From DSC:
In Part I, I looked at the new, exponential pace of change that colleges, community colleges and universities now need to deal with – observing the enormous changes that are starting to occur throughout numerous societies around the globe. If we were to plot out the rate of change, we would see that we are no longer on a slow, steady, incremental type of linear pathway; but, instead, we would observe that we are now on an exponential trajectory (as the below graphic from sparks & honey very nicely illustrates).

How should colleges and universities deal with this new, exponential pace of change?
1) I suggest that you ensure that someone in your institution is lifting their gaze and peering out into the horizons, to see what’s coming down the pike. That person – or more ideally, persons – should also be looking around them, noticing what’s going on within the current landscapes of higher education. Regardless of how your institution tackles this task, given that we are currently moving at an incredibly fast pace, this trend analysis is very important. The results from this analysis should immediately be integrated into your strategic plan. Don’t wait 3-5 years to integrate these new findings into your plan. The new, exponential pace of change is going to reward those organizations who are nimble and responsive.
2) I recommend that you look at what programs you are offering and consider if you should be developing additional programs such as those that deal with:
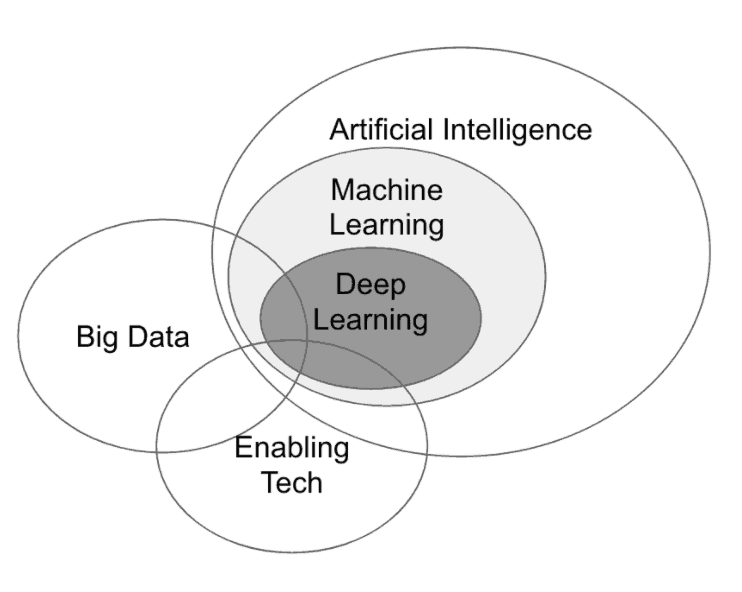
- Artificial Intelligence (Natural Language Processing, deep learning, machine learning, bots)
- New forms of Human Computer Interaction such as Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality
- User Experience Design, User Interface Design, and/or Interaction Design
- Big data, data science, working with data
- The Internet of Things, machine-to-machine communications, sensors, beacons, etc.
- Blockchain-based technologies/systems
- The digital transformation of business
- Freelancing / owning your own business / entrepreneurship (see this article for the massive changes happening now!)
- …and more
3) If you are not already doing so, I recommend that you immediately move to offer a robust lineup of online-based programs. Why do I say this? Because:
- Without them, your institution may pay a heavy price due to its diminishing credibility. Your enrollments could decline if learners (and their families) don’t think they will get solid jobs coming out of your institution. If the public perceives you as a dinosaur/out of touch with what the workplace requires, your enrollment/admissions groups may find meeting their quotas will get a lot harder as the years go on. You need to be sending some cars down the online/digital/virtual learning tracks. (Don’t get me wrong. We still need the liberal arts. However, even those institutions who offer liberal arts lineups will still need to have a healthy offering of online-based programs.)
- Online-based learning methods can expand the reach of your faculty members while offering chances for individuals throughout the globe to learn from you, and you from them
- Online-based learning programs can increase your enrollments, create new revenue streams, and develop/reach new markets
- Online-based learning programs have been proven to offer the same learning gains – and sometimes better learning results than – what’s being achieved in face-to-face based classrooms
- The majority of pedagogically-related innovations are occurring within the online/digital/virtual realm, and you will want to have built the prior experience, expertise, and foundations in order to leverage and benefit from them
- Faculty take their learning/experiences from offering online-based courses back into their face-to-face courses
- Due to the increasing price of obtaining a degree, students often need to work to help get them (at least part of the way) through school; thus, flexibility is becoming increasingly important and necessary for students
- An increasing number of individuals within the K-12 world as well as the corporate world are learning via online-based means. This is true within higher education as well, as, according to a recent report from Digital Learning Compass states that “the number of higher education students taking at least one distance education course in 2015 now tops six million, about 30% of all enrollments.”
- Families are looking very closely at their return on investments being made within the world of higher education. They want to see that their learners are being prepared for the ever-changing future that they will encounter. If people in the workforce often learn online, then current students should be getting practice in that area of their learning ecosystems as well.
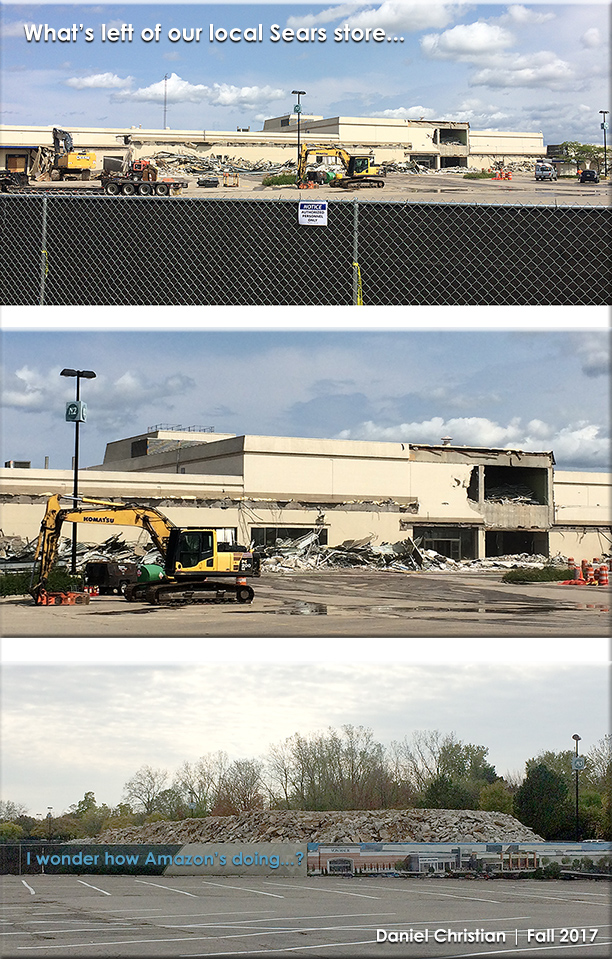
- As the (mostly) online-based Amazon.com is thriving and retail institutions such as Sears continue to close, people are in the process of forming more generalized expectations that could easily cross over into the realm of higher education. By the way, here’s how our local Sears building is looking these days…or what’s left of it.

