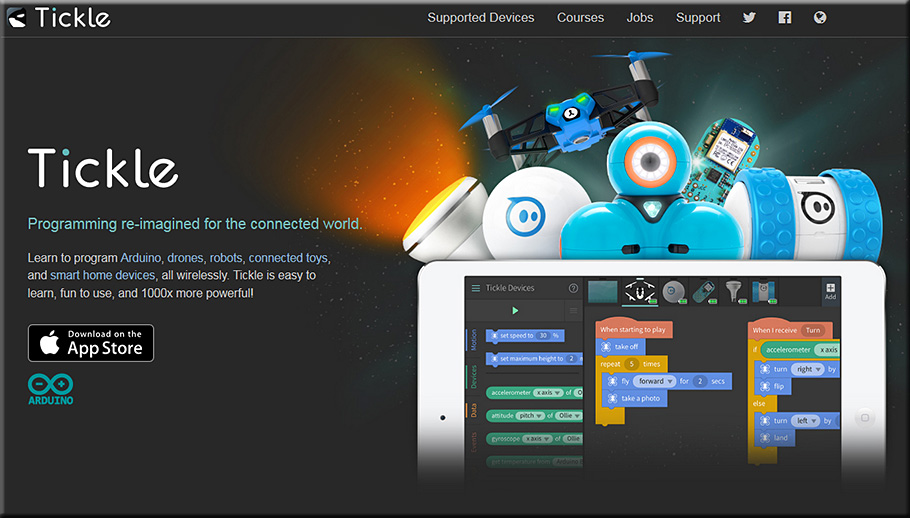
Cisco’s John Chambers on the digital era — from mckinsey.com
How significant is the digital era? It’s the biggest technology transition in history, according to Cisco’s executive chairman—and requires a proportional response from companies.
Excerpts:
If you’re a leader in today’s world, whether you’re a government leader or a business leader, you have to focus on the fact that this is the biggest technology transition ever. This digital era will dwarf what’s occurred in the information era and the value of the Internet today. As leaders, if you don’t transform and use this technology differently—if you don’t reinvent yourself, change your organization structure; if you don’t talk about speed of innovation—you’re going to get disrupted. And it’ll be a brutal disruption, where the majority of companies will not exist in a meaningful way 10 to 15 years from now.
…
This digital age is the connectivity of going from a thousand devices connected to the Internet to 500 billion. It will transform business.
…
Business models will rise and fall at a tremendous speed. It will create huge opportunities—probably $19 trillion in economic value over the next decade, incremental above what we’re seeing today. That’s the size of the US economy, plus some.
…
But it will also result in tremendous disruption. And this is where it’s so important…that you either disrupt or you get disrupted.
…
It’s simple to describe, but it really means you’re dealing with intelligent networks—a next generation of the Internet, if you will. But connecting 500 billion devices doesn’t get the job done. It’s the process change behind it. So you’ve got technologies like cloud or mobility and cybersecurity and the Internet of Things that are very important. That’s actually the easy part. The hard part is how do you change your organization structure? How do you change your culture to be able to think in terms of outcomes for your customers? It’s all about speed of innovation and changing the way you do business. The majority of companies will be digital within five years, yet the majority of their digital efforts will fail, which speaks to what a CEO has to do differently.
…
They have to reinvent themselves. They have to reinvent their company. Not stay doing the right thing too long, if you will.
…
Not enabled by technology—technology will become the company.
…
The first step is merely making it an independent group, because if you do it inside your organization, your existing culture will kill it.
…
Companies fail to understand the implications of how quickly this technology will transform their business. And they underestimate what it really means to their economic growth or that of their competitors.
