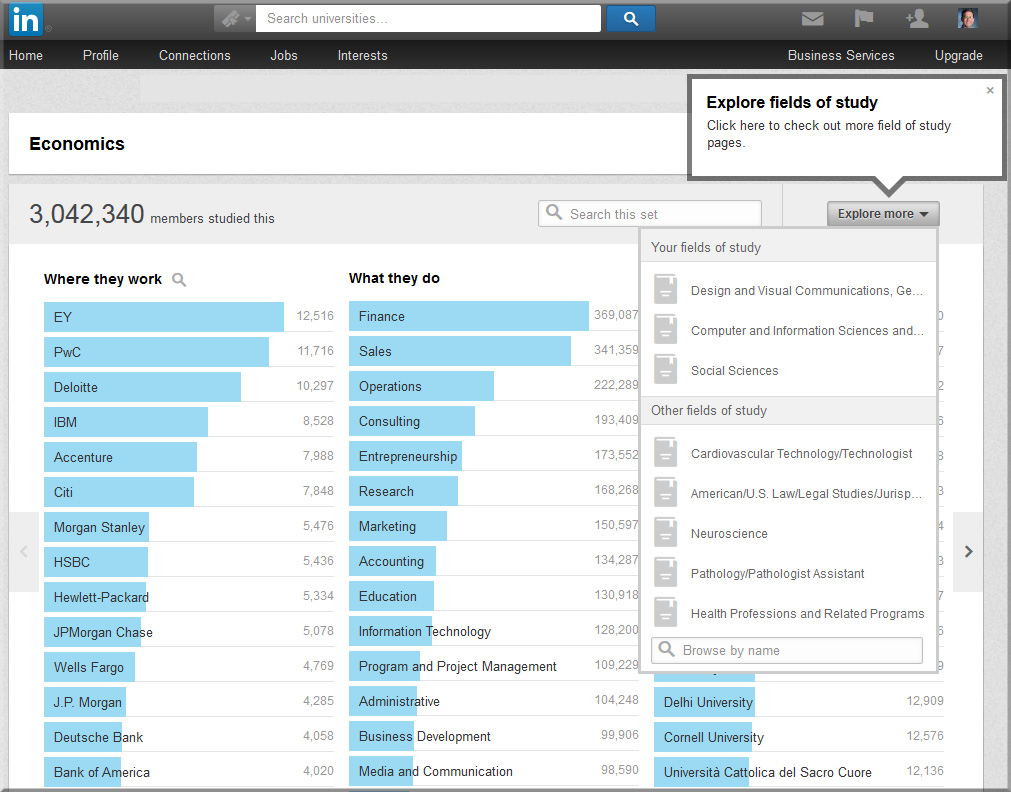
From DSC:
First of all, let me say that I’m a big fan and supporter of a liberal arts education — my degree was in economics (from Northwestern University’s College of Arts & Sciences, as the school was called at the time) and I currently work at a Christian liberal arts college.
That said, within the current higher education landscape, we’re already seeing and hearing more and more about competency-based education, credits for prior learning, and other forms of obtaining a credential in less time. I don’t have data on this, but my mental picture of these things is that such initiatives have had a limited impact, at least so far.
However, as the pace of change has increased, I wonder…what if hiring decisions move significantly more towards “Show me what you can DO…? That’s already taking place to a significant degree in many hiring situations, but my reflection revolves around questions such as:
- What if it takes too long to wait for someone to get a 2 or 4-year degree? Will employers start looking more towards what competencies someone has today or can acquire much more quickly?
- Will people look outside of traditional higher education to get those skills?
Again, these reflections involve the increasing pace of change.

Anyway, such a shift could open doors for new “providers” such as:
Then, consider some quotes from the following article, Tottering Ivory Towers:
Excerpts:
…there is growing interest in new ways of measuring the quality of a degree. The variety of scorecards now available, for instance, means students and their parents have much better and more granular measures of quality than accreditation provides. For another, employers are gradually making greater use of independent, competency-based measures and credentialed courses rather than relying on accredited degrees and credit hours (derided as “seat time” by its critics). Try getting a job in computer network management if you can’t show which Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer courses you have passed. Meanwhile, Udacity is partnering with Google, AT&T, and other technology firms in an “Open Education Alliance” to provide top-level technical skills. Nevertheless, when it comes to alternatives to accreditation, the United States is generally playing catch-up with some other countries. In Britain, for instance, students can earn employer-union certified City & Guilds qualifications while studying at almost any institution, and there are standard competency measures in a variety of professional fields.
…
In a New York Times interview, Google’s senior vice president for people operations, Laszlo Bock, admitted that transcripts, test scores, and even degrees are less useful than other data as predictors of employee success.3 In this environment, an industry-led move to create a more dependable measure of knowledge and ability than a transcript will become increasingly attractive.
…
The critical lesson from the transformation of other industries is that it is likely to be a disastrous mistake to assume you can just tweak an existing business model and be all right. That can work only for a while.
Dmitry Sheynin writes in his article, Is innovation outpacing education? “With the ever-increasing pace of innovation, traditional colleges and universities are failing to train and retrain workers quickly enough. The model of two and four-year degrees, [futurist Thomas Frey] says, is largely incompatible with an industry that gets flipped on its head every couple of quarters.” Again, according to Frey, “The main factor driving change in the labor force is new innovations rendering old jobs obsolete, but no mechanism is in place yet to help workers grow at the pace of evolving technology.”
Self-directed learning, or heutagogy, is key in this fast-paced environment. We all need to be constantly learning, growing, and reinventing ourselves. However, not everyone is comfortable with such an approach. So there are some gaps/opportunities opening up for those organizations who are innovative enough to experiment and to change.
Also see:
-
It’s time to ditch the ‘old academic identity’ to survive funding cuts — from theconversation.com by Fry and Schutt
Excerpt:
In short, what you do with what you create. Increasingly, the sector is being called to account on this as the world changes around us.
-
This article re: Southern New Hampshire’s self-paced $10,000 competency-based degree program
- Udacity & the Future of Nanodegrees — from etale.org by Bernard Bull
.
- A $10,560 bachelor’s degree? — from marketplace.org
Excerpt:
“We’re not going to see bachelor’s programs in English, math, history, sociology, chemistry and all of those fields that are traditional liberal arts fields,” said Constance Carroll, Chancellor of the San Diego Community College District, and a member of the California Community College Baccalaureate Degree Study Group. “What we will see are baccalaureate programs in workforce fields where there is high demand.” Fields like dental hygiene, information technology, and automotive-technology management.
Addendum on 9/17/14:
Excerpt:
Argosy University System is among the first institutions in a movement toward competency-based education, creating new models of direct assessment that promise to reduce time-to-degree and offer greater relevance for graduates in the job market. CT talked with Argosy University System’s vice chancellor for academic affairs to learn how that institution tackled competency-based education — creating the first WASC-accredited MBA in its region based on a direct assessment, competency model. Now, Argosy is developing hybrid approaches that combine direct assessment with traditional seat time-based courses.
Addendum on 10/2/14:
Addendum on 10/8/14:
Addendum on 10/13/14:
.