.
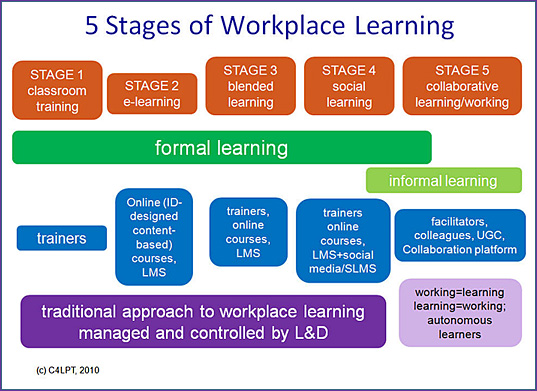
5 Stages of Workplace Learning — from Jane Hart
I interrupt my series of postings on Collaboration Platforms, to talk a little about the stages of Workplace Learnng
As I have read the comments on my recent postings as well as tweets and postings on other blogs, I’ve identified what I think are 5 main stages of workplace learning. I’ve tried to capture these, in a very rough and ready way, in the diagram below.
…
But some of the key mindset changes that will move organisations into Stage 5 are:
- recognising that working=learning; learning=working
- understanding that informal learning needs to be enabled, supported and encouraged – but not designed or managed
- “letting go”, so that there is a move from learner control to learner autonomy
- realising that autonomous, independent and inter-dependent, self-directed learners are essential in an agile organisation
Justin Bigart, Founder + President
Wisetail / The social side of e-learning
www.wisetail.com / www.learningecosystems.com
From DSC:
While listening to Justin, several things that he said jumped out at me:
- Learning is social
- Audience engagement is critical
- The definition of what is considered training content has to evolve and should be more conversational in nature; more of this material needs to be created by the people in your organization who are interacting with your clients
- Your audience is changing
Also:
- Use video-based content, built around storytelling
- Use people within your organization that are the best at that act or who model that behavior or who are the ambassadors of the concept that you are trying to relay/implement
- Make it raw, real, unscripted
- Use socially-aware technologies and layer that with advocacy-based / video-based training
Powering social learning: Bloomfire formalizes informal learning — from mlive.com by Olivia Pulsinelli, Business Review West Michigan
(Emphasis below by DSC)
According to its Web site, “Bloomfire is everything traditional learning is not.”
Bloomfire founder Josh Little compared his new company, a hub of online learning communities, to gardens. Companies or other groups can sign up for Bloomfire, a monthly service which officially launches March 15, and each group’s “garden” of informal, social-learning opportunities can be dedicated to anything from sales strategies to fishing.
“Whatever a group or whatever a community would like to teach each other, you could deploy a Bloomfire,” said Little, who is based in Kalamazoo.
From his work at Pfizer and Stryker — and most recently, from working with other corporations through his online training-course development company, Maestro eLearning — Little and his team came up with the idea to create a tool companies could use as a way for employees to quickly and easily share knowledge and help each other build on that knowledge.
Bloomfire focuses on informal learning, which Little said contributes to about 90 percent of the knowledge that most people need to do their jobs. Informal learning usually comes from conversations and on-the-job or trial-and-error experiences.
“Bloomfire is a way to take all that informal learning and formalize it — somehow capture and harness that,” Little said.
On Bloomfire, one can do three things — teach, learn and manage.
From DSC:
The following article got me to thinking of the future again…
Thousands to lose jobs as universities prepare to cope with cuts — from guardian.co.uk (original posting from Stephen Downes)
Post-graduates to replace professors | Staff poised to strike over proposals of cuts
I post this here because I believe that we are at the embryonic stages of some massive changes that will take place within the world of higher education. The timeframe for these changes, as always, is a bit uncertain. However, I would expect to see some of the following changes to occur (or continue to occur) yet this year:
- Cost cutting
- The cutting of programs
- Laying off of staff and faculty
- Not filling open positions
- More outsourcing
- The move towards using more cloud-based-computing models
- The movement of students to lower-cost alternatives
- Greater utilization of informal learning
- The rise of online-exchange oriented offerings (i.e. the matching up of those who teach a subject and those who want to learn that subject)
- The threat to traditional ways of doing things and to traditional organizations — including accreditation agencies — will cause people within those agencies to be open to thinking differently (though this one will take longer to materialize)
- The continued growth of online learning — albeit at a greatly-reduced price
- …and more.
