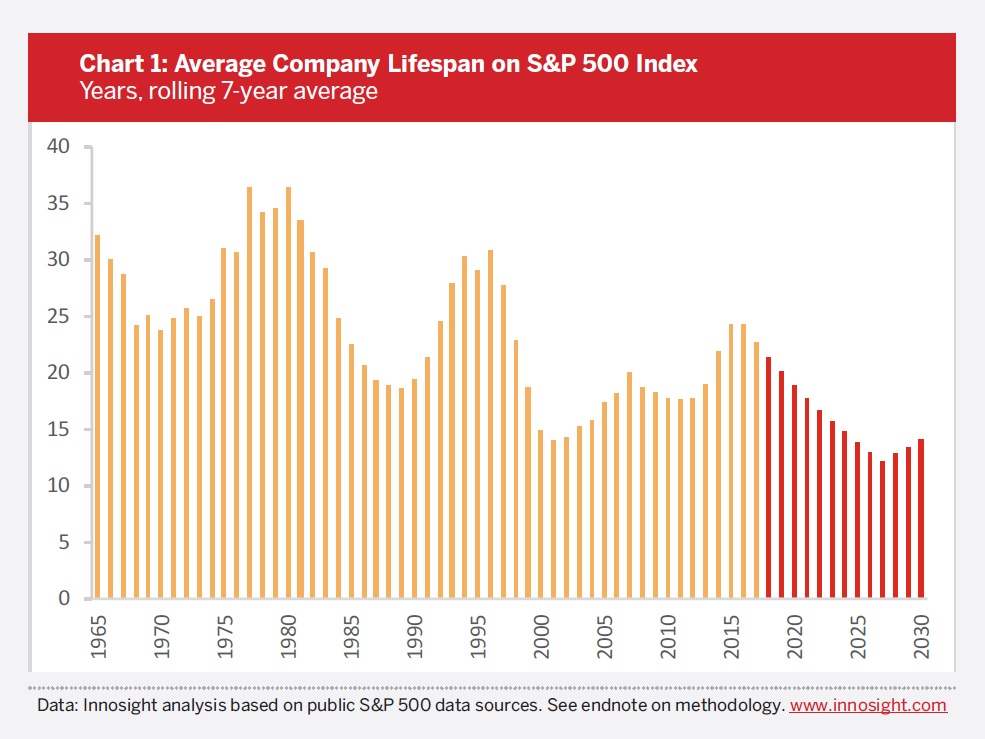
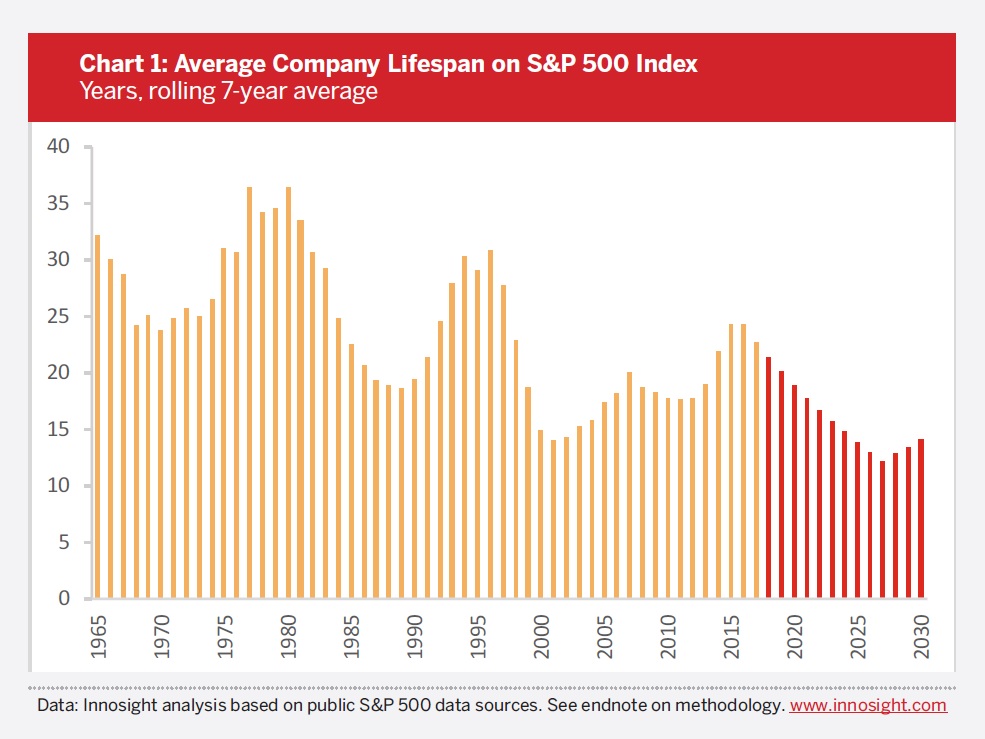
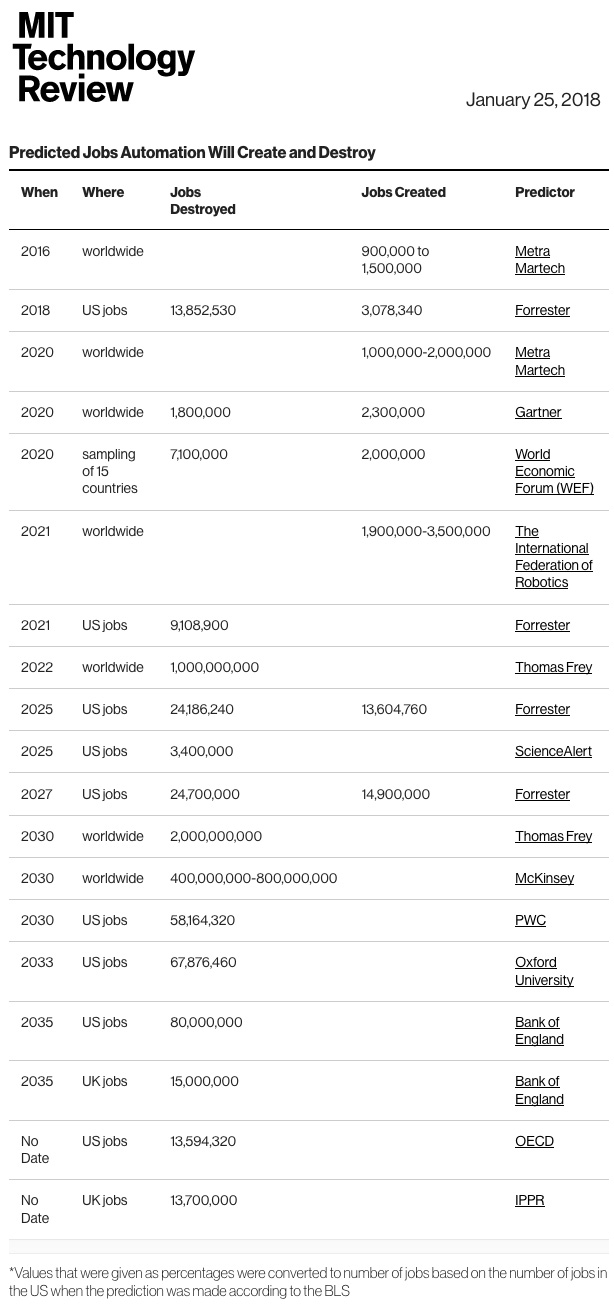
From DSC:
From an early age, we need to help our students learn how to learn. What tips, advice, and/or questions can we help our students get into the habit of asking themselves? Along these lines, the article below,”How Metacognition Boosts Learning,” provides some excellent questions.
Speaking of questions…I’ll add some more, but of a different sort:
- How can all educators do a better job of helping their students learn how to learn?
- How can Instructional Designers and Instructional Technologists help out here? Librarians? Provosts? Deans? Department Chairs? Teachers? Trainers (in the corporate L&D space)?
- How might technologies come into play here in terms of building more effective web-based learner profiles that can be fed into various platforms and/or into teachers’ game plans?
…
I appreciate Bill Knapp and his perspectives very much (see here and here; Bill is GRCC’s Executive Director of Distance Learning & Instructional Technologies). The last we got together, we wondered out loud:
- Why don’t teachers, professors, school systems, administrations within in K-20 address this need/topic more directly…? (i.e., how can we best help our students learn how to learn?)
- Should we provide a list of potentially helpful techniques, questions, tools, courses, modules, streams of content, or other resources on how to learn?
- Should we be weaving these sorts of things into our pedagogies?
- Are there tools — such as smartphone related apps — that can be of great service here? For example, are there apps for sending out reminders and/or motivational messages?
