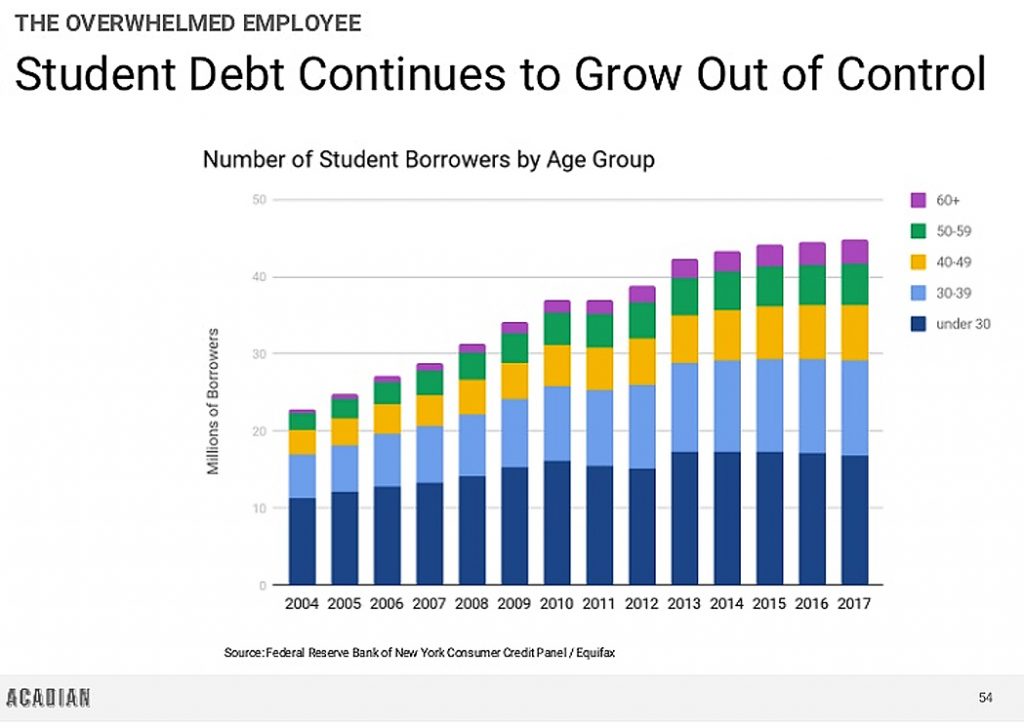
Facial recognition has to be regulated to protect the public, says AI report — from technologyreview.com by Will Knight
The research institute AI Now has identified facial recognition as a key challenge for society and policymakers—but is it too late?
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Artificial intelligence has made major strides in the past few years, but those rapid advances are now raising some big ethical conundrums.
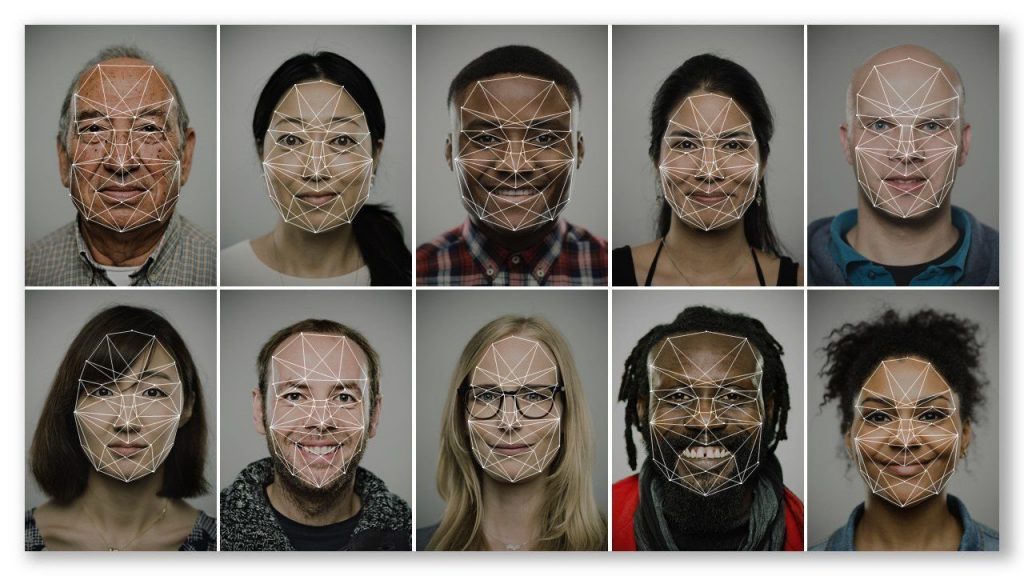
Chief among them is the way machine learning can identify people’s faces in photos and video footage with great accuracy. This might let you unlock your phone with a smile, but it also means that governments and big corporations have been given a powerful new surveillance tool.
