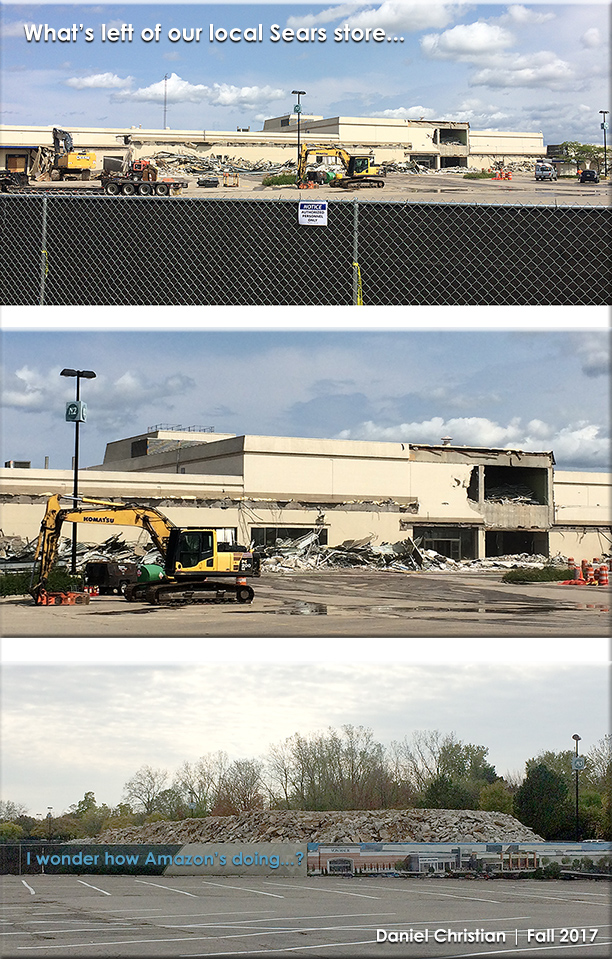
From DSC:
DC: Will Amazon get into delivering education/degrees? Is is working on a next generation learning platform that could highly disrupt the world of higher education? Hmmm…time will tell.
But Amazon has a way of getting into entirely new industries. From its roots as an online bookseller, it has branched off into numerous other arenas. It has the infrastructure, talent, and the deep pockets to bring about the next generation learning platform that I’ve been tracking for years. It is only one of a handful of companies that could pull this type of endeavor off.
And now, we see articles like these:
Amazon Snags a Higher Ed Superstar — from insidehighered.com by Doug Lederman
Candace Thille, a pioneer in the science of learning, takes a leave from Stanford to help the ambitious retailer better train its workers, with implications that could extend far beyond the company.
Excerpt:
A major force in the higher education technology and learning space has quietly begun working with a major corporate force in — well, in almost everything else.
Candace Thille, a pioneer in learning science and open educational delivery, has taken a leave of absence from Stanford University for a position at Amazon, the massive (and getting bigger by the day) retailer.
Thille’s title, as confirmed by an Amazon spokeswoman: director of learning science and engineering. In that capacity, the spokeswoman said, Thille will work “with our Global Learning Development Team to scale and innovate workplace learning at Amazon.”
No further details were forthcoming, and Thille herself said she was “taking time away” from Stanford to work on a project she was “not really at liberty to discuss.”
Amazon is quietly becoming its own university — from qz.com by Amy Wang
Excerpt:
Jeff Bezos’ Amazon empire—which recently dabbled in home security, opened artificial intelligence-powered grocery stores, and started planning a second headquarters (and manufactured a vicious national competition out of it)—has not been idle in 2018.
The e-commerce/retail/food/books/cloud-computing/etc company made another move this week that, while nowhere near as flashy as the above efforts, tells of curious things to come. Amazon has hired Candace Thille, a leader in learning science, cognitive science, and open education at Stanford University, to be “director of learning science and engineering.” A spokesperson told Inside Higher Ed that Thille will work “with our Global Learning Development Team to scale and innovate workplace learning at Amazon”; Thille herself said she is “not really at liberty to discuss” her new project.
What could Amazon want with a higher education expert? The company already has footholds in the learning market, running several educational resource platforms. But Thille is famous specifically for her data-driven work, conducted at Stanford and Carnegie Mellon University, on nontraditional ways of learning, teaching, and training—all of which are perfect, perhaps even necessary, for the education of employees.
From DSC:
It could just be that Amazon is simply building its own corporate university and will stay focused on developing its own employees and its own corporate learning platform/offerings — and/or perhaps license their new platform to other corporations.
But from my perspective, Amazon continues to work on pieces of a powerful puzzle, one that could eventually involve providing learning experiences to lifelong learners:
- Personal assistants
- Voice recognition / Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- The development of “skills” at an incredible pace
- Personalized recommendation engines
- Cloud computing and more
If Alexa were to get integrated into a AI-based platform for personalized learning — one that features up-to-date recommendation engines that can identify and personalize/point out the relevant critical needs in the workplace for learners — better look out higher ed! Better look out if such a platform could interactively deliver (and assess) the bulk of the content that essentially does the heavy initial lifting of someone learning about a particular topic.
Amazon will be able to deliver a cloud-based platform, with cloud-based learner profiles and blockchain-based technologies, at a greatly reduced cost. Think about it. No physical footprints to build and maintain, no lawns to mow, no heating bills to pay, no coaches making $X million a year, etc. AI-driven recommendations for digital playlists. Links to the most in demand jobs — accompanied by job descriptions, required skills & qualifications, and courses/modules to take in order to master those jobs.
Such a solution would still need professors, instructional designers, multimedia specialists, copyright experts, etc., but they’ll be able to deliver up-to-date content at greatly reduced costs. That’s my bet. And that’s why I now call this potential development The New Amazon.com of Higher Education.
[Microsoft — with their purchase of Linked In (who had previously
purchased Lynda.com) — is another such potential contender.]
















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)