From DSC:
Big data is a big theme these days — in a variety of industries. Higher ed is no exception, where several vendors continue to develop products that hope to harness the power of big data (and to hopefully apply the lessons learned in a variety of areas, including retention).
However as an Instructional Designer, when I think of capturing and using data in the context of higher education, I’m not thinking about institutional type of data mining and the corresponding dashboards that might be involved therein. I’m thinking of something far more granular — something that resembles a tool for an individual professor to use.
I’m thinking more about individual students and their learning. I’m thinking about this topic in terms of providing additional information for a faculty member to use to gauge the learning within his or her particular classes — and to be able to highlight issues for them to address.
So, for example, when I’m thinking about how a mathematics professor might obtain and use data, I’m thinking of things like:
- How did each individual do on this particular math problem?
- Who got it right? Who got it wrong?
- What percentage of the class got it right? What percentage of the class got it wrong?
- For those who got the problem wrong, where in the multi-step process did they go wrong?
So perhaps even if we’re only obtaining students’ final answers — whether that be via clickers, smartphones, laptops, and/or tablets — data is still being created. Data that can then be analyzed and used to steer the learning. This type of information can then help the mathematics professor follow up accordingly — either with some individuals or with the entire class if he/she saw many students struggling with a new concept.
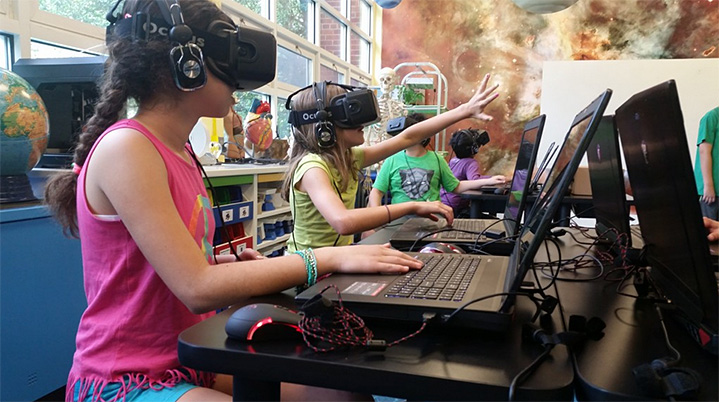
Such data gathering can get even more granular if one is using elearning types of materials. Here, the developers can measure and track things like mouse clicks, paths taken, and more. So like the approaching Internet of Things, data can get produced on a massive scale.
But very few mathematics professors have the time to:
- manually track X/Y/or Z per student
- manually capture how an entire class just did on a math problem
- manually document where each student who got a problem incorrect went wrong
So in the way that I’m thinking about this topic, this entire push/idea of using data and analytics in education requires things to happen digitally — where results can automatically be stored without requiring any manual efforts on the part of the professor.
The ramifications of this are enormous.
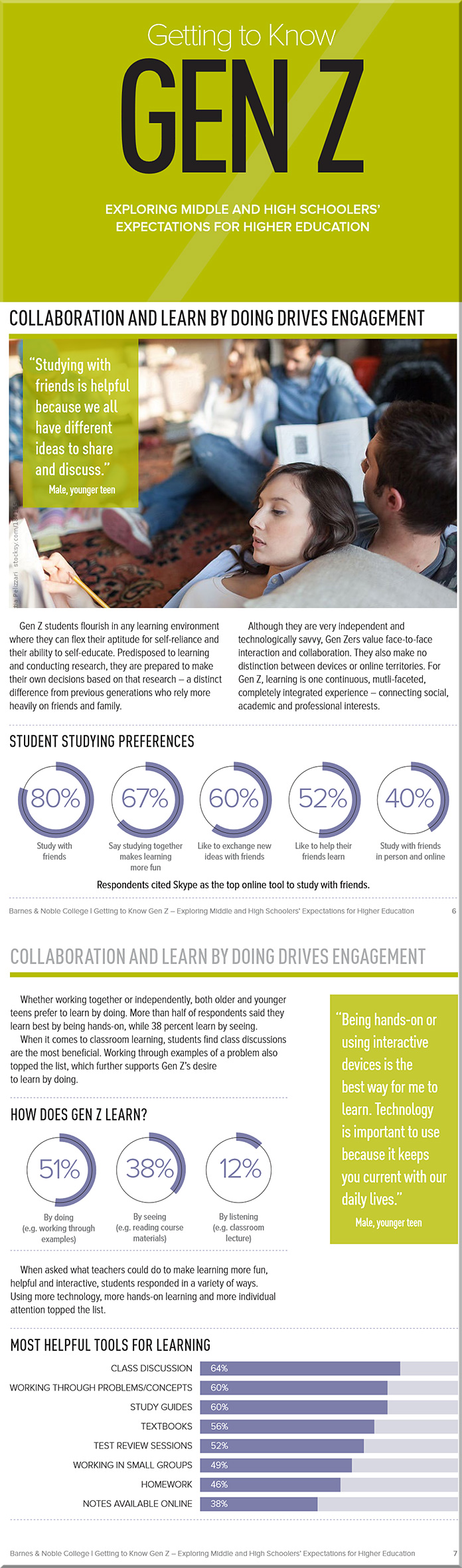
That is, the push to use analytics in education — at least at the personalized learning level that I’m thinking of — really represents and actually requires a push towards using blended and/or online-based learning. Using strictly 100% face-to-face based classrooms and environments — without any digital components involved — won’t cut it if we want to harness the power of analytics/data mining to improve student learning.
Though this may seem somewhat obvious, again, the ramifications are huge for how faculty members structure their courses and what tools/methods that they choose to utilize. But this goes way beyond the professor. It also has enormous implications for those departments and teams who are working on creating/revising learning spaces — especially in terms of the infrastructures such spaces offer and what tools might be available within them. It affects decision makers all the way up to the board-level as well (who may not be used to something other than a face-to-face setting…something they recall from their own college days).
What do you think? Are you and/or your institution using big data and analytics? If so, how?
Also see:
Big data and higher education: These apps change everything — from bigdatalandscape.com
Excerpt:
Big Data is going to college. The companies on this list have been developing innovative higher education analytics apps. Universities are realizing the importance of harnessing Big Data for the purposes of helping students to succeed, helping instructors to know what students still need to learn, analyzing efficiency in all areas, boosting enrollment, and more.
For example, CourseSmart embeds analytics directly into digital textbooks. These analytics provide an “engagement index score,” which measures how much students are interacting with their eTextbooks (viewing pages, highlighting, writing notes, etc.). Researchers have found that that the engagement index score helps instructors to accurately predict student outcomes more than traditional measurement methods, such as class participation.
In addition, there are dashboards that enable Big Data analytics and visualization for the purpose of monitoring higher education KPIs such as enrollment, accreditation, effectiveness, research, financial information, and metrics by class and by department. Read on to find out about the companies that are shaping Big Data analytics in higher education.
How five edtech start-ups are using big data to boost business education — from businessbecause.com by Seb Murray
MOOC platforms explore analytics with b-school partners
Excerpts:
“Data is an amazing resource for teachers, who glean detailed feedback on how learners are processing information,” says Julia Stiglitz, director of business development at Coursera, the online learning site with 17 million users.
Coursera, which works with the b-schools IE, Yale and Duke Fuqua, offers a dashboard that gives teachers insight into when students are most likely to stop watching a video, and the percentage who answer assessment questions correctly the first time around.
…
“By carefully assessing course data, from mouse clicks to time spent on tasks to evaluating how students respond to various assessments, researchers hope to shed light on how learners access information and master materials,” says Nancy Moss, edX’s director of communications.