A new report from the AI Now Institute (large PDF), an influential research institute based in New York, has just identified facial recognition as a key challenge for society and policymakers.
Also see:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
At the core of the cascading scandals around AI in 2018 are questions of accountability: who is responsible when AI systems harm us? How do we understand these harms, and how do we remedy them? Where are the points of intervention, and what additional research and regulation is needed to ensure those interventions are effective? Currently there are few answers to these questions, and the frameworks presently governing AI are not capable of ensuring accountability. As the pervasiveness, complexity, and scale of these systems grow, the lack of meaningful accountability and oversight – including basic safeguards of responsibility, liability, and due process – is an increasingly urgent concern.
Building on our 2016 and 2017 reports, the AI Now 2018 Report contends with this central
problem and addresses the following key issues:
- The growing accountability gap in AI, which favors those who create and deploy these
technologies at the expense of those most affected
- The use of AI to maximize and amplify surveillance, especially in conjunction with facial
and affect recognition, increasing the potential for centralized control and oppression
- Increasing government use of automated decision systems that directly impact individuals and communities without established accountability structures
- Unregulated and unmonitored forms of AI experimentation on human populations
- The limits of technological solutions to problems of fairness, bias, and discrimination
Within each topic, we identify emerging challenges and new research, and provide recommendations regarding AI development, deployment, and regulation. We offer practical pathways informed by research so that policymakers, the public, and technologists can better understand and mitigate risks. Given that the AI Now Institute’s location and regional expertise is concentrated in the U.S., this report will focus primarily on the U.S. context, which is also where several of the world’s largest AI companies are based.
From DSC:
As I said in this posting, we need to be aware of the emerging technologies around us. Just because we can, doesn’t mean we should. People need to be aware of — and involved with — which emerging technologies get rolled out (or not) and/or which features are beneficial to roll out (or not).
One of the things that’s beginning to alarm me these days is how the United States has turned over the keys to the Maserati — i.e., think an expensive, powerful thing — to youth who lack the life experiences to know how to handle such power and, often, the proper respect for such power. Many of these youthful members of our society don’t own the responsibility for the positive and negative influences and impacts that such powerful technologies can have (and the more senior execs have not taken enough responsibility either)!
If you owned the car below, would you turn the keys of this ~$137,000+ car over to your 16-25 year old? Yet that’s what America has been doing for years. And, in some areas, we’re now paying the price.

The corporate world continues to discard the hard-earned experience that age brings…as they shove older people out of the workforce. (I hesitate to use the word wisdom…but in some cases, that’s also relevant/involved here.) Then we, as a society, sit back and wonder how did we get to this place?
Even technologists and programmers in their 20’s and 30’s are beginning to step back and ask…WHY did we develop this application or that feature? Was it — is it — good for society? Is it beneficial? Or should it be tabled or revised into something else?
Below is but one example — though I don’t mean to pick on Microsoft, as they likely have more older workers than the Facebooks, Googles, or Amazons of the world. I fully realize that all of these companies have some older employees. But the youth-oriented culture in American today has almost become an obsession — and not just in the tech world. Turn on the TV, check out the new releases on Netflix, go see a movie in a theater, listen to the radio, cast but a glance at the magazines in the check out lines, etc. and you’ll instantly know
what I mean.
In the workplace, there appears to be a bias against older employees as being less innovative or tech-savvy — such a perspective is often completely incorrect. Go check out LinkedIn for items re: age discrimination…it’s a very real thing. But many of us over the age of 30 know this to be true if we’ve lost a job in the last decade or two and have tried to get a job that involves technology.
Microsoft argues facial-recognition tech could violate your rights — from finance.yahoo.com by Rob Pegoraro
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
On Thursday, the American Civil Liberties Union provided a good reason for us to think carefully about the evolution of facial-recognition technology. In a study, the group used Amazon’s (AMZN) Rekognition service to compare portraits of members of Congress to 25,000 arrest mugshots. The result: 28 members were mistakenly matched with 28 suspects.
The ACLU isn’t the only group raising the alarm about the technology. Earlier this month, Microsoft (MSFT) president Brad Smith posted an unusual plea on the company’s blog asking that the development of facial-recognition systems not be left up to tech companies.
Saying that the tech “raises issues that go to the heart of fundamental human rights protections like privacy and freedom of expression,” Smith called for “a government initiative to regulate the proper use of facial recognition technology, informed first by a bipartisan and expert commission.”
But we may not get new laws anytime soon.

Just because we can…