The ‘soft skills’ employers are looking for — from blogs.wsj.com by Kate Davidson
Communication, teamwork, punctuality and critical thinking are in high demand, an analysis of 2.3 million LinkedIn profiles shows
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Want to craft a standout resume? Try adding skills like communication, organization and punctuality.
Nearly 58% of employees who touted stellar communication skills were hired over the course of a year, according to an analysis of 2.3 million LinkedIn profiles for The Wall Street Journal.
Employers are increasingly looking for workers with strong soft skills—those traits that don’t show up in a job posting but are essential for succeeding in the workplace, like working well with others and taking initiative. But many employers say it has gotten harder to find those applicants as the labor market tightens.
…
Communication, at the top of the list, was followed by organization, teamwork, punctuality, critical thinking, social skills, creativity, interpersonal communication, adaptability and having a friendly personality.
From DSC:
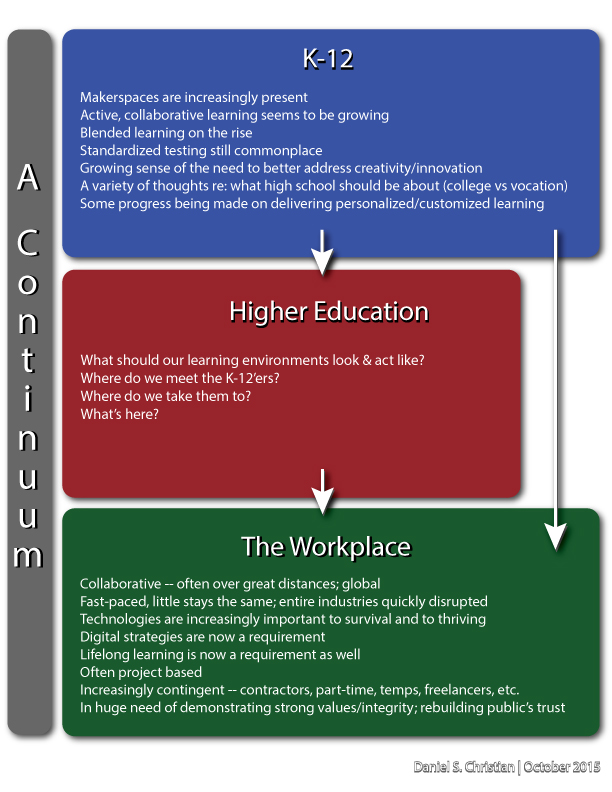
Looking at the list of top skills desired by employers, there seems to be a major breakdown in the entire spectrum/continuum.
Hmmm….standardized testing doesn’t really bring out the collaborative side of us, does it? In fact, you would likely get shown the door if you tried to collaborate (or show social skills) on a test, right? Teamwork. Hmmm….again, not on the exam. Punctuality? Nope…not that either. Organization…perhaps…maybe a little bit on the exam, but not much.
Which set of goals are we pursuing? Standardized testing and all of what that means…or are we trying to produce students who have the soft skills mentioned above and who can reinvent themselves over and over again (to which I’d add entrepreneurship/innovation/ability to freelance, the ability to look up and out into the future, and the ability to keep the relevant landscapes on their radars).
The answer seems to be that we’re trying to do both. That said, the corporate world seems to be saying that the standardized testing is winning out in this clash of goals.
This is why I try to pulse check the worlds of K-12, higher ed, and the corporate space all at the same time. We are not islands. What happens in earlier phases of people’s lives matters. What’s currently happening in the earlier portions of the continuum matters.
Addendum on 9/10/16:
The Unemployable Graduate Crisis and How We Can Fix It — from linkedin.com by Alistair Cox
Excerpt:
What is going wrong?
There remains a fundamental mismatch between market demand and supply of skills. The longstanding concerns around a drought of STEM and digital talent have been well publicised, but the issue extends beyond that. Students are graduating with degrees offering neither technical nor vocational knowledge, yet these are what employers are often looking for first.
Recent research in the US found that while 87% of recent graduates feel well prepared to hit the ground running in their new job, only half of hiring managers agreed. The shortfall across hard and soft skills is plain to see – one in four roles go unfilled due to the technical skills gap and hiring managers report worrying gaps in graduates’ critical thinking, communication and leadership skills. Around the world, many graduates simply aren’t employable in the roles being created today, yet will have spent at least 3 years racking up debt to study a course that will not help them find a relevant role.
If steps are not taken to address this, then I genuinely fear for our graduates, employers and the global economy. We are already seeing the skills gap widening into a skills chasm.




















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)