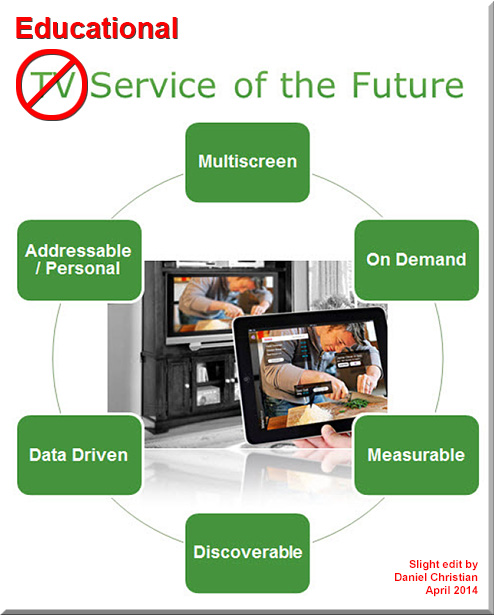
Every learner is different but not because of their learning styles — from clive-shepherd.blogspot.com by Clive Sheperd
Excerpt:
I’ve been reading Make it Stick: The Science of Successful Learning by Peter Brown and Henry Roediger (Harvard University Press, 2014). What a great book! It provides a whole load of useful tips for learners, teachers and trainers based on solid research.
…
Finishing this book coincides with The Debunker Club’s Debunk Learning Styles Month. And learning styles really do need debunking, not because we, as learners, don’t have preferences, but because there is no model out there which has been proven to be genuinely helpful in predicting learner performance based on their preferences.
Learning Styles are NOT an Effective Guide for Learning Design — from debunker.club
Excerpt:
Strength of Evidence Against
The strength of evidence against the use of learning styles is very strong. To put it simply, using learning styles to design or deploy learning is not likely to lead to improved learning effectiveness. While it may be true that learners have different learning preferences, those preference are not likely to be a good guide for learning. The bottom line is that when we design learning, there are far better heuristics to use than learning styles.
…
The weight of evidence at this time suggests that learning professionals should avoid using learning styles as a way to design their learning events. Still, research has not put the last nail in the coffin of learning styles. Future research may reveal specific instances where learning-style methods work. Similarly, learning preferences may be found to have long-term motivational effects.
…
Debunking Resources — Text-Based Web Pages
Learning Styles Or Learning Preference? — from learndash.com by Justin Ferriman
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
There are fewer buzzwords in the elearning industry that result in a greater division than “learning style”. I know from experience. There have been posts on this site related to the topic which resulted in a few passionate comments (such as this one).
…
As such, my intent isn’t to discuss learning styles. Everyone has their mind made up already. It’s time to move the discussion along.
Learner Preference & Motivation
If we bring the conversation “up” a level, we all ultimately agree that every learner has preferences and motivation. No need to cite studies for this concept, just think about yourself for a moment.
You enjoy certain things because you prefer them over others.
You do certain things because you are motivated to do so.
In the same respect, people prefer to learn information in a particular way. They also find some methods of learning more motivating than others. Whether you attribute this to learning styles or not is completely up to you.
How to respond to learning-style believers – from Cathy Moore
Excerpt:
First, the research
These resources link to or summarize research that debunks learning styles:
Are Learning Styles Going out of Style? — from mindtools.com by Bruce Murray
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Their first conclusion was that learners do indeed differ from one another. For example, some learners may have more ability, more interest, or more background than their classmates. Second, students do express preferences for how they like information to be presented to them… Third, after a careful analysis of the literature, the researchers found no evidence showing that people do in fact learn better when an instructor tailors their teaching style to mesh with their preferred learning style.
The idea of matching lessons to learning styles may be a fashionable trend that will go out of style itself. In the meantime, what are teachers and trainers to do? My advice is to leave the arguments to the academics. Here are some common-sense guidelines in planning a session of learning.
Follow your instincts. If you’re teaching music or speech, for example, wouldn’t auditory-based lessons make the most sense? You wouldn’t teach geography with lengthy descriptions of a coastline’s contours when simply showing a map would capture the essence in a heartbeat, right?
Since people clearly express learning style preferences, why not train them in their preferred style? If you give them what they want, they’ll be much more likely to stay engaged and expand their learning.
Do Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic Learners Need Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic Instruction? — from aft.org by Daniel T. Willingham
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Question: What does cognitive science tell us about the existence of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners and the best way to teach them?
The idea that people may differ in their ability to learn new material depending on its modality—that is, whether the child hears it, sees it, or touches it—has been tested for over 100 years. And the idea that these differences might prove useful in the classroom has been around for at least 40 years.
What cognitive science has taught us is that children do differ in their abilities with different modalities, but teaching the child in his best modality doesn‘t affect his educational achievement. What does matter is whether the child is taught in the content‘s best modality. All students learn more when content drives the choice of modality. In this column, I will describe some of the research on matching modality strength to the modality of instruction. I will also address why the idea of tailoring instruction to a student‘s best modality is so enduring—despite substantial evidence that it is wrong.
From DSC:
Given the controversies over the phrase “learning styles,” I like to use the phrase “learning preferences” instead. Along these lines, I think our goal as teachers, trainers, professors, SME’s should be to make learning enjoyable — give people more choice and more control. Present content in as many different formats as possible. Give them multiple pathways to meet the learning goals and objectives. If we do that, learning can be more enjoyable and the engagement/motivation levels should rise — resulting in enormous returns on investment over learners’ lifetimes.
Addendum on 6/17/15:
Addendum on 7/14/15:
- New Scientific Review of Learning Styles — from willatworklearning.com
Excerpt:
Just last month at the Debunker Club, we debunked the learning-styles approach to learning design based on our previous compilation of learning-styles debunking resources.
.
Now, there’s a new research review by Daniel Willingham, debunker extraordinaire, and colleagues.
.
Willingham, D. T., Hughes, E. M., & Dobolyi, D. G. (2015). The scientific status of learning styles theories. Teaching of Psychology, 42(3), 266-271. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0098628315589505













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)