Social media as a learning tool: Five suggested sses for the classroom — from frontierinternet.com; with thanks to Laura Tscholl, Communications Specialist | The Gateway for this resource




Social media as a learning tool: Five suggested sses for the classroom — from frontierinternet.com; with thanks to Laura Tscholl, Communications Specialist | The Gateway for this resource
From DSC:
I have often reflected on differentiation or what some call personalized learning and/or customized learning. How does a busy teacher, instructor, professor, or trainer achieve this, realistically?
It’s very difficult and time-consuming to do for sure. But it also requires a team of specialists to achieve such a holy grail of learning — as one person can’t know it all. That is, one educator doesn’t have the necessary time, skills, or knowledge to address so many different learning needs and levels!
Educators and trainers have so many things on their plates that it’s very difficult to come up with _X_ lesson plans/agendas/personalized approaches, etc. On the other side of the table, how do students from a vast array of backgrounds and cognitive skill levels get the main points of a chapter or piece of text? How can they self-select the level of difficulty and/or start at a “basics” level and work one’s way up to harder/more detailed levels if they can cognitively handle that level of detail/complexity? Conversely, how do I as a learner get the boiled down version of a piece of text?
Well… just as with the flipped classroom approach, I’d like to suggest that we flip things a bit and enlist teams of specialists at the publishers to fulfill this need. Move things to the content creation end — not so much at the delivery end of things. Publishers’ teams could play a significant, hugely helpful role in providing customized learning to learners.
Some of the ways that this could happen:
Use an HTML like language when writing a textbook, such as:
<MainPoint> The text for the main point here. </MainPoint>
<SubPoint1>The text for the subpoint 1 here.</SubPoint1>
<DetailsSubPoint1>More detailed information for subpoint 1 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SubPoint2>The text for the subpoint 2 here.</SubPoint2>
<DetailsSubPoint2>More detailed information for subpoint 2 here.</DetailsSubPoint2>
<SubPoint3>The text for the subpoint 3 here.</SubPoint3>
<DetailsSubPoint3>More detailed information for subpoint 3 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SummaryOfMainPoints>A list of the main points that a learner should walk away with.</SummaryOfMainPoints>
<BasicsOfMainPoints>Here is a listing of the main points, but put in alternative words and more basic ways of expressing those main points. </BasicsOfMainPoints>
<Conclusion> The text for the concluding comments here.</Conclusion>
<BasicsOfMainPoints> could be called <AlternativeExplanations>
Bottom line: This tag would be to put things forth using very straightforward terms.
Another tag would be to address how this topic/chapter is relevant:
<RealWorldApplication>This short paragraph should illustrate real world examples
of this particular topic. Why does this topic matter? How is it relevant?</RealWorldApplication>
On the students’ end, they could use an app that works with such tags to allow a learner to quickly see/review the different layers. That is:
It’s like the layers of a Microsoft HoloLens app of the human anatomy:
Or it’s like different layers of a chapter of a “textbook” — so a learner could quickly collapse/expand the text as needed:
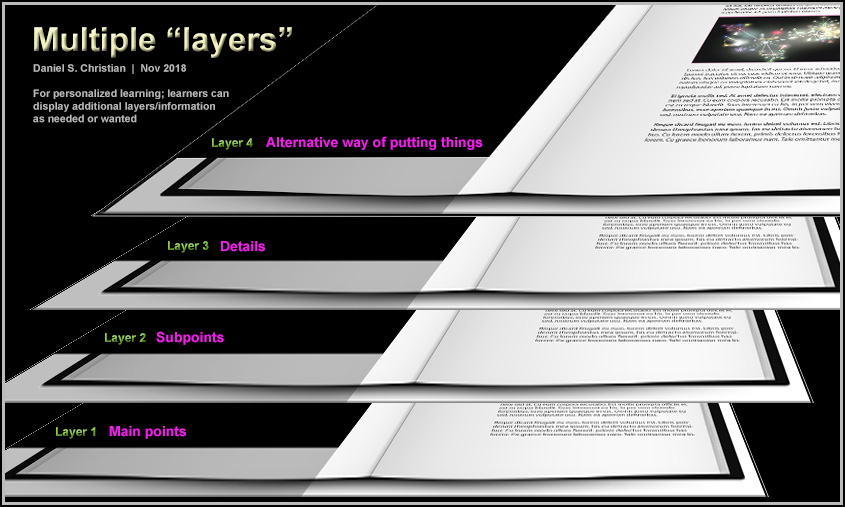
This approach could be helpful at all kinds of learning levels. For example, it could be very helpful for law school students to obtain outlines for cases or for chapters of information. Similarly, it could be helpful for dental or medical school students to get the main points as well as detailed information.
Also, as Artificial Intelligence (AI) grows, the system could check a learner’s cloud-based learner profile to see their reading level or prior knowledge, any IEP’s on file, their learning preferences (audio, video, animations, etc.), etc. to further provide a personalized/customized learning experience.
To recap:
Top Trends in Active and Collaborative Learning — from thesextantgroup.com by Joe Hammett
Excerpts:
My daughter is a maker. She spends hours tinkering with sewing machines and slime recipes, building salamander habitats and the like. She hangs out with her school friends inside apps that teach math and problem solving through multi-player games. All the while, they are learning to communicate and collaborate in ways that are completely foreign to their grandparent’s generation. She is 10 years old and represents a shift in human cognitive processing brought about by the mastery of technology from a very young age. Her generation and those that come after have never known a time without technology. Personal devices have changed the shared human experience and there is no turning back.
The spaces in which this new human chooses to occupy must cater to their style of existence. They see every display as interactive and are growing up knowing that the entirety of human knowledge is available to them by simply asking Alexa. The 3D printer is a familiar concept and space travel for pleasure will be the norm when they have children of their own.
Current trends in active and collaborative learning are evolving alongside these young minds and when appropriately implemented, enable experiential learning and creative encounters that are changing the very nature of the learning process. Attention to the spaces that will support the educators is also paramount to this success. Lesson plans and teaching style must flip with the classroom. The learning space is just a room without the educator and their content.
…
8. Flexible and Reconfigurable
With floor space at a premium, classrooms need to be able to adapt to a multitude of uses and pedagogies. Flexible furniture will allow the individual instructor freedom to set up the space as needed for their intended activities without impacting the next person to use the room. Construction material choices are key to achieving an easily reconfigurable space. Raised floors and individually controllable lighting fixtures allow a room to go from lecture to group work with ease. Whiteboard paints and rail mounting systems make walls reconfigurable too!.
Active Learning, Flipped Classroom, SCALE-UP, TEAL Classroom, whatever label you choose to place before it, the classroom, learning spaces of all sorts, are changing. The occupants of these spaces demand that they are able to effectively, and comfortably, share ideas and collaborate on projects with their counterparts both in person and in the ether. A global shift is happening in the way humans share ideas. Disruptive technology, on a level not seen since the assembly line, is driving a change in the way humans interact with other humans. The future is collaborative.
Robots won’t replace instructors, 2 Penn State educators argue. Instead, they’ll help them be ‘more human.’ — from edsurge.com by Tina Nazerian
Excerpt:
Specifically, it will help them prepare for and teach their courses through several phases—ideation, design, assessment, facilitation, reflection and research. The two described a few prototypes they’ve built to show what that might look like.
Also see:
The future of education: Online, free, and with AI teachers? — from fool.com by Simon Erickson
Duolingo is using artificial intelligence to teach 300 million people a foreign language for free. Will this be the future of education?
Excerpts:
While it might not get a lot of investor attention, education is actually one of America’s largest markets.
The U.S. has 20 million undergraduates enrolled in colleges and universities right now and another 3 million enrolled in graduate programs. Those undergrads paid an average of $17,237 for tuition, room, and board at public institutions in the 2016-17 school year and $44,551 for private institutions. Graduate education varies widely by area of focus, but the average amount paid for tuition alone was $24,812 last year.
Add all of those up, and America’s students are paying more than half a trillion dollars each year for their education! And that doesn’t even include the interest amassed for student loans, the college-branded merchandise, or all the money spent on beer and coffee.
Keeping the costs down
Several companies are trying to find ways to make college more affordable and accessible.
But after we launched, we have so many users that nowadays if the system wants to figure out whether it should teach plurals before adjectives or adjectives before plurals, it just runs a test with about 50,000 people. So for the next 50,000 people that sign up, which takes about six hours for 50,000 new users to come to Duolingo, to half of them it teaches plurals before adjectives. To the other half it teaches adjectives before plurals. And then it measures which ones learn better. And so once and for all it can figure out, ah it turns out for this particular language to teach plurals before adjectives for example.
So every week the system is improving. It’s making itself better at teaching by learning from our learners. So it’s doing that just based on huge amounts of data. And this is why it’s become so successful I think at teaching and why we have so many users.
From DSC:
I see AI helping learners, instructors, teachers, and trainers. I see AI being a tool to help do some of the heavy lifting, but people still like to learn with other people…with actual human beings. That said, a next generation learning platform could be far more responsive than what today’s traditional institutions of higher education are delivering.
