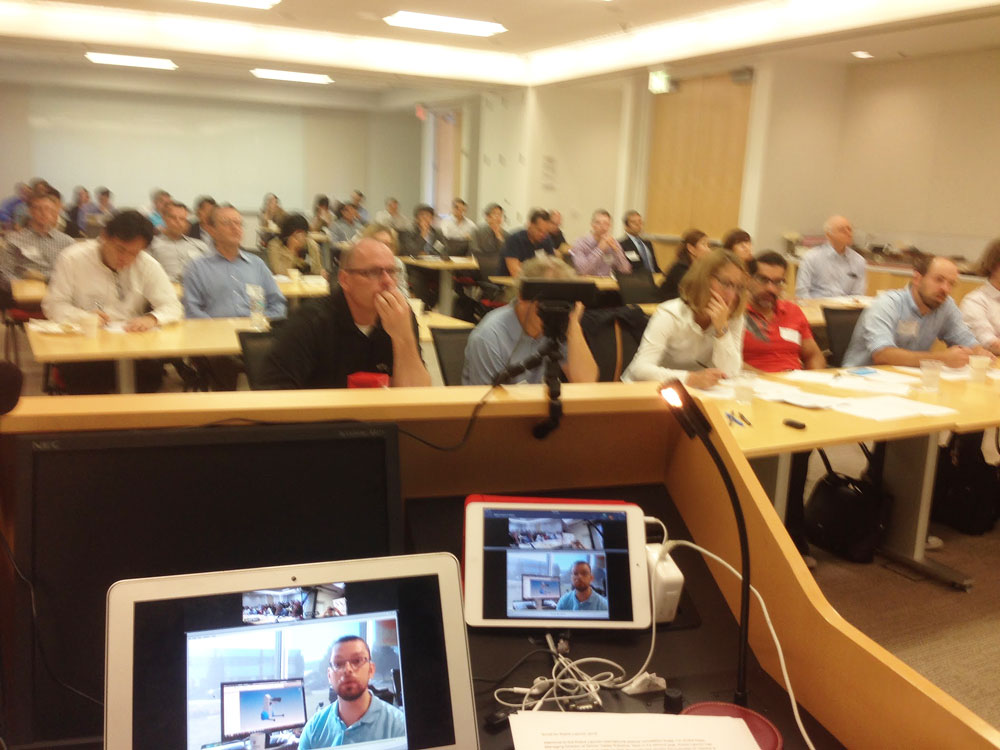
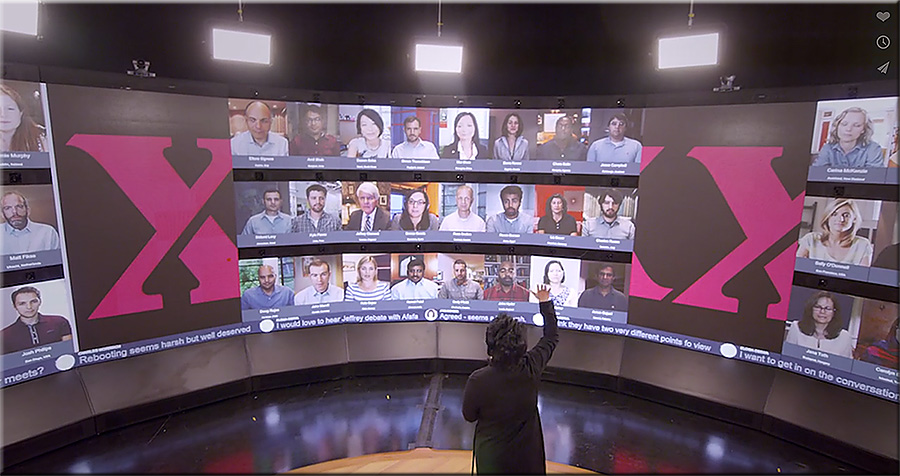
U.S. Department of Education Launches Campaign to Encourage Schools to #GoOpen with Educational Resources — from ed.gov, with thanks to Sheila Soule for this resource
Department proposes rule requiring educational materials created with federal grants to be openly licensed so that any school has access
Excerpt:
The U.S. Department of Education announced [on 10/29/15] the launch of #GoOpen, a campaign to encourage states, school districts and educators to use openly licensed educational materials. As part of the campaign, the Department is proposing a new regulation that would require all copyrightable intellectual property created with Department grant funds to have an open license.
“In order to ensure that all students – no matter their zip code – have access to high-quality learning resources, we are encouraging districts and states to move away from traditional textbooks and toward freely accessible, openly-licensed materials,” U.S. Education Secretary Arne Duncan said. “Districts across the country are transforming learning by using materials that can be constantly updated and adjusted to meet students’ needs.”










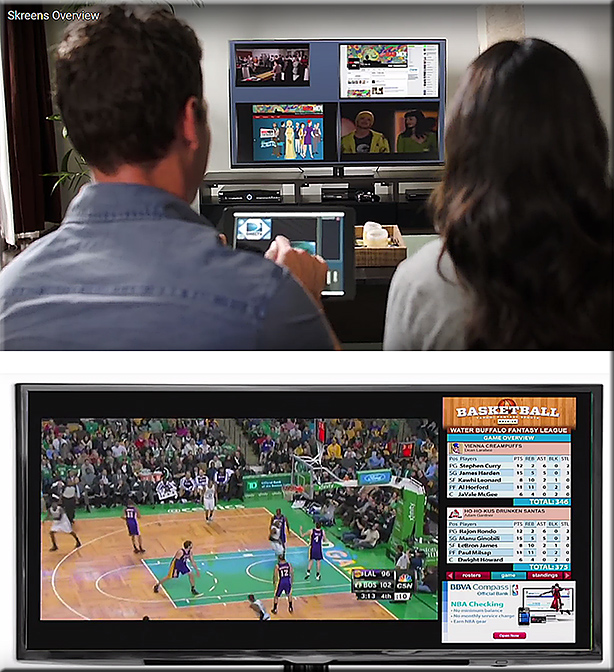
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)