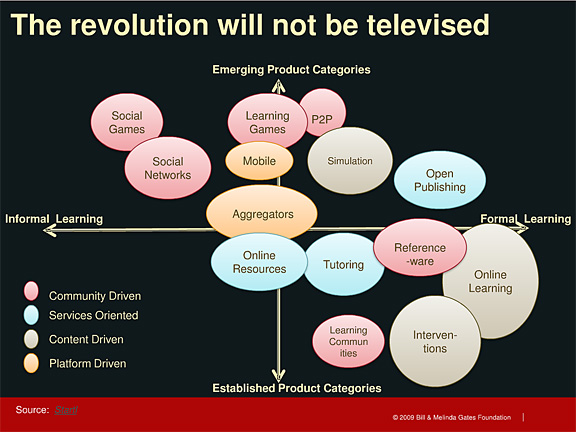
Emerging Interactive Ed. Tech: Classmate Assist and Wayang Outpost – Sensors, AI, and Context Awareness for Learning -and Teaching — by Lynn Marentette (emphasis below from DSC)
I’ve been following developments in intelligent tutoring systems for a while, and find it interesting to see how researchers are combining artificial intelligence, learning theory, affective computing, and sensor networks to create applications that might prove to be useful and effective.
The advantage of using intelligent tutoring applications in some cases is that it provides students with additional support and feedback the moment it is needed, something that is difficult for teachers to provide to students in large classrooms. With the increase in use of smartphones and other mobile devices such as the iPad, there is a good chance that this sort of technology will be used to support learning anywhere, anytime.
Although most intelligent tutoring systems are geared for 1-1 computing, I think there are some components that could be tweaked and then transfered to create intelligent “tutoring” systems for collaborative learning. Students like game-based learning, and what could be more fun than playing AND learning with a partner or group of peers? (I plan to revisit the research in this area in an upcoming post.)
Below I’ve highlighted two “intelligent” tutoring systems that incorporate the use of sensors in one form or another to generate information about student learning in a way that simulates what good teachers do every day. The ClassroomAssist application was developed by researchers at Intel, in collaboration with several universities. The Wayang Outpost application was developed by researchers at UMASS, and is aligned with the principles of Universal Design for Learning.