New Virtual 3D Microscope Lab Program Offered for Online Students by Oregon State University — from virtuallyinspired.org
OSU solves degree completion issue for online biology students
Excerpt:
“We had to create an alternative that gives students the foundational experience of being in a lab where they can maneuver a microscope’s settings and adjust the images just as they would in a face-to-face environment,” said Shannon Riggs, the Ecampus director of course development and training.
Multimedia developers mounted a camera on top of an actual microscope and took pictures of what was on the slides. Using 3D modeling software, the photos were interweaved to create 3D animation. Using game development software enabled students to adjust lighting, zoom and manipulate the images, just like in a traditional laboratory. The images were programmed to create a virtual simulation.
The final product is “an interactive web application that utilizes a custom 3D microscope and incorporates animation and real-life slide photos,” according to Victor Yee, an Ecampus assistant director of course development and training.
Also see:
Affordable and at-scale — from insidehighered.com by Ray Schroeder
Affordable degrees at scale have arrived. The momentum behind this movement is undeniable, and its impact will be significant, Ray Schroeder writes.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
How many times have we been told that major change in our field is on the near horizon? Too many times, indeed.
The promises of technologies and practices have fallen short more often than not. Just seven years ago, I was part of the early MOOC movement and felt the pulsating potential of teaching thousands of students around the world in a single class. The “year of the MOOC” was declared in 2012. Three years later, skeptics declared that the MOOC had died an ignominious death with high “failure” rates and relatively little recognition by employers.
However, the skeptics were too impatient, misunderstood the nature of MOOCs and lacked the vision of those at Georgia Tech, the University of Illinois, Arizona State University, Coursera, edX and scores of other institutions that have persevered in building upon MOOCs’ premises to develop high-quality, affordable courses, certificates and now, degrees at scale.
No, these degrees are not free, but they are less than half the cost of on-campus versions. No, they are not massive in the hundreds of thousands, but they are certainly at large scale with many thousands enrolled. In computer science, the success is felt across the country.
Georgia Tech alone has enrolled 10,000 students over all in its online master’s program and is adding thousands of new students each semester in a top 10-ranked degree program costing less than $7,000. Georgia Tech broke the new ground through building collaborations among several partners. Yet, that was just the beginning, and many leading universities have followed.
Also see:
Trends for the future of education with Jeff Selingo — from steelcase.com
How the future of work and new technology will make place more important than ever.
Excerpt:
Selingo sees artificial intelligence and big data as game changers for higher education. He says AI can free up professors and advisors to spend more time with students by answering some more frequently-asked questions and handling some of the grading. He also says data can help us track and predict student performance to help them create better outcomes. “When they come in as a first-year student, we can say ‘People who came in like you that had similar high school grades and took similar classes ended up here. So, if you want to get out of here in four years and have a successful career, here are the different pathways you should follow.’”
Are ‘smart’ classrooms the future? — from campustechnology.com by Julie Johnston
Indiana University explores that question by bringing together tech partners and university leaders to share ideas on how to design classrooms that make better use of faculty and student time.
Excerpt:
To achieve these goals, we are investigating smart solutions that will:
…
Activities included collaborative brainstorming focusing on these questions:
From DSC:
Though many peoples’ — including faculty members’ — eyes gloss over when we start talking about learning spaces and smart classrooms, it’s still an important topic. Personally, I’d rather be learning in an engaging, exciting learning environment that’s outfitted with a variety of tools (physically as well as digitally and virtually-based) that make sense for that community of learners. Also, faculty members have very limited time to get across campus and into the classroom and get things setup…the more things that can be automated in those setup situations the better!
I’ve long posted items re: machine-to-machine communications, voice recognition/voice-enabled interfaces, artificial intelligence, bots, algorithms, a variety of vendors and their products including Amazon’s Alexa / Apple’s Siri / Microsoft’s Cortana / and Google’s Home or Google Assistant, learning spaces, and smart classrooms, as I do think those things are components of our future learning ecosystems.
2018 Students and Technology Research Study — from library.educause.edu
Topics Covered
From DSC:
Ever notice how effective Ted Talks begin? They seek to instantly grab your attention with a zinger question, a somewhat shocking statement, an interesting story, a joke, an important problem or an issue, a personal anecdote or experience, a powerful image/photo/graphic, a brief demonstration, and the like.
