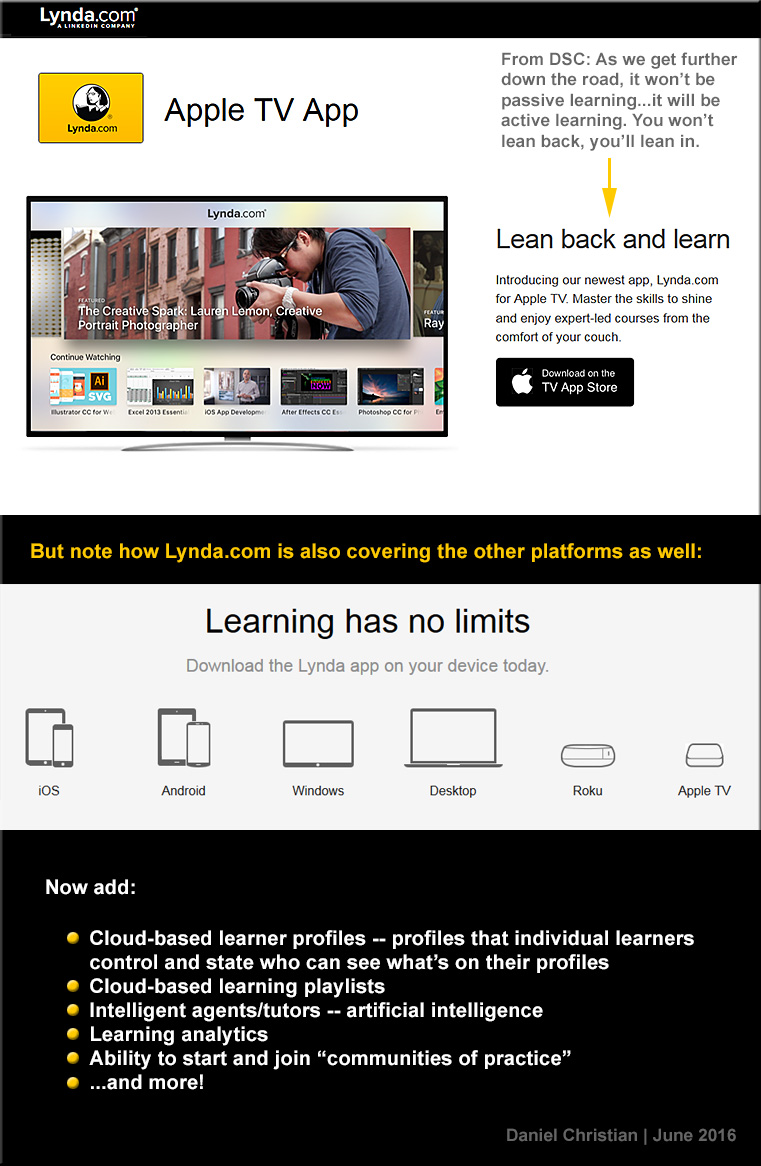
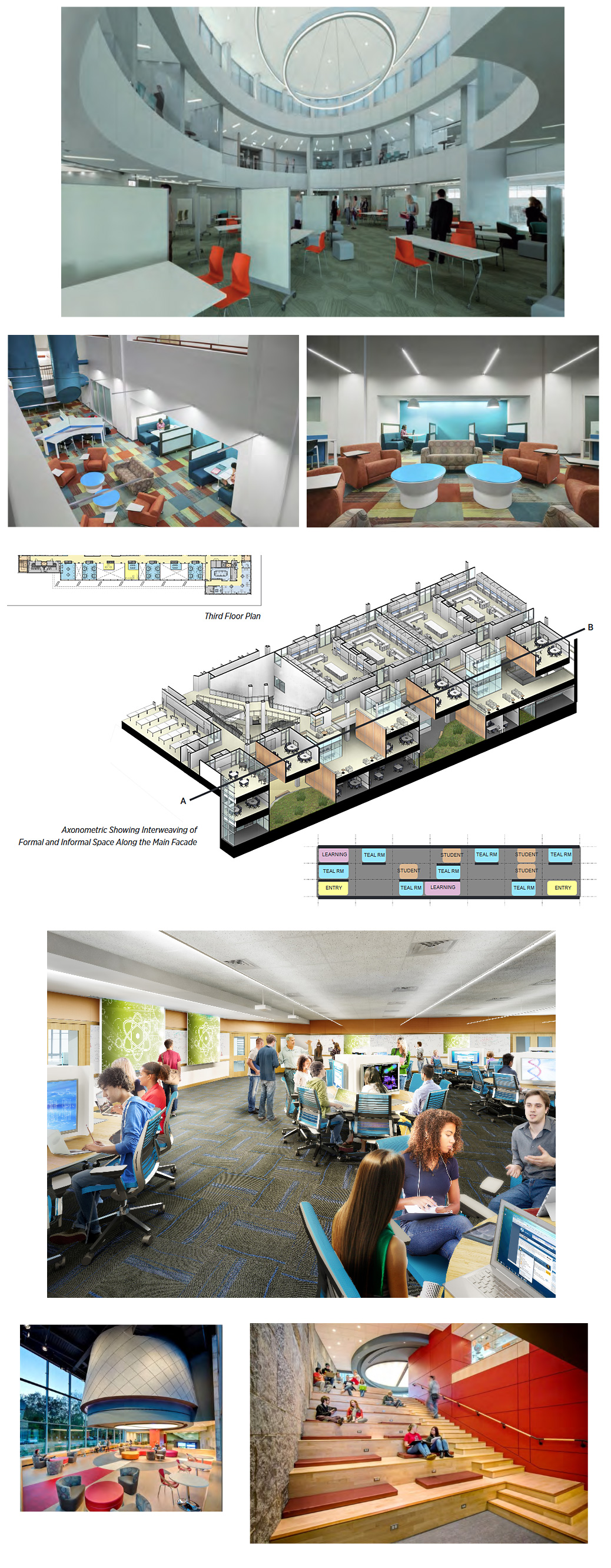
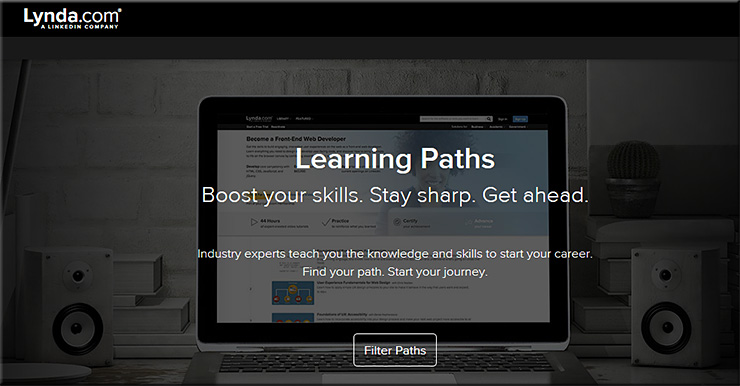
Some relatively recent additions to the education landscape include:

Also see:
Taking competency-based credentials seriously in the workforce — from campustechnology.com by John K. Waters
Companies like AT&T and Google are expanding their partnerships with online education providers, creating new educational pathways to real jobs.
Excerpt:
But in the Age of the Internet, for-profit online education providers such as Udacity and Coursera have tweaked that model by collaborating with companies to develop programs tailored to their specific needs.
…
Together the two companies created the Front-End Web Developer Nanodegree program, Udacity’s first branded microcredential. (“Nanodegree” is trademarked.)
“We worked with Udacity to develop curriculum based on tangible hiring and training needs,” said John Palmer, senior vice president and chief learning officer at AT&T, in an e-mail. “Our teams collaborated on determining what skills we needed now to address the needs of our business, but also what skills would be needed five to 10 years from now — not just at AT&T, but at other tech companies.”
uCertify
Also related:
- Students and higher ed leaders put their faith in online classes [#Infographic] — from edtechmagazine.com by Meg Conlan
As a growing number of students enroll in nontraditional college classes, the value of online education becomes more clear.
