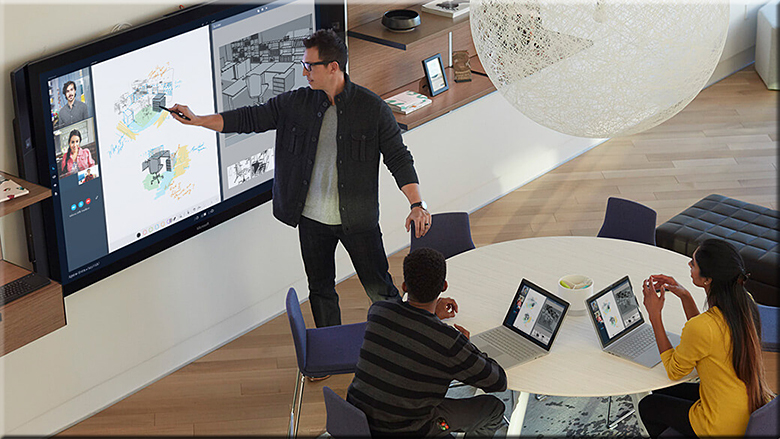
Online Learning—from Innovation to Adoption: Introducing the CHLOE Survey — from eduventures.com by Richard Garrett & Ron Legon
Excerpt:
It’s now more than 20 years since online learning came on the scene. At the outset, many skeptics questioned its quality and reliability. Online learning faced widespread resistance among faculty conditioned by centuries-old, classroom-based education and lacking in computer skills. There were substantial start-up costs, technical deficiencies, and regulatory uncertainty to overcome.
With all these obstacles, many doubted whether online learning would gain a permanent foothold in U.S. higher education. The former Babson Survey Research Group/Sloan-C survey of chief academic officers focused on the fundamental issues of counting online students and attitudes for or against its adoption.
Today, the number of online students is no longer a mystery, and there is wide acceptance of the delivery mode among administrators and faculty. This innovation, in the means of delivering higher education, is here to stay. It is no longer experimental, but a fixture in mainstream institutions, accounting for a large and still growing proportion of total postsecondary enrollment.
…
Online learning has changed higher education, but higher education has also shaped online learning. There is no doubt that online learning is here to stay, but what is far less clear is the balance between innovation and consolidation, transformation and integration within institutions and across the field as a whole going forward. The planned series of annual CHLOE Surveys will provide much-needed insight.
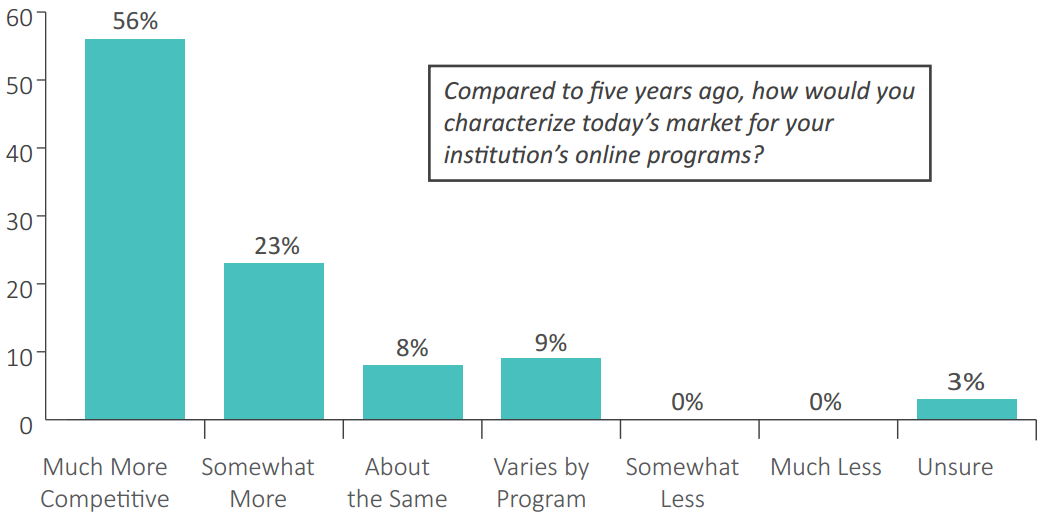
Signs of a Ceiling in Online Ed Market — from insidehighered.com by Carl Straumsheim
Report on online education landscape suggests potentially leaner times ahead for colleges hoping to profit in the market. Community colleges are already seeing it.
Excerpt:
Is the community college sector the canary in the coal mine for the online education market?