This isn’t just about a recession. The Internet is changing the game on yet another industry — this time, it’s affecting those of us in the world of higher education. When the recession’s over, we won’t be going back to the way higher education was set up previous to the year 2010.
What did those us of in higher education learn from what happened to the music industry? What did we learn from what happened to the video distribution/entertainment business? To the journalism industry? To the brokerage business? To the travel and hospitality industries? To the bookstores of the world?
Along these lines…back at the end of 2008, I posted a vision entitled, The Forthcoming Walmart of Education. So, where are we on that vision? Well…so far we have:
- Straighterline.com
- A significant open courseware movement, including MIT Open Courseware, the Open Courseware Consortium, Connexions, Open Content Alliance, OpenLearn, Intute, Globe, Open Yale Courses, Open Education, The Internet Archive and many others
- University of the People
- YouTube.edu
- iTunes U
- Academic Earth
- and more…
I realize that several of these items were in place before or during 2008…however, at that time, there was no dominant, inexpensive alternative. And there still isn’t one that has jumped into the lead (the University of Phoenix with their 150,000+ students doesn’t qualify, as their pricing is not yet nearly aggressive enough as what I’m predicting will occur).
Though we aren’t there yet, there has been significant change that has already taken place. So…if I were an administrator right now, I’d be asking myself the following key questions:
- Can we reduce tuition and fees by at least 50%? If not, how can some of our offerings be delivered at half the price (or more)?
- How are we going to differentiate ourselves?
- How are we going to deliver value?
- How are we going to keep from becoming a commodity?
- Are we using teams to create and deliver our courses? If not, why not? What’s our plans for staying competitive if we don’t use teams?
Most likely, further massive changes are forthcoming. So fasten your seatbelts and try to stay marketable!
From DSC:
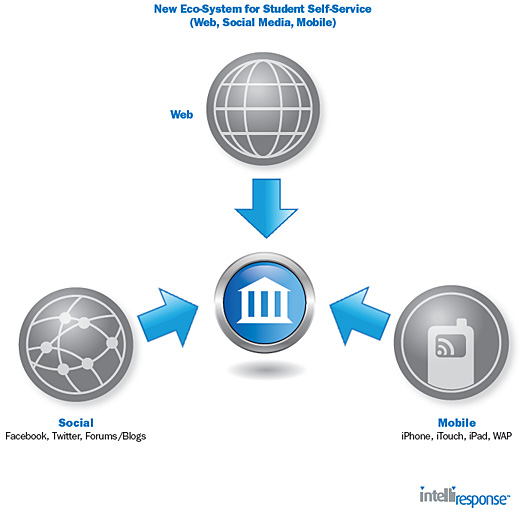
I signed up and downloaded a whitepaper from intelliresponse.com entitled, “Going Mobile: Web Self-Service for Students — Learn how higher education institutions can embrace the new multi-channel eco-system for student self-service (via Mobile, Social Media, Web)”.
I thought it was interesting how the term eco-system weaved its way through this company’s marketing literature. But it also relayed some more data on the increasing amount of mobile devices out there (now and expected in the near future). If we were to substitute the word “learning” in place of the words “self-service”, this topic becomes very relevant to this blog.
Here are a couple graphics from the paper:
From DSC:
Which question is dead? This one:
Where is the return on investment in all of this technology?
Through the last several decades, as we’ve invested in PCs, Macs, cabling/telecommunications infrastructure, wireless access points, LANs, servers, routers, etc…the question kept being asked, “Where’s the return on investment with all of this technology?”
To me, that question is being put to rest once and for all (at least in terms of those sets of technologies.) Why? Because that infrastructure is the foundation of an ever-growing, sprawling, network of connections that people are using more and more to communicate, socialize, learn, and grow. Sure, there are downsides to the Internet, but there are many upsides as well:
- You want a lesson plan? It’s out there.
- You want to hear a lecture on topic A, B, or C? It’s out there and able to start playing on your PC, Mac, iPhone, etc. in seconds
- You need to find directions to place XYZ? As you know, a huge timesaver can be found in services like Mapquest or with GPS-enabled services.
- You want to take a break and watch a show? It’s on your PC or Mac in a short period of time.
- You want to quickly orchestrate an event to catch up with a group of your friends? No problem.
- …
- …
I could go on and on, but you get my point: We are at the embryonic stages of an explosion in innovation that is now possible due to the Internet and the blazingly-fast exchanges of information. Surely, there has been an excellent ROI here!