CONTENTS
- Content discovery and synchronization
With access to rich data about their subscribers and what they do, operators can improve recommendation, encourage social TV and exploit second screen synchronization. - Recordings get more personal
One of the next big steps in multiscreen TV is giving people access to their personal recordings on every screen. This is the moment for nPVR to finally make its entrance. - Evolving the User Experience
As service providers go beyond household level and address individuals, the role of log-ins or context will become important. There is a place for social TV and big data. - The role of audio in personalization
Audio has a huge impact on how much we enjoy video services. Now it can help to personalize them. ‘Allegiance’ based audio choices are one possibility. - Making advertising more targeted
Addressable advertising is in its infancy but has a bright future, helping to fund the growth of on-demand and multiscreen viewing.
Some excerpts from this report:
Good content should be matched by good content discovery , including recommendations. The current state-of -the-art is defined by Netflix.
…
Today’s TV experience is worlds apart from the one we were talking about even five years ago. We’ve witnessed exponential growth in services such as HD and have moved from a model in which one screen is watched by many, to many screens (and devices) being available to the individual viewer, what is today called TV Everywhere. Having multiscreen access to content is driving the demand for a more personalised experience, in which the viewer can expect to see what they want, where, and when. While video on-demand (VOD) has been a great method for delivering compelling content to viewers, it is not always a truly seamless TV-like experience, and traditionally has been limited to the living room. The growing demand for the personalised experience is driving seismic change within the TV industry, and we’ve seen great strides made already, with time-shifted TV and nPVR as just two examples of how we in the industry can deliver content in the ways viewers want to watch. The next step is to move towards more advanced content discovery, effectively creating a personalised channel or playlist for the individual user.
…
As the tools become available to deliver personalized experiences to consumers, content owners can better create experiences that leverage their content. For example, for sports with multiple points of action, like motor racing, multiple camera angles and audio feeds will allow fans to follow the action that is relevant to their favourite racing team. And for movies, access to additional elements such as director’s commentaries, which have been available on Blu-ray discs for some time, can be made available over broadcast networks.
From DSC:
Some words and phrases that come to my mind:
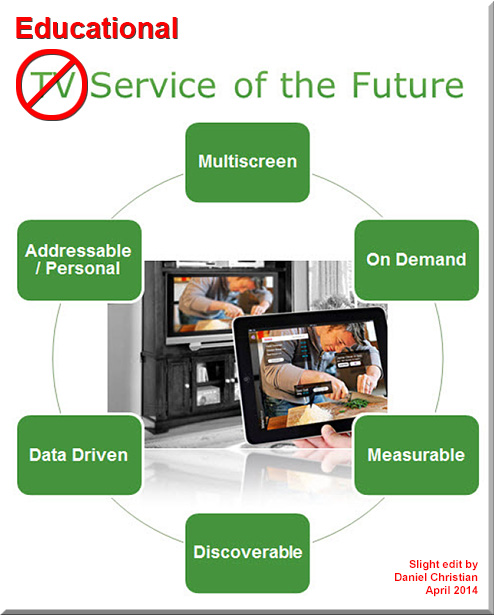
- Personalization.
- Data driven.
- Content discovery and recommendation engines (which could easily relate to educational playlists)
- Training on demand
- Learning agents
- Web-based learner profiles
- Learning hubs
- What MOOCs morph into
- More choice. More control.
- Virtual tutoring
- Interactivity and participation
- Learning preferences
- Lifelong learning
- Reinventing oneself
- Streams of content
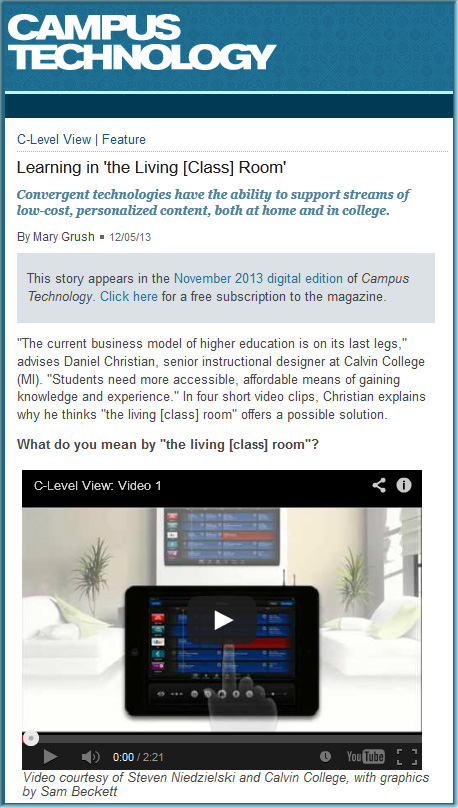
- Learning from The Living [Class] Room
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)