Does the U.S. accreditation system discriminate against online learning? — from Tony Bates
Excerpt:
Furthermore, problems remain in both Canada and the USA if students want to start taking online courses from an institution out of state or province then use that for advancement by transferring to a local university. The answer of course is more flexible credit transfer arrangements, more flexible prior learning assessment, and challenge exams, where students can demonstrate their learning without having to work through courses they have already taken elsewhere. Even some of the more prestigious research universities in Canada are realising that they need to be more flexible if they are to attract lifelong learners, for instance. Thus it’s as much up to the institutions as the regulators to ensure there is some flexibility in the system for students taking out of state or out of province online courses.
Yes, there needs to be sensible protections against fraud and fly-by-night online operators, but too often the restrictions, regulations and barriers are steeped in practices that no longer apply in an open, knowledge-based society. Every institution should be examining the structure of its courses, its admission requirements, its arrangements for credit transfer and prior learning assessment, and its strategy for lifelong learning, if it is to be fit for purpose in the 21st century. It is not an issue just of online learning.
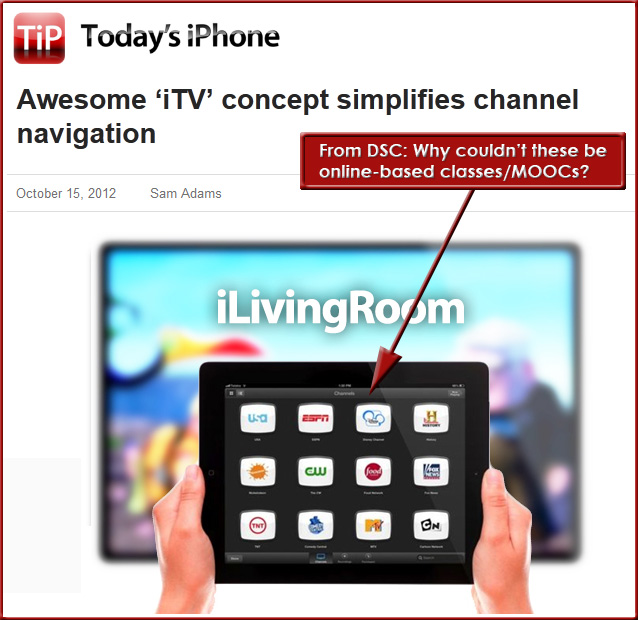
From DSC:
Questions I often ponder re: accreditation:
- Who sits on accrediting boards these days? Is it not people inside the current system?
- What responsibilities do accreditation bodies have on them to enable/support change (where appropriate)?
- Are such accreditation bodies feeling the pressure to help colleges and universities reinvent themselves in order to stay relevant? Or are they maintaining the status quo by all means possible?
- Whose interests are ultimately being served by the current methods of accreditation? (I hope it’s the students!)









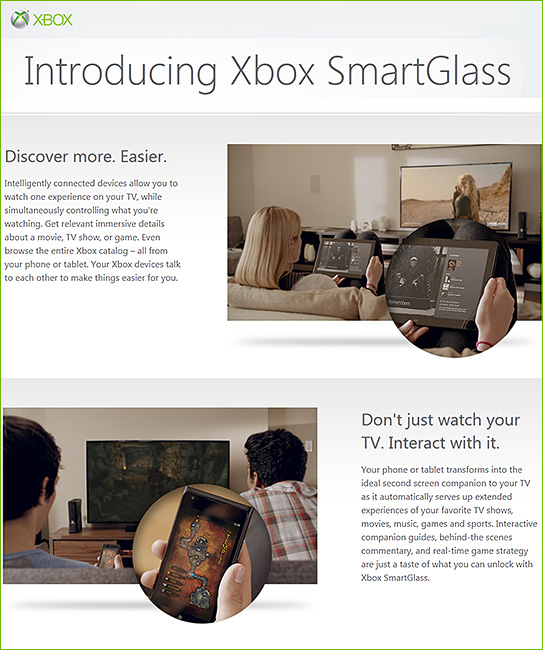


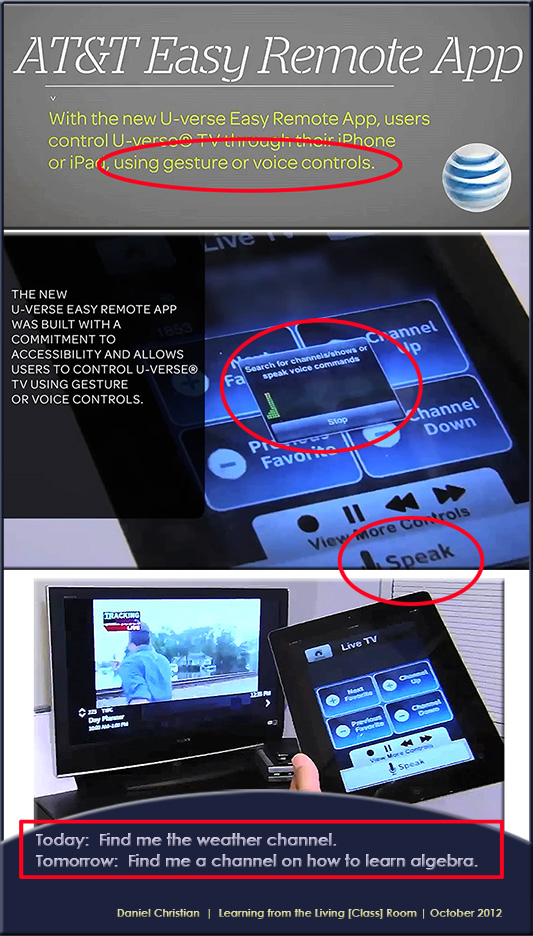

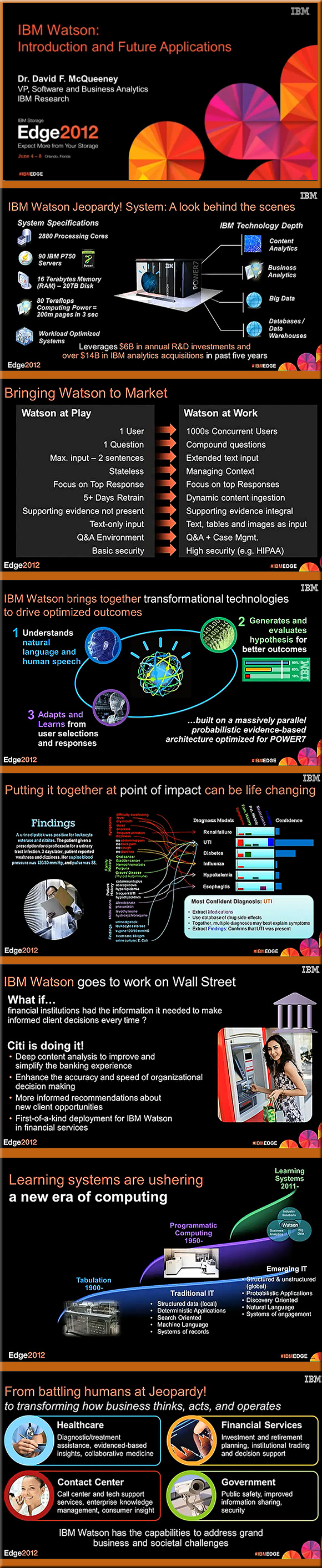
![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)