Excerpt:
As cost-effective alternatives to traditional college classes, online learning programs continue to gain steam in higher ed.
According to statistics gathered for an Online Learning Consortium infographic, 5.8 million students are now enrolled in online courses, and the majority put tremendous stock in the quality of their education: 90 percent of students say their online learning experiences are the same or better than in-classroom options.College and university leadership agrees: The infographic states that 71 percent of academic leaders say learning outcomes for online courses are the same or better than that of face-to-face classes.
Related postings:
Acquisitions, mergers and reinvention (not closures) will characterize higher ed’s future — from evolllution.com; an interview with Kenneth Hartman | Past President of Drexel University Online, Drexel University
Excerpts:
We’re going to see a lot of different alternative options popping up at alternative prices with alternative delivery mechanisms offering alternative credentials in the future. I don’t think a lot of institutions will be shutting down. There will be some that close, but it’s more likely that their assets will be acquired by other, stronger institutions.
…
These types of programs are popping up all over the country and I think the market forces tell a story. Colleges that are able to be adaptable and flexible will be the leaders in this new higher education marketplace. Adaptability, vision and flexibility are going to be critical for schools that are not heavily-endowed. If they do not have the will to do that then I think unfortunately Christensen’s prediction will probably come true. However, I’m optimistic that when the pain gets high enough, trustees of these institutions will demand that their senior leadership provide them with the way to prevent closure.
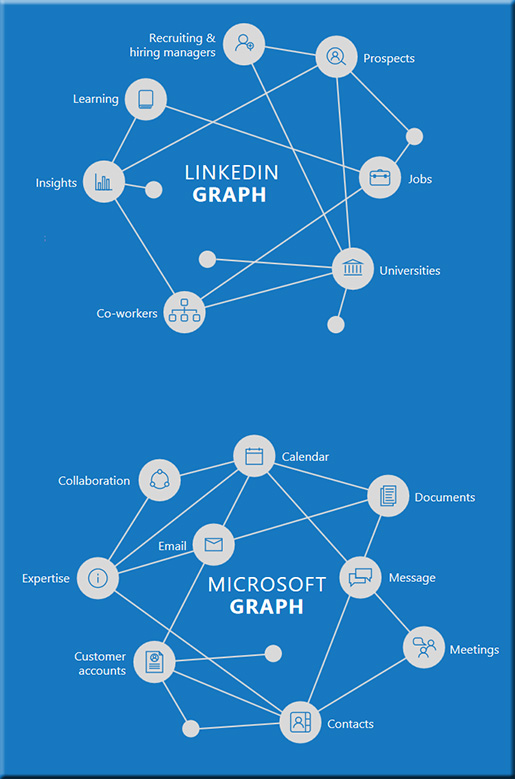
What a Microsoft-owned LinkedIn means for education — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
Excerpt:
Ironically, he suggested, higher ed is also the most vulnerable target of LinkedIn as it continues to work on development of a competency marketplace that could one day replace four-year degrees as the baseline requirement for employment.
The vision of this competency marketplace is that employers can identify candidates who are close matches for positions based on the competencies their jobs require. Likewise, job candidates can get information from LinkedIn about what competencies a given position requires and pursue that through some form of training, whether through a class at a local college, a bootcamp, online learning or some other form of instruction.
“The signal for universities that the world is about to change is when employers begin to drop degree requirements from job descriptions,” said Craig. And by the way, he added, that’s already happening at recognizable companies such as Google, Penguin Random House, EY and PwC, which have either eliminated that requirement from entry-level job descriptions or begun masking a candidate’s degree status from hiring managers because they “think the degrees are actually false or poor or misleading signals of ultimate job performance.”
