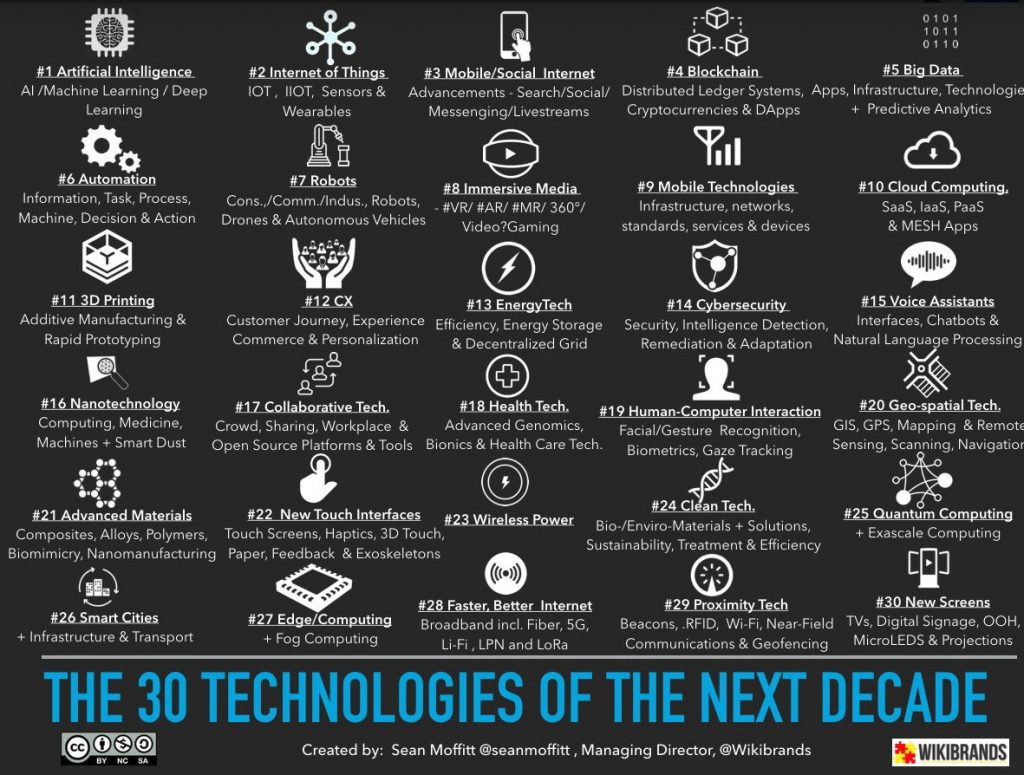
Are ‘smart’ classrooms the future? — from campustechnology.com by Julie Johnston
Indiana University explores that question by bringing together tech partners and university leaders to share ideas on how to design classrooms that make better use of faculty and student time.
Excerpt:
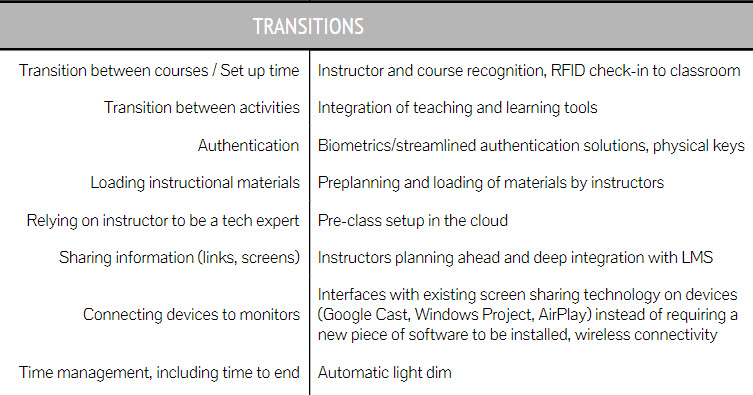
To achieve these goals, we are investigating smart solutions that will:
- Untether instructors from the room’s podium, allowing them control from anywhere in the room;
- Streamline the start of class, including biometric login to the room’s technology, behind-the-scenes routing of course content to room displays, control of lights and automatic attendance taking;
- Offer whiteboards that can be captured, routed to different displays in the room and saved for future viewing and editing;
- Provide small-group collaboration displays and the ability to easily route content to and from these displays; and
- Deliver these features through a simple, user-friendly and reliable room/technology interface.
…
Activities included collaborative brainstorming focusing on these questions:
- What else can we do to create the classroom of the future?
- What current technology exists to solve these problems?
- What could be developed that doesn’t yet exist?
- What’s next?
From DSC:
Though many peoples’ — including faculty members’ — eyes gloss over when we start talking about learning spaces and smart classrooms, it’s still an important topic. Personally, I’d rather be learning in an engaging, exciting learning environment that’s outfitted with a variety of tools (physically as well as digitally and virtually-based) that make sense for that community of learners. Also, faculty members have very limited time to get across campus and into the classroom and get things setup…the more things that can be automated in those setup situations the better!
I’ve long posted items re: machine-to-machine communications, voice recognition/voice-enabled interfaces, artificial intelligence, bots, algorithms, a variety of vendors and their products including Amazon’s Alexa / Apple’s Siri / Microsoft’s Cortana / and Google’s Home or Google Assistant, learning spaces, and smart classrooms, as I do think those things are components of our future learning ecosystems.









![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)