Grabbing someone’s attention is a key first step in getting a piece of information into someone’s short-term memory — what I call getting through “the gate.” If we can’t get through the gate into someone’s short-term memory, we have zero (0) chance of having them actually process that information and to think about and engage with that piece of content. If we can’t make it into someone’s short-term memory, we can’t get that piece of information into their long-term memory for later retrieval/recall. There won’t be any return on investment (ROI) in that case.
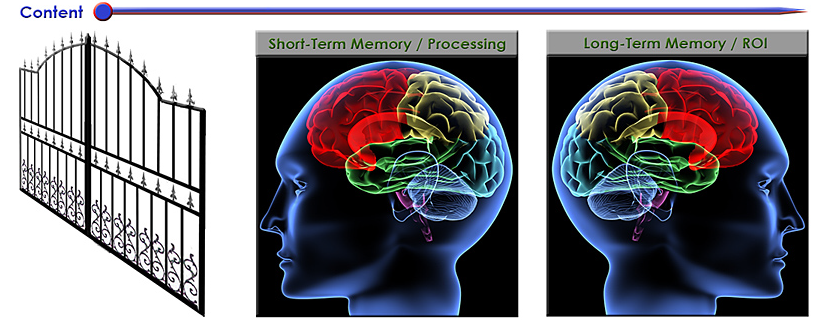
So why not try starting up one of your classes this week with a zinger question, a powerful image/photo/video, or a story from your own work experience? I’ll bet you’ll grab your students’ attentions instantly! Then you can move on into the material for a greater ROI. From there, offering frequent, low-stakes quizzes will hopefully help your students slow down their forgetting curves and help them practice recalling/retrieving that information. By the way, that’s why stories are quite powerful. We often remember them better. So if you can weave an illustrative story into your next class, your students might really benefit from it come final test time!
Also relevant/see:
Ready, set, speak: 5 strong ways to start your next presentation — from abovethelaw.com by Olga Mack, with thanks to Mr. Otto Stockmeyer for this resource
No matter which of these five ways you decide to launch your presentation, ensure that you make it count, and make it memorable.
Excerpts:
Inside Amazon’s artificial intelligence flywheel — from wired.com by Steven Levy
How deep learning came to power Alexa, Amazon Web Services, and nearly every other division of the company.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Amazon loves to use the word flywheel to describe how various parts of its massive business work as a single perpetual motion machine. It now has a powerful AI flywheel, where machine-learning innovations in one part of the company fuel the efforts of other teams, who in turn can build products or offer services to affect other groups, or even the company at large. Offering its machine-learning platforms to outsiders as a paid service makes the effort itself profitable—and in certain cases scoops up yet more data to level up the technology even more.
It took a lot of six-pagers to transform Amazon from a deep-learning wannabe into a formidable power. The results of this transformation can be seen throughout the company—including in a recommendations system that now runs on a totally new machine-learning infrastructure. Amazon is smarter in suggesting what you should read next, what items you should add to your shopping list, and what movie you might want to watch tonight. And this year Thirumalai started a new job, heading Amazon search, where he intends to use deep learning in every aspect of the service.
“If you asked me seven or eight years ago how big a force Amazon was in AI, I would have said, ‘They aren’t,’” says Pedro Domingos, a top computer science professor at the University of Washington. “But they have really come on aggressively. Now they are becoming a force.”
Maybe the force.
From DSC:
When will we begin to see more mainstream recommendation engines for learning-based materials? With the demand for people to reinvent themselves, such a next generation learning platform can’t come soon enough!

We’re about to embark on a period in American history where career reinvention will be critical, perhaps more so than it’s ever been before. In the next decade, as many as 50 million American workers—a third of the total—will need to change careers, according to McKinsey Global Institute. Automation, in the form of AI (artificial intelligence) and RPA (robotic process automation), is the primary driver. McKinsey observes: “There are few precedents in which societies have successfully retrained such large numbers of people.”
Also relevant/see:
Online education’s expansion continues in higher ed with a focus on tech skills — from educationdive.com by James Paterson
Dive Brief:
In the 2030 and beyond world, employers will no longer be a separate entity from the education establishment. Pressures from both the supply and demand side are so large that employers and learners will end up, by default, co-designing new learning experiences, where all learning counts.
OBJECTIVES FOR CONVENINGS
Three key questions guided the discussions:
This report summarizes the experts’ views on what skills will likely be needed to navigate the work + learn ecosystem over the next 10–15 years—and their suggested steps for better serving the nation’s future needs.