4) I recommend that you move towards offering more opportunities for lifelong learning, as learners need to constantly add to their skillsets and knowledge base in order to remain marketable in today’s workforce. This is where adults greatly appreciate – and need – the greater flexibility offered by online-based means of learning. I’m not just talking about graduate programs or continuing studies types of programs here. Rather, I’m hoping that we can move towards providing streams of up-to-date content that learners can subscribe to at any time (and can drop their subscription to at any time). As a relevant side note here, keep your eyes on blockchain-based technologies here.
5) Consider the role of consortia and pooling resources. How might that fit into your strategic plan?
6) Consider why bootcamps continue to come onto the landscape. What are traditional institutions of higher education missing here?
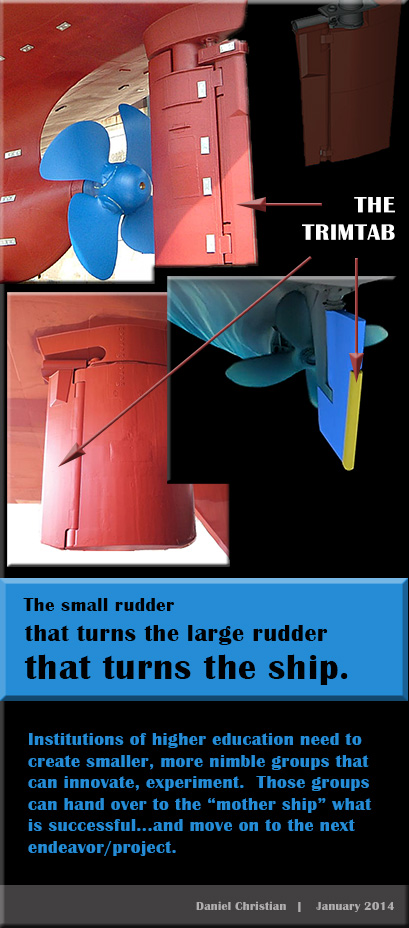
7) And lastly, if one doesn’t already exist, form a small, nimble, innovative group within your organization — what I call a TrimTab Group — to help identify what will and won’t work for your institution.




















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)