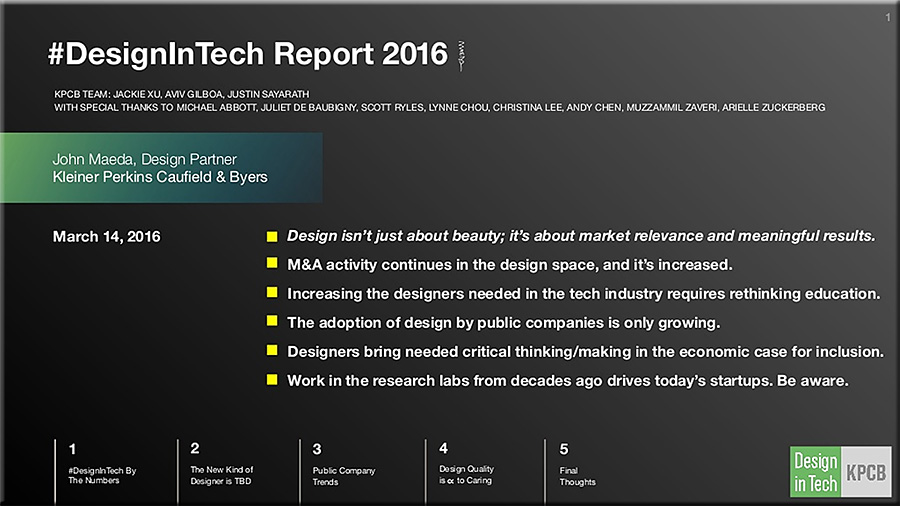
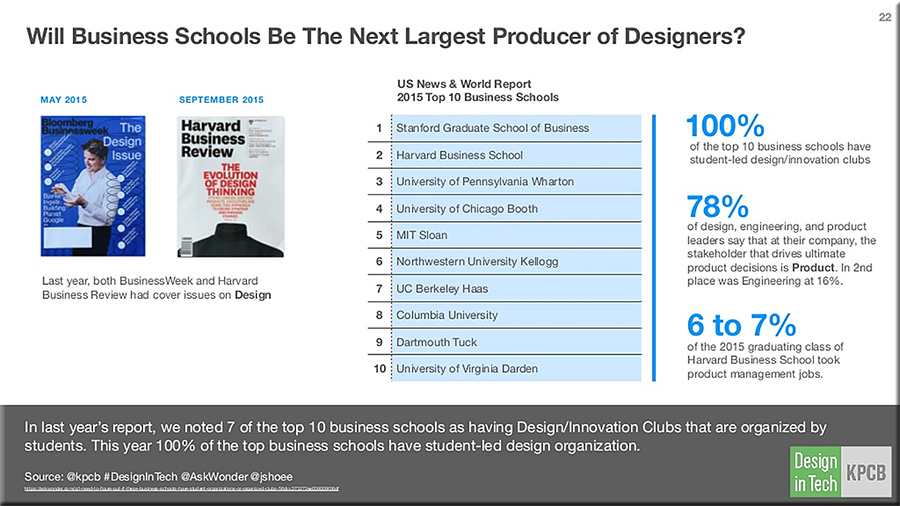
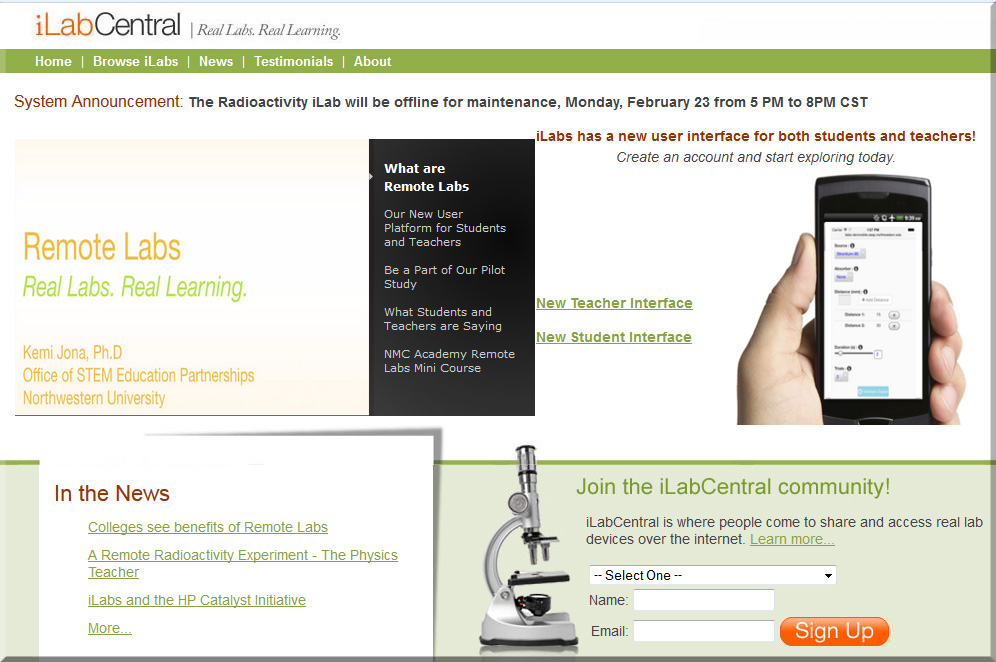
From DSC:
Some graphics come to my mind:


From DSC:
This is the world that our students are and will be graduating into. Are they ready to handle this kind of pace? Of exponential — not linear — change? How can we better prepare them to be successful in the future that they will inherit?





















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)