In a new world of work, driven especially by AI, institutionally-sanctioned curricula could give way to AI-personalized learning. This would drastically change the nature of existing social contracts between employers and employees, teachers and students, and governments and citizens. Traditional social contracts would need to be renegotiated or revamped entirely. In the process, institutional assessment and evaluation could well shift from top-down to new bottom-up tools and processes for developing capacities, valuing skills, and managing performance through new kinds of reputation or accomplishment scores.
…
In October 2017, Chris Wanstrath, CEO of Github, the foremost code-sharing and social networking resource for programmers today, made a bold statement: “The future of coding is no coding at all.” He believes that the writing of code will be automated in the near future, leaving humans to focus on “higher-level strategy and design of software.” Many of the experts at the convenings agreed. Even creating the AI systems of tomorrow, they asserted, will likely require less human coding than is needed today, with graphic interfaces turning AI programming into a drag-and-drop operation.
Digital fluency does not mean knowing coding languages. Experts at both convenings contended that effectively “befriending the machine” will be less about teaching people to code and more about being able to empathize with AIs and machines, understanding how they “see the world” and “think” and “make decisions.” Machines will create languages to talk to one another.
…
Here’s a list of many skills the experts do not expect to see much of—if at all—in the future:
Here’s a list of the most essential skills needed for the future:
The rise of machine intelligence is just one of the many powerful social, technological, economic, environmental, and political forces that are rapidly and disruptively changing the way everyone will work and learn in the future. Because this largely tech-driven force is so interconnected with other drivers of change, it is nearly impossible to understand the impact of intelligent agents on how we will work and learn without also imagining the ways in which these new tools will reshape how we live.
Benchmarking Higher Ed AV Staffing Levels — Revisited — from campustechnology.com by Mike Tomei
As AV-equipped classrooms on campus increase in both numbers and complexity, have AV departments staffed up accordingly? A recent survey sheds some light on how AV is managed in higher education.
Excerpt:
I think we can all agree that new AV system installs have a much higher degree of complexity compared to AV systems five or 10 years ago. The obvious culprits are active learning classrooms that employ multiple displays and matrix switching backends, and conferencing systems of varying complexity being installed in big and small rooms all over campus. But even if today’s standard basic classrooms are offering the same presentation functionality as they were five years ago, the backend AV technology running those systems has still increased in complexity. We’re trying to push very high resolution video signals around the room; copyright-protected digital content is coming into play; there are myriad BYOD devices and connectors that need to be supported; and we’re making a strong push to connect our AV devices to the enterprise network for monitoring and troubleshooting. This increase in AV system complexity just adds to the system design, installation and support burdens placed upon an AV department. Without an increase in FTE staff beyond what we’re seeing, there’s just no way that AV support can truly flourish on campuses.
Today we’re reopening the survey to continue to gather data about AV staffing levels, and we’ll periodically tabulate and publish the results for those that participate. Visit www.AV-Survey.com to take the survey. If you would like to request the full 2018 AV staffing survey results, including average AV department budgets, staffing levels by position, breakouts by public/private/community colleges and small/medium/large schools, please send an e-mail to me (mike@tomeiav.com) and to Craig Park from The Sextant Group (cpark@thesextantgroup.com).
MIT plans $1B computing college, AI research effort — from educationdive.com by James Paterson
Dive Brief (emphasis DSC):
Also see:
Alexa Sessions You Won’t Want to Miss at AWS re:Invent 2018 — from developer.amazon.com
Excerpts — with an eye towards where this might be leading in terms of learning spaces:
Alexa and AWS IoT — Voice is a natural interface to interact not just with the world around us, but also with physical assets and things, such as connected home devices, including lights, thermostats, or TVs. Learn how you can connect and control devices in your home using the AWS IoT platform and Alexa Skills Kit.
Connect Any Device to Alexa and Control Any Feature with the Updated Smart Home Skill API — Learn about the latest update to the Smart Home Skill API, featuring new capability interfaces you can use as building blocks to connect any device to Alexa, including those that fall outside of the traditional smart home categories of lighting, locks, thermostats, sensors, cameras, and audio/video gear. Start learning about how you can create a smarter home with Alexa.
Workshop: Build an Alexa Skill with Multiple Models — Learn how to build an Alexa skill that utilizes multiple interaction models and combines functionality into a single skill. Build an Alexa smart home skill from scratch that implements both custom interactions and smart home functionality within a single skill. Check out these resources to start learning:
Three shifts as big as print to digital — from gettingsmart.com by Tom Vander Ark
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
We just lived through the biggest shift in learning since the printing press—a 25-year shift from print to digital. While it extended access and options to billions, it didn’t prove as transformational as many of us expected. It did, however, set the stage for three shifts that will change what and how people learn.