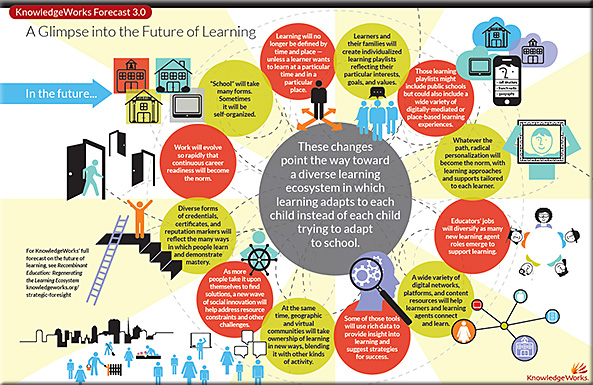
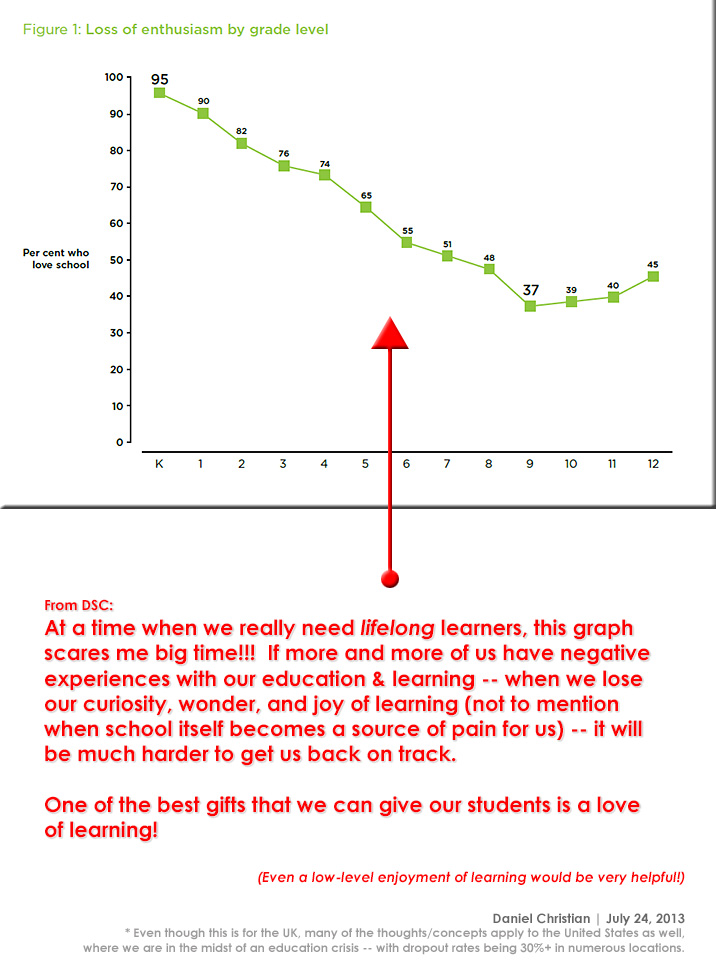
From DSC:
First, take a look at this interactive video from the Wall Street Journal:
.
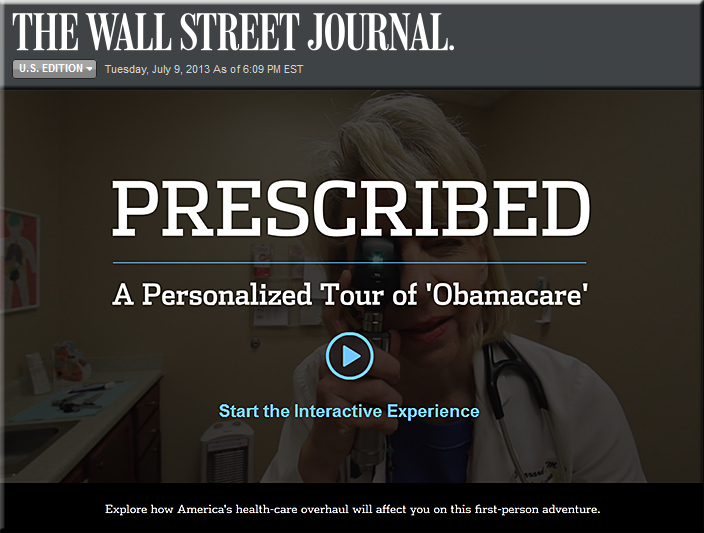
For further information on that video, you can also see:
- ‘Obamacare’ Made Easy to Understand — from /live.wsj.com
David Wessel discusses a new WSJ.com interactive video that helps viewers better understand the Affordable Health Care Act as well as its slate of rules and penalties.

.
From DSC:
Excellent, creative use of technology! Lifelong learners of the world, let me hear some noise! Your learning futures just got much more interesting, dynamic, and interactive!
You will be given more choice and more control than you’ve ever had before. You will be able to interact with digital videos, drill down, take some rights turns and come back again, and more.
For example, during the WSJ video, you can click on the radio within the digital video in order to “drill down” and listen to more about a certain topic — while the main presentation “holds on”…

…you can jump ahead to the next marker…pause…rewind…click to get some further text-based information/details on a topic of interest:

…and more. In other words, you have more choice, more control in your learning experience. This, at minimum, is a piece of online learning’s — and digital video’s — future.
But I hear you saying, so what? Flash has been doing this for a while now. And that, my friends, is the only downside I see in this implementation from the WSJ — it was done using Flash.
As Flash won’t fly on iOS-based devices, an HTML5-based solution needs to come into the picture…and this is where Touchcast shines!
.
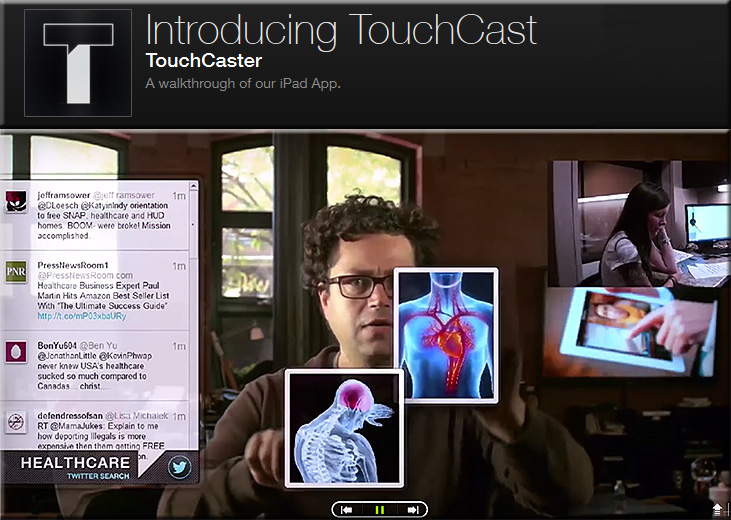
As Paul Sawers explains, you can add interactive, browsable layers onto your video and deliver it in an HTML5-based format.

.
An excerpt from Paul’s article:
Things start to get really interesting with video apps (vApps). TouchCast lets you create videos that are layered with live Web pages, video clips, maps, Twitter streams and other facets of the digital world. “We’re actually claiming that this is the future of the Web,” says Segal, TouchCasts’s CEO.
Indeed, TouchCast’s vApp library is ‘open’, so developers can create and customize their own vApps.
Bottom line:
“Digital textbooks” will never be the same again (not to mention learning modules, transmedia, ads, presentations, digital storytelling, and more)!
Also see:




















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)