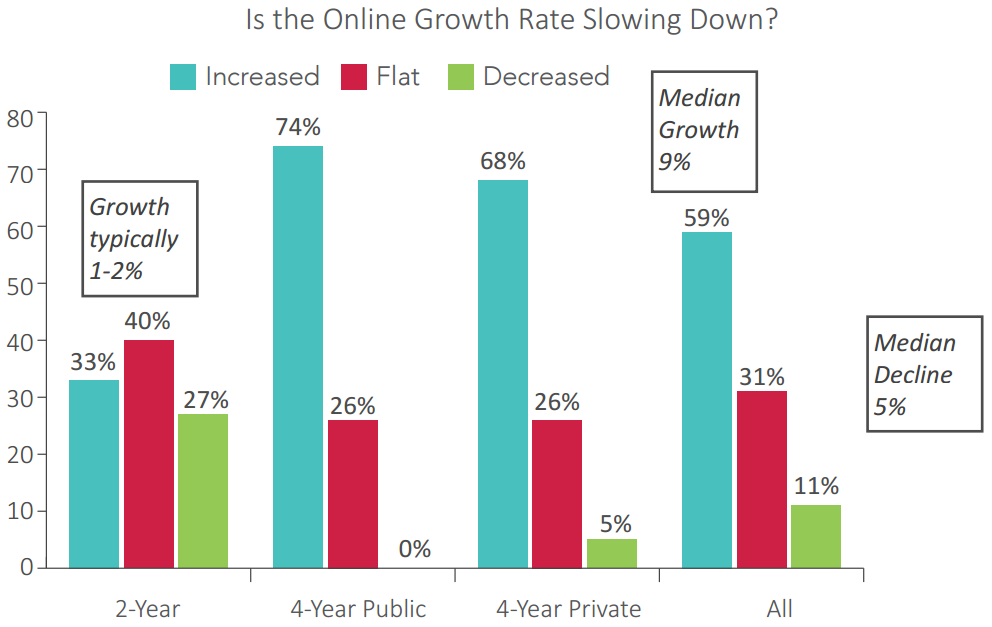
A new survey of online education administrators at 104 colleges and universities released today shows — as other studies have suggested — that public and private four-year institutions saw healthy enrollment growth in their fully online programs in spring 2016 compared to the year before, and that they are showing few signs of slowing their investments in the space.
The situation is not the same at two-year colleges. Online programs at all institutions grew on average by 9 percent year over year, but at community colleges, growth typically registered 1 to 2 percent. And while only a handful of the public or private four-year institutions surveyed said their online enrollments shrank from 2015 to 2016, findings at community colleges were mixed: 33 percent saw growth, 27 percent decline and 40 percent stability.
From DSC:
It appears that the concept of “windows of opportunity” is also true with online learning; and the key thing for all community colleges, colleges and universities to reflect upon is that these windows don’t stay open forever.
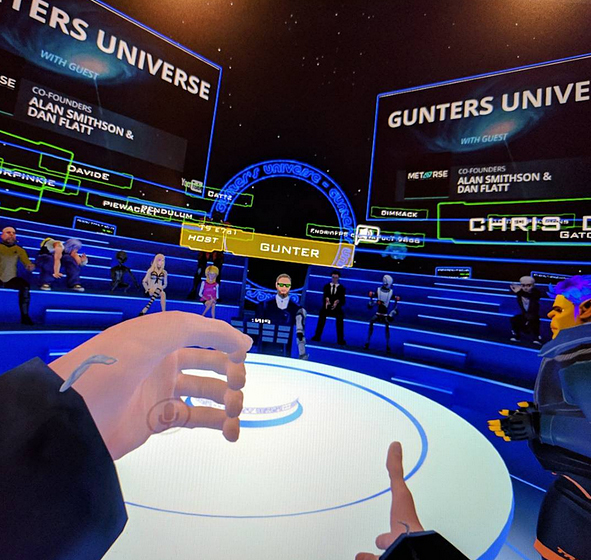
But another thing is that the world is going increasingly digital/virtual — especially in regards to the increasingly common usage of automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Our forms of Human Computer Interaction (HCI) continue to morph (AR, VR, Alexa and other personal assistants, etc.)
So some questions come to my mind:
- If one’s institution doesn’t offer a healthy assortment of online/virtually-based courses in the future, how might that situation impact the public’s perception of that particular institution? How might that situation impact recruitment and retention?
. - What’s going to happen when online-based learning experiences provide far more personalization, customization, and efficiency than our face-to-face courses can provide? Ask any faculty member speaking to 40-250+ students if they truly know the learning preferences, academic goals, and career goals of any given student — and I’ll bet you they have no idea. There’s simply not enough time to get to that level of information in many cases, and this situation is only getting tougher to do so. Don’t get me wrong. Many people will always prefer to learn in a physical environment, surrounded by other learners. But if the innovations continue to take place in the online learning-based environments, then Clayton Christensen’s theories of disruption could prove to be spot on — especially if the most innovative institutions of the future will be able to offer degrees at significantly reduced prices.













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)