Not only does LinkedIn have by far the largest collection of candidate profiles, but it has become the leading platform for distributing microcredentials, said Craig.
“You can identify education and training opportunities to remediate gaps between where you are and what the job description says you need to have to qualify. So all the pieces are there,” he said. “Currently, it’s still early, but you can see where this is going. We think that is the story of the next decade in higher education.”
12 promising non-traditional college pathways to attainment — from eddesignlab.org
Excerpt:
We hear a lot about reinventing college and how we might better design the journey from school to work. Some students want faster or more experiential pathways to prosperity, re-entry points after stop-outs or opportunities for lifelong learning. “Non-traditional pathways” is a phrase you’ll hear a lot if you hang around policy and design folks who are thinking about broadening “attainment of degrees” to include meaningful credentials that lead to career readiness. This broader college success definition is not a cop out—it’s a recognition that technology, access to micro-credentials, and access to modular learning generally are blurring the lines between vocational training, liberal arts exploration, and 21st century skill building because, increasingly, students are in a position to order all these off the menu.
Lumina Foundation strategists Holly Zanville and Amber Garrison Duncan are in the thick of these designs, and the Lab caught up with them recently to help us build a list of the most promising ways that institutions, students, and third parties are piecing together non-traditional paths to meaningful credentials. Here’s a take on our “Top 12,” but we welcome your tweaks, additions, and favorite examples.
Top-ranked coding bootcamp, Fullstack Academy, launches first alumni startup investment fund — from prnewswire.com
Will provide seed funding for its graduates to launch their own startups
Excerpt:
NEW YORK, June 15, 2016 /PRNewswire/ — Fullstack Academy, the Y Combinator-backed top coding bootcamp in the U.S., today announced Fullstack Fund, a new initiative to invest in promising startups created by its graduates. “Students who complete our software engineering program go on to work for great companies like Google and Amazon, but some have opted for the entrepreneurial startup environment,” said David Yang, CEO and co-founder of Fullstack Academy. “So we asked ourselves — how can we better support alumni with a strong entrepreneurial slant? The Fullstack Fund will empower some of the amazing teams and products that are coming out of our school.”
Addendum on 6/27/16:
Addendum on 6/30/16:


And a somewhat related posting:
More than 90% of institutions offer alternative credentials — from campustechnology.com by Sri Ravipati
The same study to report this statistic also found that millennial students prefer badging and certificates to traditional degrees.
Excerpt:
Millennial students seem to prefer badging and certificate programs to traditional bachelor’s degrees, according to a new study from University Professional and Continuing Education Association (UPCEA), Pennsylvania State University and Pearson that explored the role that alternative credentials play in higher education.
“Demographic Shifts in Educational Demand and the Rise of Alternative Credentials” includes responses from 190 institutions, including community colleges (11 percent), baccalaureate colleges (12 percent), master’s colleges or universities (27 percent) and doctorate-granting universities (50 percent). Of the 190 institutions surveyed, 61 percent were public entities. Across the board, research revealed that programs offering alternative credentialing have become widespread in higher education, with 94 percent of the institutions reporting they offer alternative credentials. Alternative credentials can take the form of digital badges, certificates and micro-credentials.
Addendum on 7/11/16:
A model for higher education where all learning counts — from marketplace.org by Amy Scott
Excerpt:
Imagine it’s 2026, and you’re one of a billion people using a new digital platform called the Ledger.
So begins a new video from the Institute for the Future and ACT Foundation, envisioning a future system that would reward any kind of learning – from taking a course, to reading a book, to completing a project at work.
“Your Ledger account tracks everything you’ve ever learned in units called Edublocks,” the video’s narrator explains. “Each Edublock represents one hour of learning in a particular subject. Anyone can grant Edublocks to anyone else.”
The Ledger would use the same technology that powers bitcoin, the virtual currency, to create a verifiable record of every learning transaction, said Jane McGonigal, director of game research and development at the Institute for the Future, a think tank in Palo Alto, California.













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)