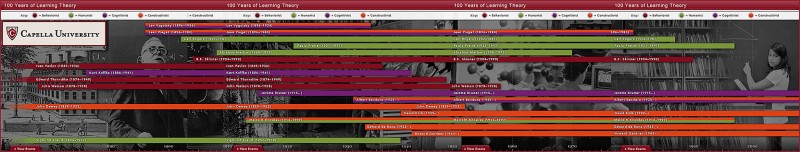
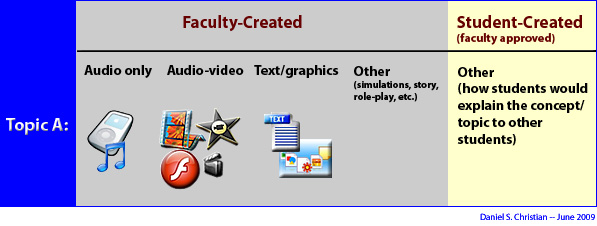
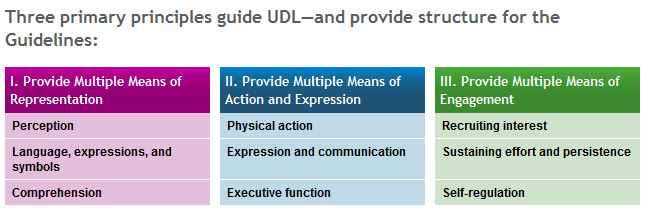
Faculty “buy-in”– to what? — from CampusTechnology.com by Trent Batson
Excerpts:
We can continue incrementally to find our generalized theory as a national and international enterprise if we are willing to wait decades and waste enormous energy and time on failed experiments. Or, we can make efforts to bring together the learning theorists and researchers with those who understand the capabilities of the technology.
At conferences of learning theorists and researchers, we hear about useful new ideas, research results, hopeful new ways of framing what we have gleaned from a century of careful thought and work about how humans learn. But, we don’t find that these learning theorists understand the dynamics of the new technologies sufficiently to recommend a path toward implementation of the theories.
At conferences of technologists, we hear of successful work in innumerable contexts across the country. But the technologists are not aware of learning theory in most cases, or they do know about learning theory but are not active in a learning theory research field. The innumerable technology implementation contexts, then, remain just anecdotal as they are not tied to a developing new theoretical construct.
…
The challenge is to build a cultural theory that guides academia to re-imagine itself in every tiny bit of being. Who is taking up this challenge? Where is our theory? Where are our theorists?
I hope our community will move away from the simplistic notion that somehow information technology can be “bolted on and not built in” to quote a colleague from last November’s ePortfolios Australia Conference in Melbourne.
Academic transformation is under way. Don’t put the technology first; put understanding of the technology implications first–the unifying learning theory. Second, start the changes on campus that will provide the road system for academics to use in our new landscape.
From DSC:
Having just completed a course re: learning theories, I greatly appreciated Trent’s article here. In that class, I was constantly looking for the applications of the learning theories. While learning to give up on the idea of a silver bullet, I was still in search of answers to questions like:
- What does all this mean?
- What’s the bottom line for such and such a learning theory?
- How does this learning theory impact someone’s teaching and learning strategies (pedagogy and/or andragogy)?
Graphically speaking, I came up with these thoughts:
(Depending upon how you are viewing them, you may need to right click on these graphics and save them down to your desktop; them up them up in a new window/application)
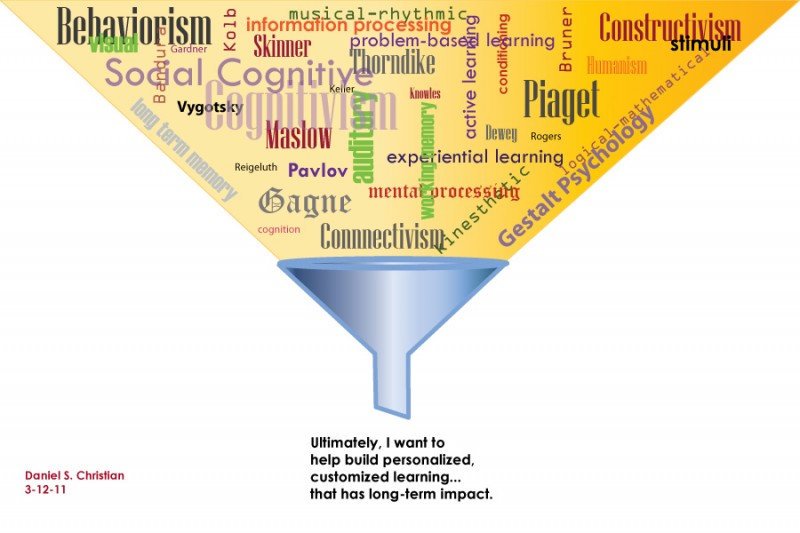

And my thanks to Capella University for the underlying graphics/information here: