College and University presidents respond to Covid-19: 2020 fall term survey — from acenet.edu by Jonathan Turk, Maria Claudia Soler Salazar, and Anna Marie Ramos
Excerpt:




College and University presidents respond to Covid-19: 2020 fall term survey — from acenet.edu by Jonathan Turk, Maria Claudia Soler Salazar, and Anna Marie Ramos
Excerpt:
From DSC:
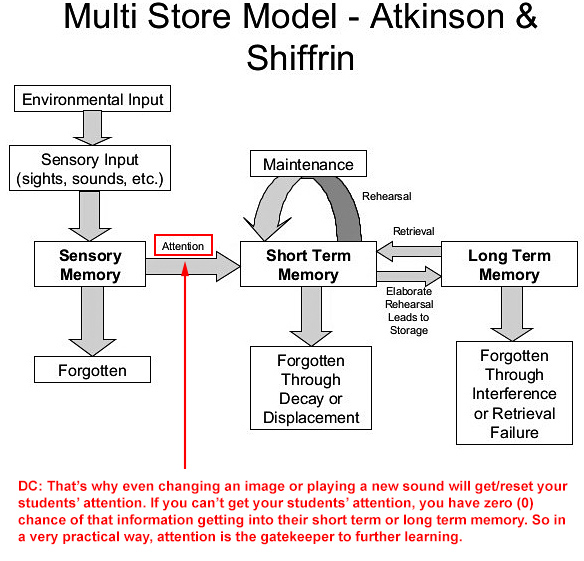
Many people talk about engagement when they discuss learning, and with good reason. It seems to me that what they are really getting at is the topic of getting and maintaining someone’s *attention.* Attention is the gatekeeper to further learning. I wonder if some of the next generation learning platforms that employ some level of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled features, will look to a learner’s preferences (as stored in their cloud-based learner’s profile) in order to help gain/maintain such attention.
And this also helps explain why allowing more learner agency — i.e., more choice, more control — in pursuing their own interests and passions really helps: A motivated learner is paying closer attention to what’s going on.

From DSC:
And along these lines, that’s one of the key reasons I’d like to see more involvement from the Theatre Departments, Computer Science Departments, and from those involved with creative writing across the land — in terms of helping develop content for remote and online-based education. Actors, actresses, set designers, costumer designers, audio/video editors, programmers/software developers, and more who could collaborate on these kinds of ideas.
Last comment on this. I don’t mean that we should present our classes like many advertisements do (i.e., running a thousand images by me within 30 seconds). But changing things up periodically — both visually and audibly — can help regain/reset your students’ attentions.
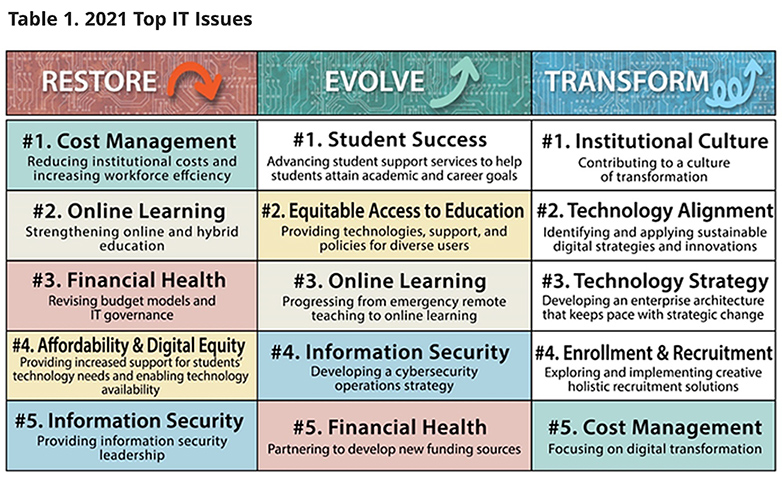
Top IT Issues, 2021: Emerging from the Pandemic — from educause.edu
Excerpt:
The EDUCAUSE Top IT Issues list has been refactored for 2021 to help higher education shape the role technology will play in the recovery from the pandemic. What different directions might institutional leaders take in their recovery strategy? How can technology help our ecosystem emerge stronger and fitter for the future?
