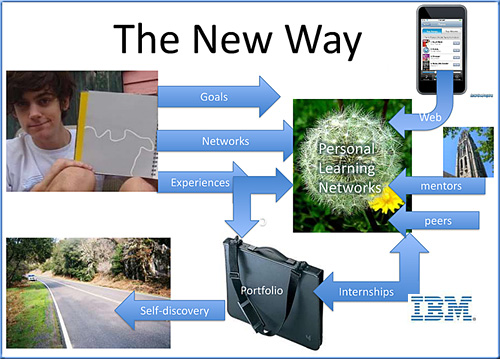
From DSC:
After looking at some items concerning Connectivism*, I’ve been reflecting upon the following questions:
- What’s the best way for us to dip our feet into the constantly moving streams of content?
(No matter the topic or discipline, the streams continue to flow.)
- What’s the optimal setup for K-12 based “courses”?
- What’s the optimal setup for “courses” within higher education?
- How should L&D departments deal with this phenomenon?
- How do publishers and textbook authors want to address this situation?
Thinking of Gonzalez (2004; as cited in Siemens (2005)) description of the challenges of rapidly diminishing knowledge life:
“One of the most persuasive factors is the shrinking half-life of knowledge. The “half-life of knowledge” is the time span from when knowledge is gained to when it becomes obsolete. Half of what is known today was not known 10 years ago. The amount of knowledge in the world has doubled in the past 10 years and is doubling every 18 months according to the American Society of Training and Documentation (ASTD). To combat the shrinking half-life of knowledge, organizations have been forced to develop new methods of deploying instruction.”
Stephen Downes addresses this and points to a possible solution to this phenomenon in his presentation from 3/15/11 entitled “Educational Projection: Supporting Distributed Learning Online.”
Excerpt/slides:


.
I need to put more thought into this, but wanted to throw this question out there…more later…
* From DSC: Some of the items I looked at regarding Connectivism — some directly related, others indirectly-related — were:
Siemens, G. (2005). Connectivism: A learning theory for the digital age. Retrieved from http://www.elearnspace.org/Articles/connectivism.htm.
Downes, S. (2005). An introduction to connective knowledge. Retrieved from http://www. downes. ca/post/33034. Downes noted that this was published in Hug, Theo (ed. ) (2007): Media, knowledge & education – exploring new spaces, relations and dynamics in digital media ecologies. Proceedings of the International Conference held on June 25-26, 2007. November 27, 2007.
Kop, R. & Hill, A. (2008). Connectivism: Learning theory of the future or vestige of the past? International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, v9 n3 p1-13 Oct 2008.
Tracey, R. (2009). Instructivism, constructivism or connectivism? Training & Development in Australia, December, 2009. p08-09, 2p. Retrieved from EBSCOhost. ISSN 0310-4664.
Kerr, B. (2007). A challenge to connectivism. Retrieved at http://learningevolves. wikispaces. com/kerr.
Sims, R. (2008). Rethinking (e)learning: A manifesto for connected generations. Distance Education Vol. 29, No. 2, August 2008, 153–164. ISSN 0158-7919 print/ISSN 1475-0198 online. DOI: 10. 1080/01587910802154954
Lisa Dawley. (2009). Social network knowledge construction: emerging virtual world pedagogy. On the Horizon, 17(2), 109-121. Retrieved from ProQuest Education Journals. (Document ID: 1880656431).
Hargadon, S. (2011). Ugh. Classic politics now extends to social networking in education. Retrieved from http://www. stevehargadon. com/2011/03/ugh-classic-politics-now-extends-to. html.
Cross, J. (2001). Crowd-inspired innovation. Retrieved from http://www.internettime.com/2011/03/crowd-inspired-innovation.
Rogers-Estable, M.. (2009). Web 2.0 and distance education: Tools and techniques. Distance Learning, 6(4), 55-60. Retrieved from ProQuest Education Journals. (Document ID: 2017059921).
Marrotte-Newman, S.. (2009). Why virtual schools exist and understanding their culture. Distance Learning, 6(4), 31-35. Retrieved from ProQuest Education Journals. (Document ID: 2017059881).
Hilton, J., Graham, C., Rich, P., & Wiley, D. (2010). Using online technologies to extend a classroom to learners at a distance. Distance Education, 31(1), 77-92. Retrieved from ProQuest Education Journals. (Document ID: 2074810921).
Attwell, G. (2010). Personal learning environments and Vygotsky. Retrieved from http://www.pontydysgu.org/2010/04/personal-learning-environments-and-vygotsky.