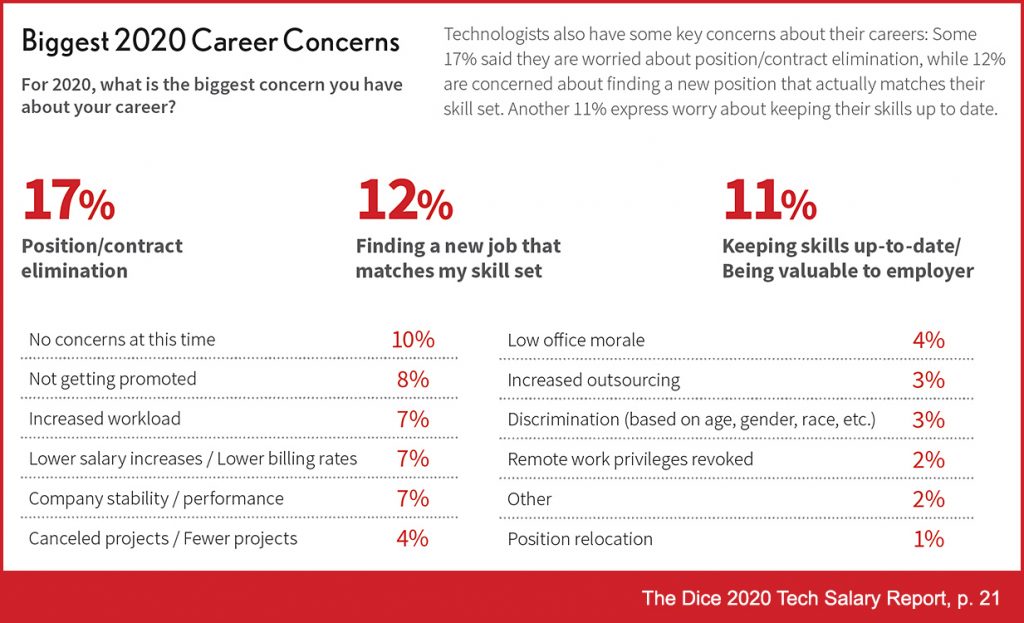
Legal technology, today and tomorrow: Don’t get left behind — from law.com by Jenn Betts
Staying on top of these developments is no longer enough to “future proof” your practice or your firm. It is imperative to look forward to avoid falling behind.
Excerpt:
Among other kinds of disruptive AI-powered tools already on the market are:
- Artificial intelligence-enabled document review tools and platforms (which make review of discovery materials quicker and cheaper);
- Artificial intelligence-enabled tools assisting organizations with selecting outside counsel (which promise more data-driven assessments of “fit” between the firm, client and case);
- Artificial intelligence patent search engines (which make patent searching easier and more accurate); and
- Artificial intelligence-powered systems delivering early-stage litigation services, such as drafting answers to complaints, discovery requests and responses, and litigation timelines (which decreases client costs and delivers greater efficiencies).
These tools raise interesting (and largely unanswered) practical and ethical issues relating to the scope of the practice of law, AI disclosure obligations to clients, confidentiality issues regarding client data and the necessity of independent judgment by attorneys.
The pace of development of AI and other advanced technologies is moving at an unprecedented pace.
From DSC:
I agree. The pace of change has changed. It’s now an exponential pace of change. This new pace is having an increasing impact on the legal industry.