The 2021 EDUCAUSE IT Issues project explores these questions using a very different approach from previous years. Anticipating potential ways institutions might emerge from the pandemic, this year we offer three Top IT Issues lists and examine the top 5 issues within three scenarios that may guide institutional leaders’ use of technology: restore, evolve, and transform.
Also see:
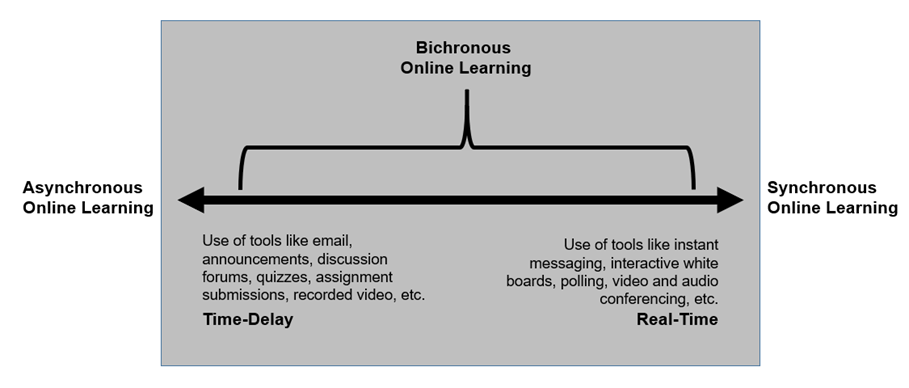
Bichronous Online Learning: Blending Asynchronous & Synchronous Online Learning — from er.educause.edu by Florence Martin, Drew Polly and Albert Ritzhaupt
Excerpt:
Overall, research shows that when synchronous communication features are integrated with asynchronous features, the online course is more engaging, increasing learning outcomes, positive attitudes, and retention.
OPM Market Landscape and Dynamics: Fall 2020 updates — from philonedtech.com by Phil Hill; with thanks to Edsurge.com for this resource
Excerpt:
There has been growing interest in the Online Program Management (OPM) market, as more schools try to develop a strategy and revenue model for online programs (particularly for master’s level). In addition, there has been a broad question to what degree schools would turn to OPM partners to help out with the Covid-driven move to online education in 2020 and beyond. We’re in the middle of the chaotic period of the pandemic, so there are no clear answers yet, but the consistent message is that OPM vendors are seeing a marked increase in interest from colleges and universities this year.
From DSC:
In our future learning experiences, I wonder what taking a break might look and sound like…? That is, we’re going along learning something from/with others (virtually/digitally) and then the teacher, professor, Subject Matter Expert (SME), trainer, or whoever says to take a break. What could happen then?
In the online/digital/virtual-based realm, that could mean that you have the option to set your “break” setting to bring up Spotify, or Vimeo, or YouTube, or Pandora, some VR-based app, other. The lights in your “learning space” could dim and the music could come on. Or you reach for a VR headset and watch a sunset or position yourself by a picturesque brook. Or your favorite podcast/vodcast picks up where you left off.
Hmmm…should be some interesting innovation and affordances along these lines.

