Why GCs Aren’t Buying What Legal Tech Is Selling and Why It Matters for Firms — from law.com by Zach Warren and Gina Passarella Cipriani
Legal technology companies have to get out of their own way in vying for law department adoption, and buyers need to know what they want.
Excerpt:
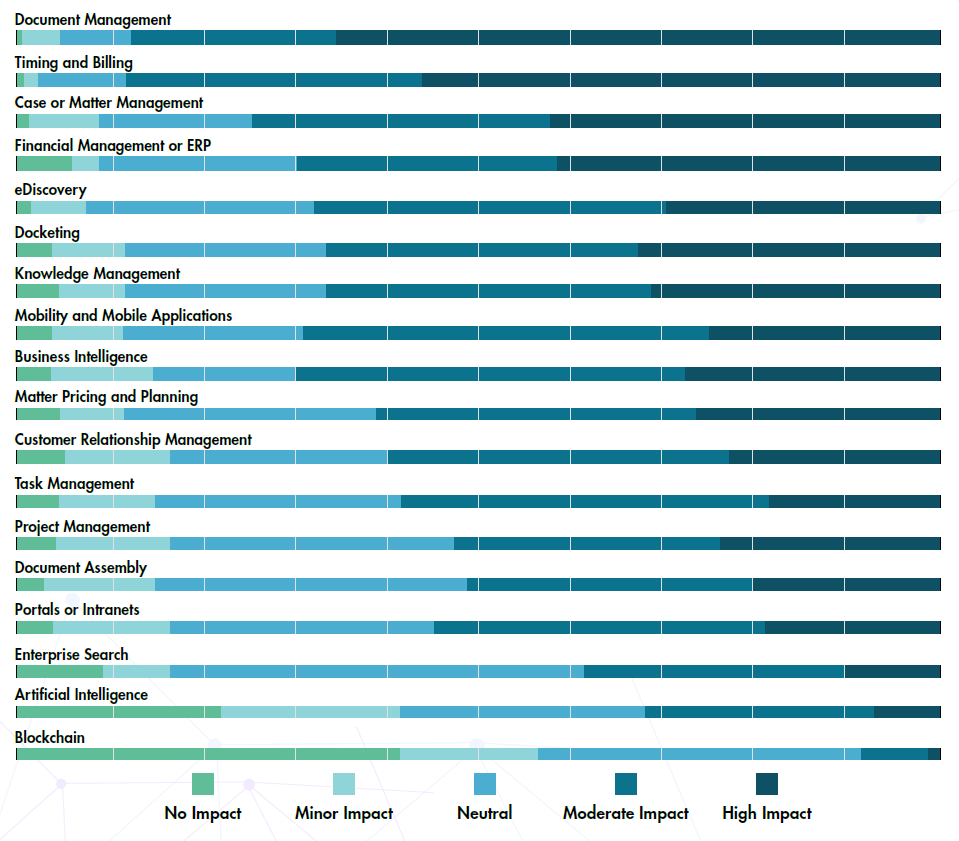
The legal technology industry has some significant hurdles to overcome in its increased push to sell into legal departments, general counsel say. And GCs admit that they are part of the problem.
On the one hand, technology companies aren’t doing themselves any favors by flooding the market with, at times, dozens of the same offerings, few of which solve specific problems the in-house community has, GCs say. But at the same time, general counsel admit to being distracted, budget-constrained and often unfamiliar with the capabilities of the products they are being pitched.
“It’s overwhelming,” says HUB International chief legal officer John Albright. “There are hundreds of these vendors, and most of them you’ve never heard of.”
As Albright sees it, the legal technology industry is “heavily fragmented,” with vendors selling solutions to a discrete issue that doesn’t necessarily solve the full problem he has or fit into the larger organization’s information systems.
Also see:
- Artificial Intelligence Further Exacerbates Inequality In Discrimination Lawsuits — from forbes.com by Patricia Barnes
Excerpt:
The legal system just keeps getting more and more unequal for American workers who are victims of employment discrimination, wage and hour theft, etc. The newest development is that America’s top employers and the law firms that represent them are using artificial intelligence (AI) tools to automate their responses to workers’ legal claims, thereby increasing efficiency while cutting costs.