As Bill asserted, we need to help our students build self-efficacy and a mindset of how to learn. Then learners can pivot into new areas with much more confidence. I agree. In an era that continues to emphasize freelancing and entrepreneurship — plus dealing with a rapidly-changing workforce — people now need to be able to learn quickly and effectively. They need to have the self confidence to be able to pivot. So how can we best prepare our students for their futures?
Also, on a relevant but slightly different note (and I suppose is of the flavor of a Universal Design for Learning approach)…I think that “tests” given to special needs children — for example that might have to do with executive functioning, and/or identifying issues, and/or providing feedback as to how a particular learner might best absorb information — would be helpful for ALL students to take. If I realize that the way my brain learns best is to have aural and visual materials presented on any given topic, that is very useful information for me to realize — and the sooner the better!
How Metacognition Boosts Learning — from edutopia.org by Youki Terada
Students often lack the metacognitive skills they need to succeed, but they can develop these skills by addressing some simple questions.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Strategies that target students’ metacognition—the ability to think about thinking—can close a gap that some students experience between how prepared they feel for a test and how prepared they actually are. In a new study, students in an introductory college statistics class who took a short online survey before each exam asking them to think about how they would prepare for it earned higher grades in the course than their peers—a third of a letter grade higher, on average. This low-cost intervention helped students gain insight into their study strategies, boosting their metacognitive skills and giving them tools to be more independent learners.