State of Student Success and Trends in Higher Education — from instructure.com
2020 Global Research Study and Trends
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
In the following report, we’ve identified six leading trends for student success and engagement in today’s world:
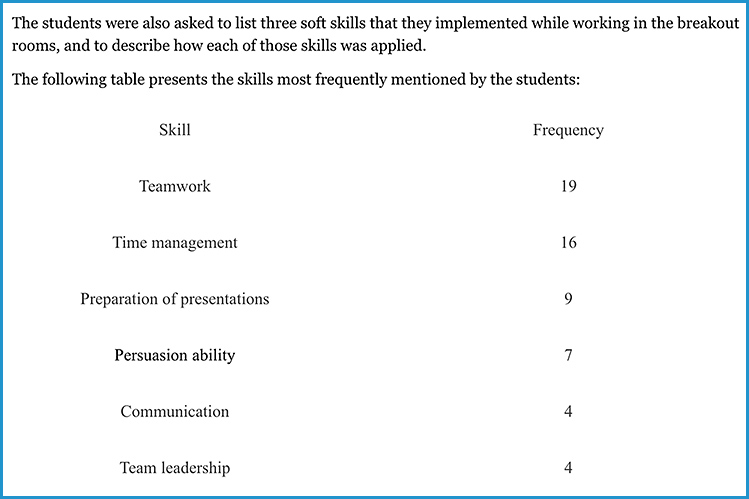
The Advantages of Teaching Soft Skills to CS Undergrads Online — from cacm.acm.org by Orit Hazzan; with thanks to Sarah Huibregtse for posting this out on LinkedIn.
Excerpt:
At first, I wondered whether teaching soft skills online is even possible since, unlike theoretical courses, I assumed that close face-to-face (F2F) interaction is required in order to practice such skills. Eventually, I realized that teaching this course online has, in fact, some advantages, that this teaching format opens up new opportunities, and that this medium can even foster several soft skills that I had not previously considered teaching in the F2F format. This blog demonstrates these advantages by focusing on the use of the breakout rooms option available in Zoom, which I used extensively in the course.
Expert Tips for Using PowerPoint Presenter View (2 screens, Windows) in Zoom or Teams — from thinkoutsidetheslide.com; with thanks to Tamara Kravits for this resource
Except:
In this article I want to share some of the expert tips for using the features of Presenter View. I will use the common scenario of Presenter View showing on one screen while the slides show on a second screen which is shared in the meeting platform. This allows easy access to all the Presenter View features.
If you need to add a second screen, check out the options in this article and if you want to learn more about using Presenter View in different setups, I have complete guides to using Presenter View in Zoom and in Teams.
From DSC:
Along the lines of using two monitors with a videoconferencing application, below is a graphic I created for our faculty members at the WMU-Cooley Law School.

Also relevant/see:
The State of AI in Higher Education — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
Both industry and higher ed experts see opportunities and risk, hype and reality with AI for teaching and learning.
Excerpts:
Kurt VanLehn, the chair for effective education in STEM in the School of Computing, Informatics and Decision Systems Engineering at Arizona State University, knows how challenging it can be people to come up with examples of effective AI in education. Why? “Because learning is complicated.”
…
Nuno Fernandes, president and CEO of Ilumno, an ed tech company in Latin America, isn’t ready to count adaptive learning out yet, if only because adaptivity has worked in other industries, such as social platforms like Netflix and Amazon, to identify what could work best for the user, based on previous activities and preferred formats of curriculum.
As Ilumno’s Fernandes asserted, AI won’t “substitute for faculty in any of our lifetimes. What it will do is give us tools to work better and to complement what is being done by humans.”
From DSC:
The article is a very balanced one. On one hand, it urges caution and points out that learning is messy and complex. On the other hand, it points out some beneficial applications of AI that already exist in language learning and in matching alumni with students for mentorship-related reasons.
From my perspective, I think AI-based systems will be used to help us scan job descriptions to see what the marketplace needs and is calling for. Such a system would be a major step forward in at least pointing out the existing hiring trends, needed skillsets, job openings, and more — and to do so in REAL-TIME!
Colleges, universities, and alternatives to traditional higher education could use this information to be far more responsive to the needs of the workplace. Then, such systems could match what the workplace needs with courses, microlearning-based feeds, apprenticeships, and other sources of learning that would help people learn those in-demand skills.
That in and of itself is HUGE. Again, HUGE. Given the need for people to reinvent themselves — and to do so quickly and affordably — that is incredibly beneficial.
Also, I do think there will be cloud-based learner profiles…data that each of us control and say who has access to it. Credentials will be stored there, for example. AI-based systems can scan such profiles and our desired career goals and suggest possible matches.
