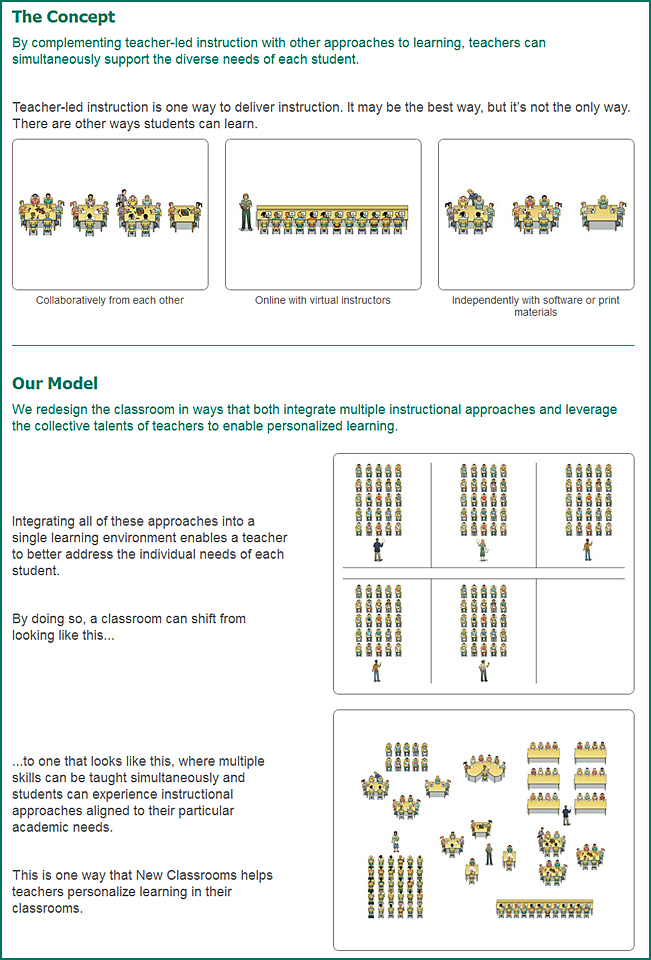
Harvard, MIT to partner in $60 million initiative to offer free online classes to all — from Boston.com by Mary Carmichael and Johanna Kaiser, Globe Staff and Globe Correspondent
Excerpt:
CAMBRIDGE — Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology said today they will team up to launch a $60 million initiative to offer free, online, college-level courses under a joint superbrand known as edX.
The announcement instantly makes the entity a preeminent player in the burgeoning worldwide online education sector, which has seen several major start-ups — including some affiliated with top-tier universities — in recent months.
Also see:
- MIT and Harvard announce edX — from mit.edu
Joint partnership builds on MITx and Harvard distance learning; aims to benefit campus-based education and beyond. - EdX: A platform for more MOOCs and an opportunity for more research about teaching and learning online — from InsideHigherEd.com by Audrey Watters
Excerpt:
At a joint press conference today, Harvard University President Drew Faust and MIT President Susan Hockfield announced a new nonprofit partnership, edX, that would offer free open online courses. If the “X” sounds familiar when paired with MIT, it’s because the Massachusetts Institute of Technology unveiled its plans for MITx late last year, its online learning initiative that would allow anyone with an Internet connection to take an online class from the university and receive a certificate upon successful completion. The first class, 6.002x Circuits and Electronics, is currently underway. - EdX: The Future of Online Education is Now
- Harvard and MIT launch edX to offer free online classes — from CNN.com by James O’Toole
NEW YORK (CNNMoney) — Always wanted to take a Harvard class? Soon you’ll be able to do so from the comfort of your own home. -
Massive Courses, Massive Data — from InsideHigherEd.com by Steve Kolowich
Harvard joins MT in platform to offer massive online courses