9 Best Augmented Reality Smart Glasses 2016 — from appcessories.co.uk
Excerpt:
2016 has been promoted as the year of virtual reality. In the space of a few months, we have seen brands like Facebook, Samsung and Sony have all come out with VR products of their own. But another closely related industry has been making a growing presence in the tech industry. Augmented reality, or simply AR, is gaining ground among tech companies and even consumers. Google was the first contender for coolest AR product with its Google Glass. Too bad that did not work out; it felt like a product too ahead of its time. Companies like Microsoft, Magic Leap and even Apple are hoping to pick up from where Google left off. They are creating their own smart glasses that will, hopefully, do better than Google Glass. In our article, we look at some of the coolest Augmented Reality smart glasses around.
Some of them are already out while others are in development.
The holy grail of Virtual Reality: A complete suspension of disbelief — from labster.com by Marian Reed
Excerpt:
It’s no secret that we here at Labster are pretty excited about VR. However, if we are to successfully introduce VR into education and training we need to know how to create VR simulations that unlock these new great ways of learning.
Computer science researchers create augmented reality education tool — from ucalgary.ca by Erin Guiltenane
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
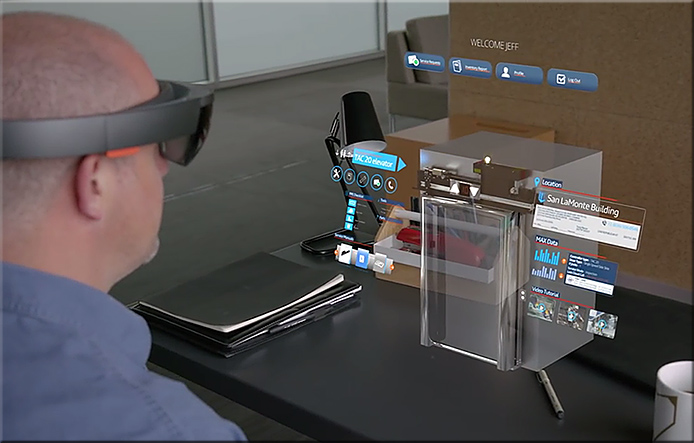
Christian Jacob and Markus Santoso are trying to re-create the experience of the aforementioned agents in Fantastic Voyage. Working with 3D modelling company Zygote, they and recent MSc graduate Douglas Yuen have created HoloCell, an educational software. Using Microsoft’s revolutionary HoloLens AR glasses, HoloCell provides a mixed reality experience allowing users to explore a 3D simulation of the inner workings, organelles, and molecules of a healthy human cell.
Upload, Google, HTC and Udacity join forces for new VR education program — from uploadvr.com
Excerpt:
Upload is teaming up with Udacity, Google and HTC to build an industry-recognized VR certification program.
…
According to Udacity representatives, the organization will now be adding a VR track to its “nanodegree”program. Udacity’s nanodegrees are certification routes that can be completed completely online at a student’s own pace. These courses typically take between 6-12 months and cost $199 per month. Students will also receive half of their tuition back if they complete a course within six months. The new VR course will follow this pattern as well.
The VR nanodegree program was curated by Udacity after the organization interviewed dozens of VR savvy companies about the type of skills they look for in a potential new hire. This information was then built into a curriculum through a joint effort between Google, HTC and Upload.
Virtual reality helps Germany catch last Nazi war criminals — from theguardian.com by Agence France-Presse
Lack of knowledge no longer an excuse as precise 3D model of Auschwitz, showing gas chambers and crematoria, helps address atrocities
Excerpt:
German prosecutors and police have developed 3D technology to help them catch the last living Nazi war criminals with a highly precise model of Auschwitz.
Also related to this:
Auschwitz war criminals targeted with help of virtual reality — from jpost.com by
Excerpt:
German prosecutors and police have begun using virtual reality headsets in their quest to bring the last remaining Auschwitz war criminals to justice, AFP reported Sunday.
Using the blueprints of the death camp in Nazi-occupied Poland, Bavarian state crime office digital imaging expert Ralf Breker has created a virtual reality model of Auschwitz which allows judges and prosecutors to mimic moving around the camp as it stood during the Holocaust.
How the UN thinks virtual reality could not only build empathy, but catalyze change, too — from yahoo.com by Lulu Chang
Excerpt:
Technology is hoping to turn empathy into action. Or at least, the United Nations is hoping to do so. The intergovernmental organization is more than seven decades old at this point, but it’s constantly finding new ways to better the world’s citizenry. And the latest tool in its arsenal? Virtual reality.
Last year, the UN debuted its United Nations Virtual Reality, which uses the technology to advocate for communities the world over. And more recently, the organization launched an app made specifically for virtual reality films. First debuted at the Toronto International Film Festival, this app encourages folks to not only watch the UN’s VR films, but to then take action by way of donations or volunteer work.
Occipital Wants to Turn iPhones into Mixed Virtual Reality Headsets — from next.reality.news by Adam Dachis
Excerpt:
If you’re an Apple user and want an untethered virtual reality system, you’re currently stuck with Google Cardboard, which doesn’t hold a candle to the room scale VR provided by the HTC Vive (a headset not compatible with Macs, by the way). But spatial computing company Occipital just figured out how to use their Structure Core 3D Sensor to provide room scale VR to any smartphone headset—whether it’s for an iPhone or Android.
‘The Body VR’ Brings Educational Tour Of The Human Body To HTC Vive Today — from uploadvr.com by Jamie Feltham on October 3rd, 2016
Excerpt:
The Body VR is a great example of how the Oculus Rift and Gear VR can be used to educate as well as entertain. Starting today, it’s also a great example of how the HTC Vive can do the same.
The developers previously released this VR biology lesson for free back at the launch of the Gear VR and, in turn, the Oculus Rift. Now an upgraded version is available on Valve and HTC’s Steam VR headset. You’ll still get the original experience in which you explore the human body, travelling through the bloodstream to learn about blood cells and looking at how organelles work. The piece is narrated as you go.
Virtual Reality Dazzles Harvard University — from universityherald.com
Excerpt:
For a moment, students were taken into another world without leaving the great halls of Harvard. Some students had a great time exploring the ocean floor and saw unique underwater animals, others tried their hand in hockey, while others screamed as they got into a racecar and sped on a virtual speedway. All of them, getting a taste of what virtual and augmented reality looks like.
All of these, of course, were not just about fun but on how especially augmented and virtual reality can transform every kind of industry. This will be discussed and demonstrated at the i-lab in the coming weeks with Rony Abovitz, CEO of Magic Leap Inc., as the keynote speaker.
Abovitz was responsible for developing the “Mixed Reality Lightfield,” a technology that combines augmented and virtual reality. According to Abovitz, it will help those who are struggling to “transfer two-dimensional information or text into “spatial learning.”
“I think it will make life easier for a lot of people and open doors for a lot of people because we are making technology fit how our brains evolved into the physics of the universe rather than forcing our brains to adapt to a more limited technology,” he added.
Addendum on 10/6/16:
- PS VR Review Roundup: Great Design And Price Is Marred By Poor Tracking And Content — from uploadvr.com
- 4 types of augmented reality for events — from bizbash.com