…
More recently, a team of psychologists and neuroscientists published a comprehensive analysis of 10 learning techniques commonly used by students. They discovered that one of the most popular techniques—rereading material and highlighting key points—is also one of the least effective because it leads students to develop a false sense of mastery. They review a passage and move on without realizing that they haven’t thoroughly understood and absorbed the material.
…
Metacognition helps students recognize the gap between being familiar with a topic and understanding it deeply. But weaker students often don’t have this metacognitive recognition—which leads to disappointment and can discourage them from trying harder the next time.
…
To promote students’ metacognition, middle and high school teachers can implement the following strategies. Elementary teachers can model or modify these strategies with their students to provide more scaffolding.
…
During class, students should ask themselves:
- What are the main ideas of today’s lesson?
- Was anything confusing or difficult?
- If something isn’t making sense, what question should I ask the teacher?
- Am I taking proper notes?
- What can I do if I get stuck on a problem?
…
Before a test, students should ask themselves:
- What will be on the test?
- What areas do I struggle with or feel confused about?
- How much time should I set aside to prepare for an upcoming test?
- Do I have the necessary materials (books, school supplies, a computer and online access, etc.) and a quiet place to study, with no distractions?
- What strategies will I use to study? Is it enough to simply read and review the material, or will I take practice tests, study with a friend, or write note cards?
- What grade would I get if I were to take the test right now?
…
After a test, students should ask themselves:
- What questions did I get wrong, and why did I get them wrong?
- Were there any surprises during the test?
- Was I well-prepared for the test?
- What could I have done differently?
- Am I receiving useful, specific feedback from my teacher to help me progress?
From DSC:
Below are a few resources more about metacognition and learning how to learn:
- Students should be taught how to study. — from Daniel Willingham
Excerpt:
Rereading is a terribly ineffective strategy. The best strategy–by far–is to self-test–which is the 9th most popular strategy out of 11 in this study. Self-testing leads to better memory even compared to concept mapping (Karpicke & Blunt, 2011).
- The Lesson You Never Got Taught in School: How to Learn! — from bigthink.com
Excerpt:
Have you ever wondered whether it is best to do your studying in large chunks or divide your studying over a period of time? Research has found that the optimal level of distribution of sessions for learning is 10-20% of the length of time that something needs to be remembered. So if you want to remember something for a year you should study at least every month, if you want to remember something for five years you should space your learning every six to twelve months. If you want to remember something for a week you should space your learning 12-24 hours apart. It does seem however that the distributed-practice effect may work best when processing information deeply – so for best results you might want to try a distributed practice and self-testing combo.There is however a major catch – do you ever find that the amount of studying you do massively increases before an exam? Most students fall in to the “procrastination scallop” – we are all guilty at one point of cramming all the knowledge in right before an exam, but the evidence is pretty conclusive that this is the worst way to study, certainly when it comes to remembering for the long term. What is unclear is whether cramming is so popular because students don’t understand the benefits of distributed practice or whether testing practices are to blame – probably a combination of both. One thing is for sure, if you take it upon yourself to space your learning over time you are pretty much guaranteed to see improvements.
Addendum on 1/22/18:
Using Metacognition to Promote Learning
IDEA Paper #63 | December 2016
By Barbara J. Millis
Excerpt:
Some Definitions of Metacognition
Metacognition, simplistically defined, can be described as “cognition about cognition” or “thinking about thinking” (Flavell, Miller & Miller, 2002, p. 175; Shamir, Metvarech, & Gida, 2009, p. 47; Veeman, Van Hout-Wolters, & Afflerbach, 2006, p. 5). However, because metacognition is multifaceted and multi-layered (Dunlosky & Metcalf, 2009, p. 1; Flavell, 1976; Hall, Danielewicz, & Ware , 2013, p. 149; Lovett, 2013, p. 20), more complex definitions are called for. Basically, metacognition must be viewed as an ongoing process that involves reflection and action. Metacognitive thinkers change both their understandings and their strategies. The clearest definitions of metacognition emphasize its nature as a process or cycle.
Several authors (Nilson, 2013, p. 9; Schraw, 2001; & Zimmerman, 1998; 2000; 2002) narrow this process down to three ongoing stages. The first stage, pre-planning, emphasizes the need for reflection on both one’s own thinking and the task at hand, including reflection on past strategies that might have succeeded or failed. Following this self-reflection, during planning, metacognitive thinkers develop and implement—put into action—a plan. In the third and final stage—post-planning adjustments/revisions—subsequent analysis following implementation leads to modifications, revised decisions, and new future plans. In an excellent summary, Wirth states that “metacognition requires students both to understand how they are learning and to develop the ability to make plans, to monitor progress and to make adjustments” (as cited in Jaschik, 2011, p. 2).
Conclusion: As we have seen, metacognition is a complex but valuable skill that can nurture students’ learning and their self-awareness of the learning process. It is best conceived as a three-step process that can occur through deliberately designed activities. Such activities can take place before, during, and after face-to-face lessons or through online learning. They can also be built around both multiple choice and essay examinations. Immersing students in these metacognitive activities—assuming there are opportunities for practice and feedback—can result in students who are reflective learners.











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)