We can change our career goals. We don’t have to be locked into a particular track or tracks. We can reinvent ourselves. In fact, many of us will have to.
From DSC…by the way, another title for this blog could have been:
WIN-WIN situations all around! The Theatre Departments out there could collaborate with other depts/disciplines to develop highly engaging, digitally-based learning experiences!
The future of drama and the theatre — as well as opera, symphonies, and more — will likely include a significant virtual/digital component to them. While it’s too early to say that theatre needs to completely reinvent itself and move “the stage” completely online, below is an idea that creates a variety of WIN-WIN situations for actors, actresses, stage designers, digital audio/video editors, fine artists, graphic designers, programmers, writers, journalists, web designers, and many others as well — including the relevant faculty members!
A new world of creative, engaging, active learning could open up if those involved with the Theatre Department could work collaboratively with students/faculty members from other disciplines. And in the end, the learning experiences and content developed would be highly engaging — and perhaps even profitable for the institutions themselves!
Though the integration of acting with online-based learning materials is not a new idea, this post encourages a far more significant interdisciplinary collaboration between the Theatre Department and other departments/disciplines.
Consider a “Dealing with Bias in Journalism” type of topic, per a class in the Digital Media and Journalism Major.
Colleges and universities could share content with each other and/or charge others for their products/content/learning experiences. In the future, I could easily see a marketplace for buying and selling such engaging content. This could create a needed new source of revenue — especially given that those large auditoriums and theaters are likely not bringing in as much revenue as they typically do.
Colleges and universities could also try to reach out to local acting groups to get them involved and continue to create feeders into the world of work.
Other tags/categories could include:
Also see:
What improv taught me about failure: As a teacher and academic — from scholarlyteacher.com by Katharine Hubbard
In improv, the only way to “fail” is to overthink and not have fun, which reframed what failure was on a grand scale and made me start looking at academia through the same lens. What I learned about failure through improv comes back to those same two core concepts: have fun and stop overthinking.
…
Students are more engaged when the professor is having fun with the materials (Keller, Hoy, Goetz, & Frenzel, 2016), and teaching is more enjoyable when we are having fun ourselves.
Per “Instructure Launches Canvas Certified Educator Program” out at The Journal by Dian Schaffhauser:
Each course is expected to take about four weeks to finish. They include:
Richard Mayer Has Spent Decades On Educational Research. Here are His Pandemic Teaching Tips. — from edsurge.com by Jeff Young
Excerpt:
EdSurge recently reached out to Mayer, who is a professor of psychology at the University of California at Santa Barbara, to get his thoughts on the lessons his research reveals that can guide teachers and professors.
…
One finding is that students learn better if they see a video of the professor actually working out a math problem or concept on a whiteboard, than if they see a video of the same professor standing next to a whiteboard where the problem has already been worked out.
New benchmarking tool for higher ed seeks to address workplace soft skills gap — from chieflearningofficer.com by Elizabeth Loutfi
Quality Assurance Commons’ new Employability Self-Assessment will support higher education programs as they develop proficiency in teaching eight 21st century soft skills critical to today’s employers.
Excerpt:
A new assessment tool created for higher education institutions to track and measure the career success of their graduates was launched this week by nonprofit organization Quality Assurance Commons. The tool, which is called the Employability Self-Assessment, helps institutions identify the key skills employers want in candidates in the current and post-pandemic workplace.
The ESA has already been piloted at 20 colleges and universities and is being implemented at eight higher education institutions in the Connecticut State Colleges & Universities System, according to a company press release.
According to the report, the top three missing soft skills reported by employers were problem solving, critical thinking, innovation and creativity; ability to deal with complexity and ambiguity; and communication.
From DSC:
Hmmm…do our current ways of doing things get students to that point? Are the ways in which we structure our educational systems facilitating the development of those skills? Apparently not. What needs to change? For me, it’s offering “More choice. More control.” to the students. And watch the energy, curiosity, and enjoyment of learning greatly increase.